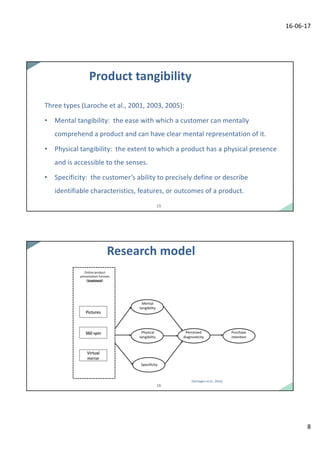
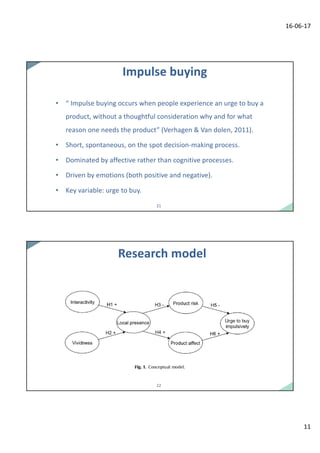
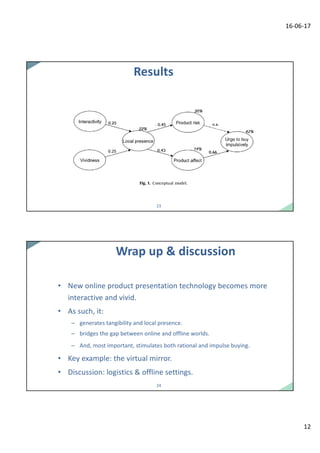
Dr. Tibert Verhagen presented research on new online product presentation technologies and their ability to create a sense of local presence and tangibility. Three studies examined how virtual mirrors and other interactive formats influenced rational and impulse buying behaviors. The results showed that more vivid and interactive formats generated feelings of product tangibility and local presence, bridging the gap between online and offline experiences. This stimulated both rational consideration and impulse buying of products. Specifically, the virtual mirror was found to be effective at translating the in-store mirror experience online. The research implications and potential logistical role of virtual mirrors were discussed.