This document provides an overview of HIV and AIDS, including:
- Definitions of HIV as the virus and AIDS as the final stage of the disease caused by HIV infection.
- Differences between HIV and AIDS, with HIV being the virus and AIDS being the result of HIV progression.
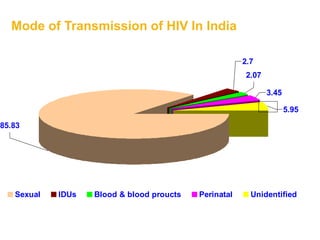
- Modes of HIV transmission including unprotected sex, blood transfusions, and mother-to-child transmission.
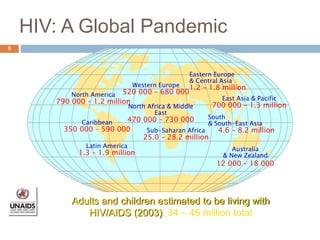
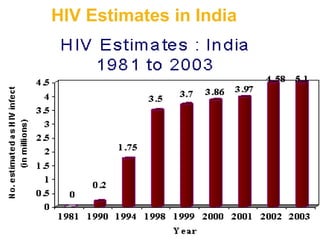
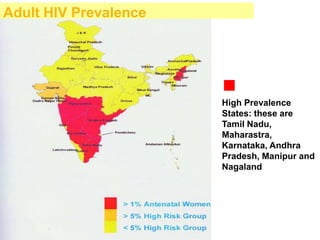
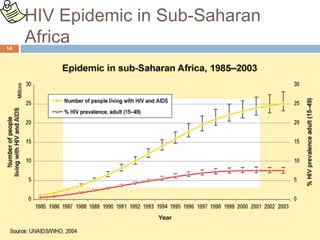
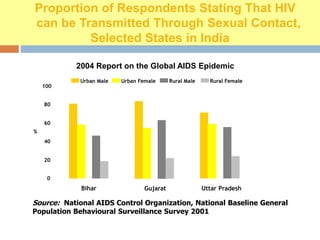
- Global and national statistics on people living with HIV/AIDS and new infections, with sub-Saharan Africa having the most severe epidemic.
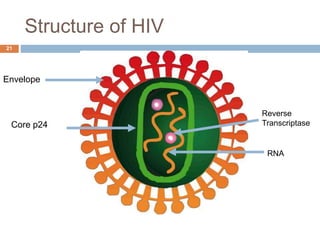
- The structure of the HIV virus and differences between HIV-1 and HIV-2.
- Recommended preventive measures like safe sex practices