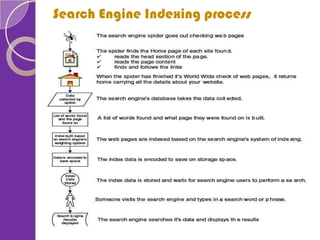
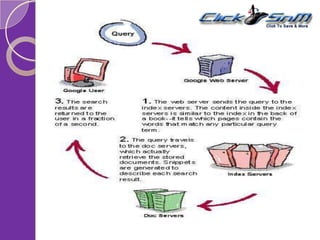
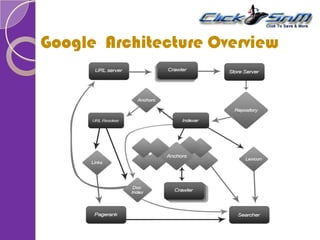
The document explains key components of Google's search engine, focusing on PageRank, which assigns numerical values to web pages based on their importance through link analysis. It also describes the search engine indexing process, detailing how data is collected and optimized for quick retrieval, and emphasizes the role of search engine optimization (SEO) in enhancing website visibility. Overall, it highlights Google's architecture aimed at delivering high-quality and relevant search results.