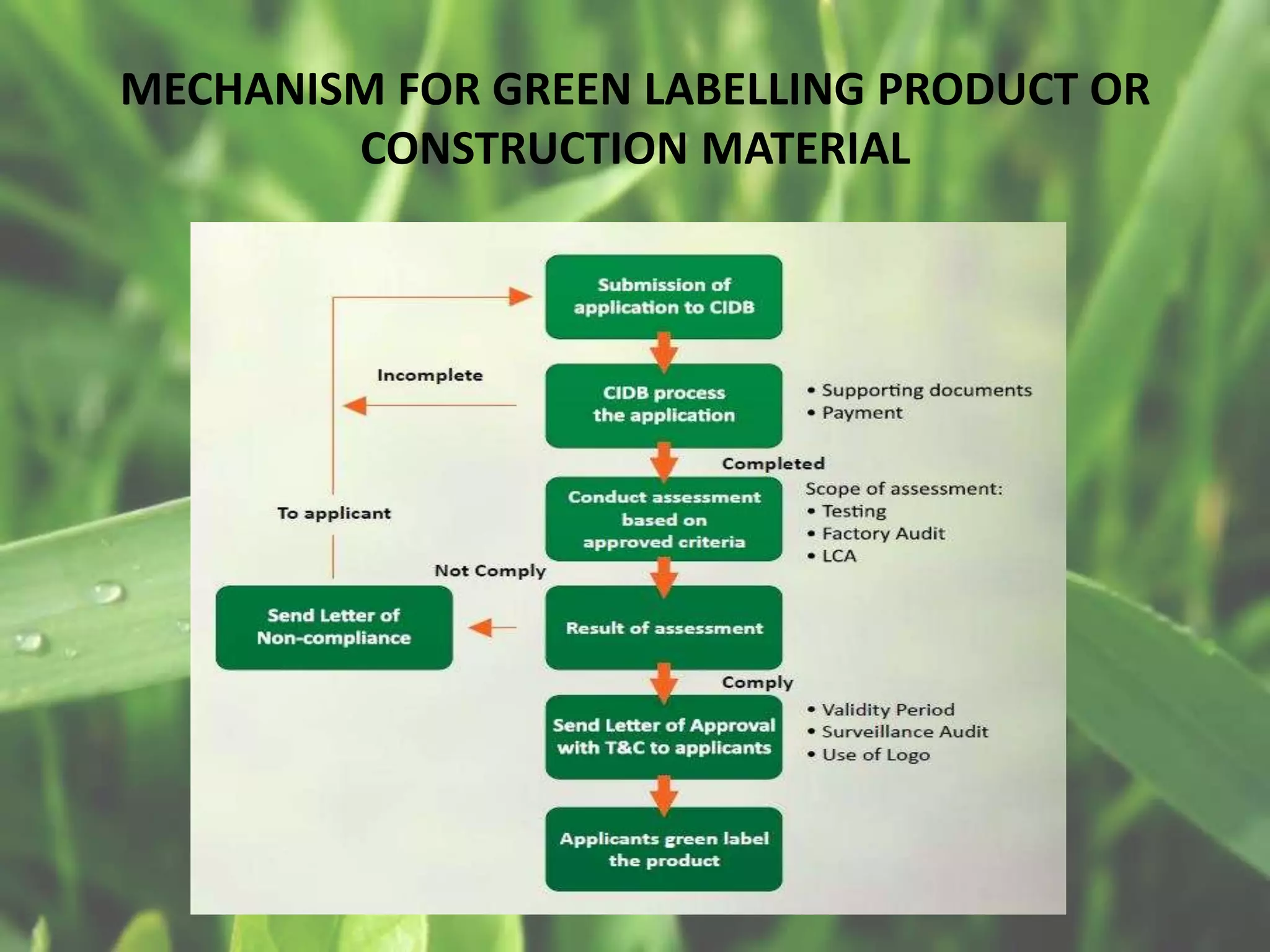
The document discusses how the Construction Industry Development Board (CIDB) of Malaysia aims to promote green technologies among construction contractors. It outlines various strategies, including the publication of guidelines, training modules, and the implementation of green contractor accreditation and labeling mechanisms. The overall goal is to enhance environmental management practices within the construction industry and improve sustainability.