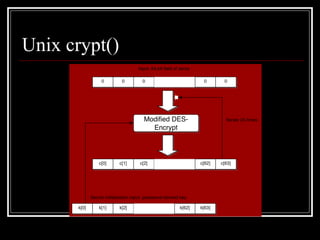
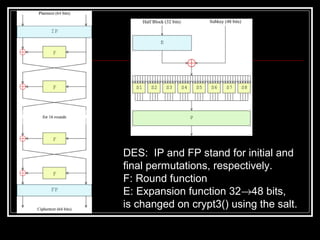
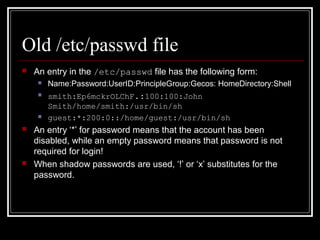
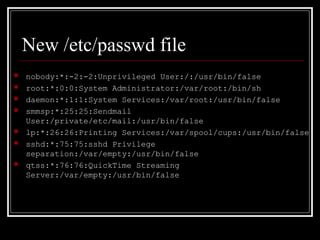
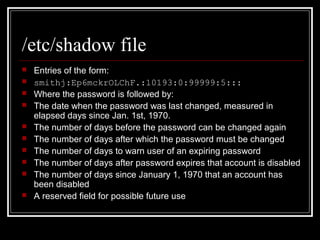
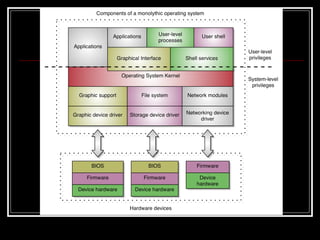
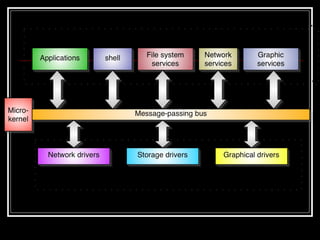
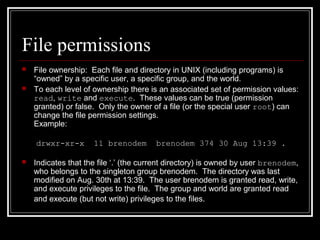
Host security measures aim to comprehensively protect individual hosts through host-centric approaches tailored to the host's architecture and configuration. This involves securing configurations, access controls, permissions and services on Unix-like systems. Common weaknesses include password issues, exploitable services and improper permissions. Unix uses users, groups and world permissions on files and directories to control access. Proper configuration of these permissions and use of setuid programs is important for security. The Unix password system has evolved from storing passwords in plaintext to using shadow files and stronger encryption.







![Changing ownership and
permissions
The root user can change ownership and permissions on files at
will.
In some distributions, a user may change ownership of its own files
to other users.
To change group ownership of a file, you must own the file and you
must belong to the new group the file will be assigned to:
chown username filename
chgrp groupname filename
To change permissions, you must be the file’s owner
chmod [o|g|a|u][+|-][r|w|x] filename
example: chmod og+wx filename adds permissions to write and
execute the file to both the file owner and file group owner.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hostsecurity-131126064548-phpapp01/85/Host-security-11-320.jpg)