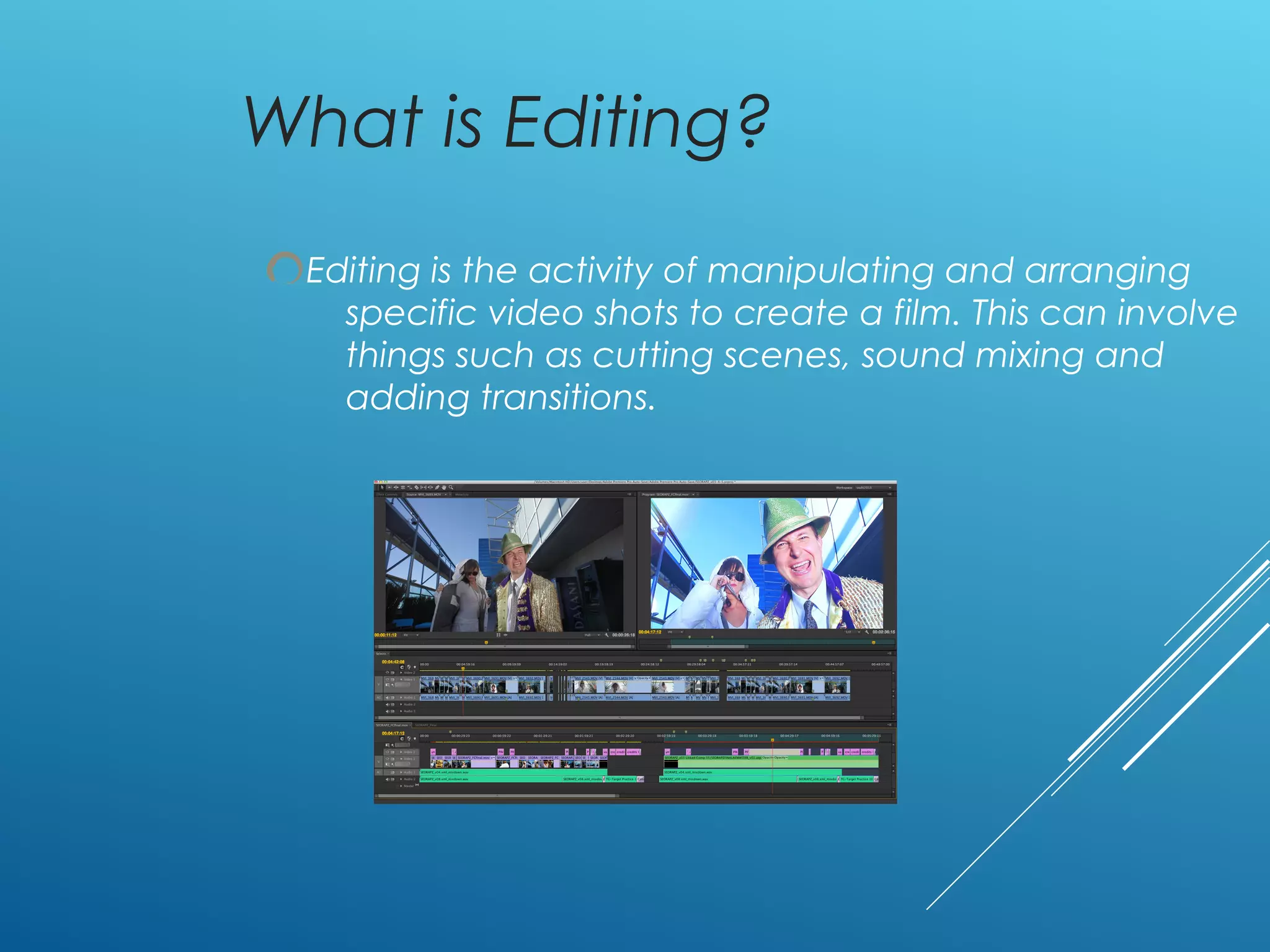
Editing evolved from simply filming scenes sequentially to intentionally arranging and cutting shots to tell a story. Early editors physically spliced film together, but techniques developed like continuity editing used by D.W. Griffith in "The Birth of a Nation" to advance emotions through varied camera angles. Soviet filmmakers also pioneered montage editing to manipulate audiences' reactions by how shots were assembled. Later, innovations allowed for sound in film and non-linear digital editing simplified the process.