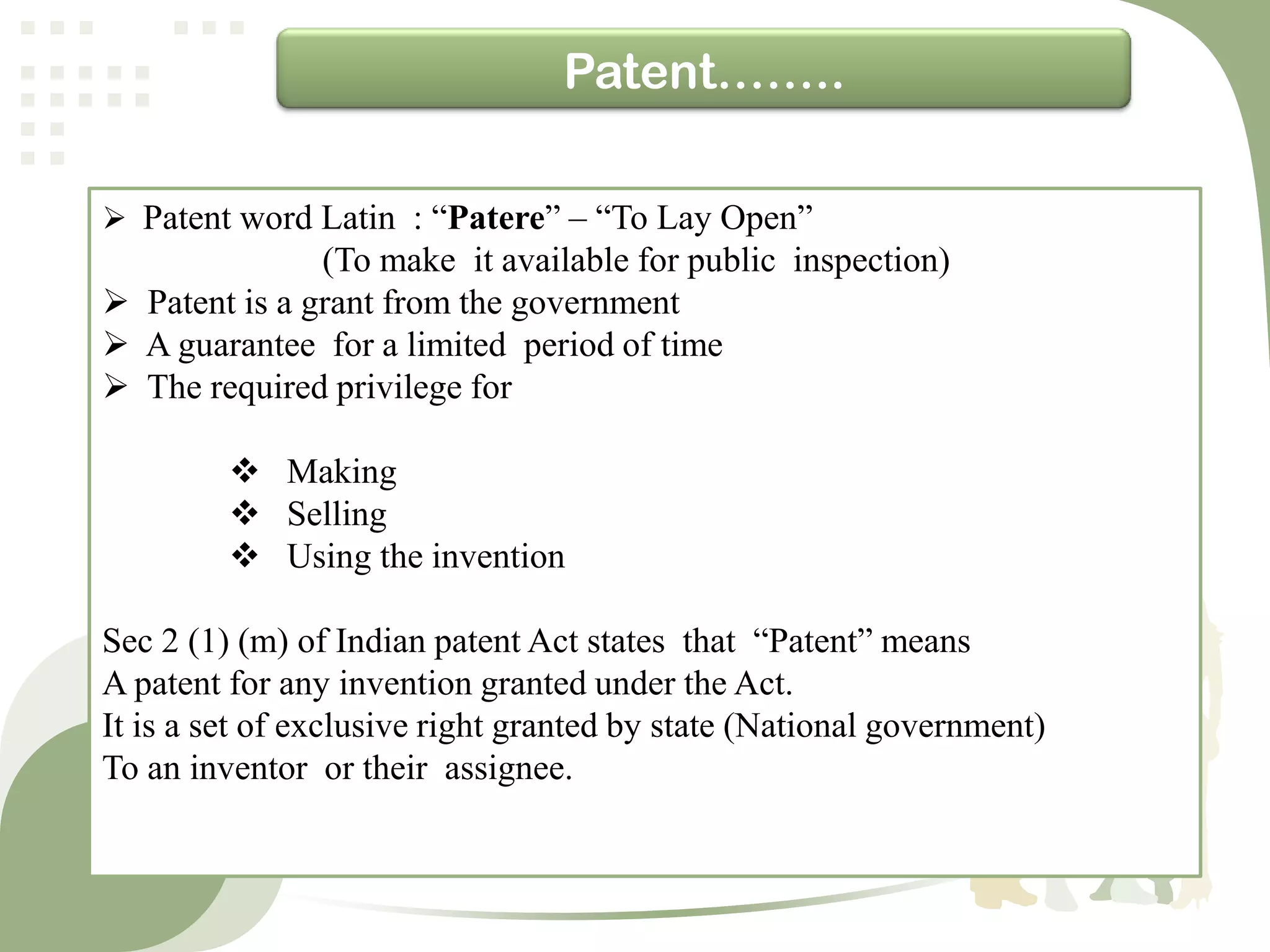
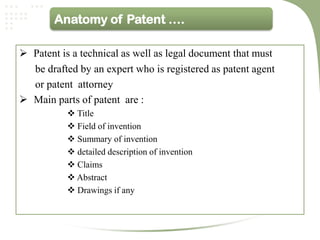
- Patent is a grant from the government that provides exclusive rights over an invention for a limited period of time, allowing the inventor to commercially benefit from the invention [1].
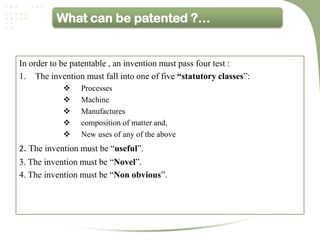
- The key requirements for patentability are that the invention must be novel, non-obvious, and industrially applicable [2].
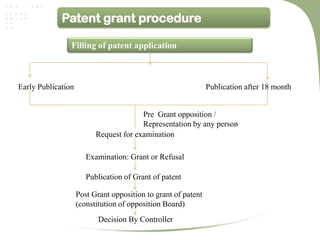
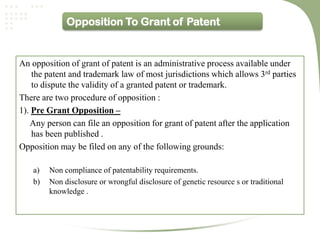
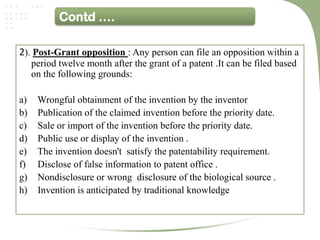
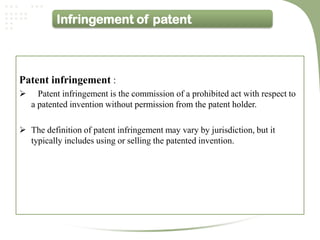
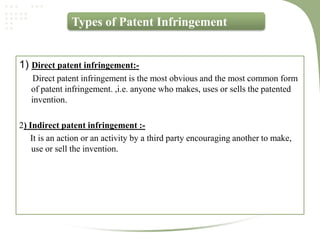
- The patent process involves filing an application, examination by the patent office, potential pre-grant opposition, publication if granted, and the ability for post-grant opposition challenging the validity of the patent [3].








![WTO and patent rules:
The grant and enforcement of patents are governed by
national laws and international treaties.
There is a trend towards global harmonization of patent
laws and the WTO is actively participating in this area.
The TRIPS [ Trade Related Intellectual Property Rights]
agreement has been successful in providing a forum for
nations to agree on an aligned set of patent laws.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/patntact-120506004830-phpapp01/85/Patnt-act-20-320.jpg)
