The document discusses universal references and perfect forwarding in C++, focusing on solutions provided in C++11. It outlines the challenges of perfect forwarding prior to C++11 and explains how reference-collapsing rules and universal references simplify the process. It also covers the use of std::forward for preserving value categories and type qualifications during argument forwarding.








![Universal References: Examples
template<typename Arg> // [1.1]
void foo(Arg&& arg);
arg is universal reference
void bar(Bar&& op); // [1.2]
std::string&& s = …; // [1.3]
Fully specified type ⇒ no type deduction, op and s are rvalue references
template<typename Arg> // [1.4]
void foo(const Arg&& arg);
Should be exactly type&& were type is deduced ⇒ arg is const rvalue
reference
template<typename Arg> // [1.5]
void foo(Arg& arg);
Should be type&& ⇒ arg is lvalue reference
9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-9-320.jpg)
![Universal References: Examples
template<typename T>
class Vector {
Vector(Vector&& rhs); // [2.1]
…
void push_back(T&& t); // [2.2]
};
Fully specified type (When function is called the template is already
instantiated so Vector and T are “fixed”) ⇒ no type deduction, rhs and t
are rvalue references
template<typename T>
class Vector {
template<typename U> // [2.3]
Vector(U&& rhs);
…
};
rhs is universal reference
10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-10-320.jpg)
![Universal References: Examples
template<typename T> // [3.1]
void print(std::vector<T>&& arg);
Should be exactly type&& were type is deduced ⇒ arg is rvalue
reference
template<typename... Args> // [3.2]
void foo(Args&&... args);
Parameter pack of universal references
auto&& i = …; // [3.3]
It is exactly type&& where type is deduced ⇒ i is universal reference
[](auto&& arg) {…}; // [3.4] C++14 lambda
It is exactly type&& where type is deduced ⇒ arg is universal
reference
11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-11-320.jpg)

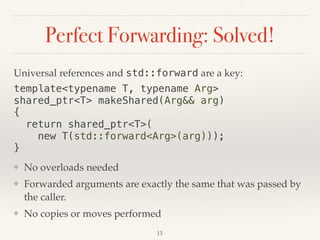



![URefs And std::forward Go Together
A universal reference is [almost] always used in
combination with std::forward. If you see former
without latter or vice versa, look for error!
Remember its second name a forwarding reference.
17
template<typename T>
void logAndBar(T&& t) {
std::cout << t << ‘n’;
bar(std::forward<T>(t)));
}
template<typename T>
Foo makeFoo(T&& t) {
return std::forward<T>(t);
}
template<class T>
struct Wrapper {
…
template<class U>
Wrapper(int id, U&& v)
: m_id(id)
, m_val(std::forward<U>(v))
{}
};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-17-320.jpg)

![Avoid Overloading on URefs
Imagine that we want to differently process rvalues (first overload)
and lvalues (second one):
template<typename T>
void foo(T&& t) {… std::move(t); …} // [1] rvalues
template<typename T>
void foo(T const& t) {…} // [2] lvalues
std::string s = “wow”;
foo(s);
WTF, overload [1] is called! Only const lvalues go to [2], all the rest
including non-const lvalues go to [1] because it takes universal
reference ⇒ accepts everything ⇒ a better match for everything
except const lvalue ref.
19](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-19-320.jpg)
![Avoid Overloading on URefs
Imagine that we want to have overload for integers:
template<typename T>
void foo(T&& t) {…} // [1] general case
void foo(long t) {…} // [2] integers
short s = 42;
foo(s);
WTF, overload [1] is called! Only longs go to [2], all the rest
including integers that need to be promoted to long integer go to
[1] because it takes universal reference ⇒ accepts everything ⇒
a better match for everything except a long integer.
20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-20-320.jpg)



![URefs And Copy Constructor
template<typename T>
struct Wrapper {
T m_value;
…
template<typename U>
explicit Wrapper(U&& u)
: m_value(std::forward<U>(u)) {}
};
Looks OK?
Wrapper<std::string> w1(“Hello, World!”);
Wrapper<std::string> w2(w1); // Compilation error
For non-const lvalue reference the forwarding constructor is a better
match than [generated] copy constructor:
Wrapper(const Wrapper& rhs);
24](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hotcuniversalreferencesandperfectforwarding-171116110053/85/Hot-Universal-References-And-Perfect-Forwarding-24-320.jpg)







