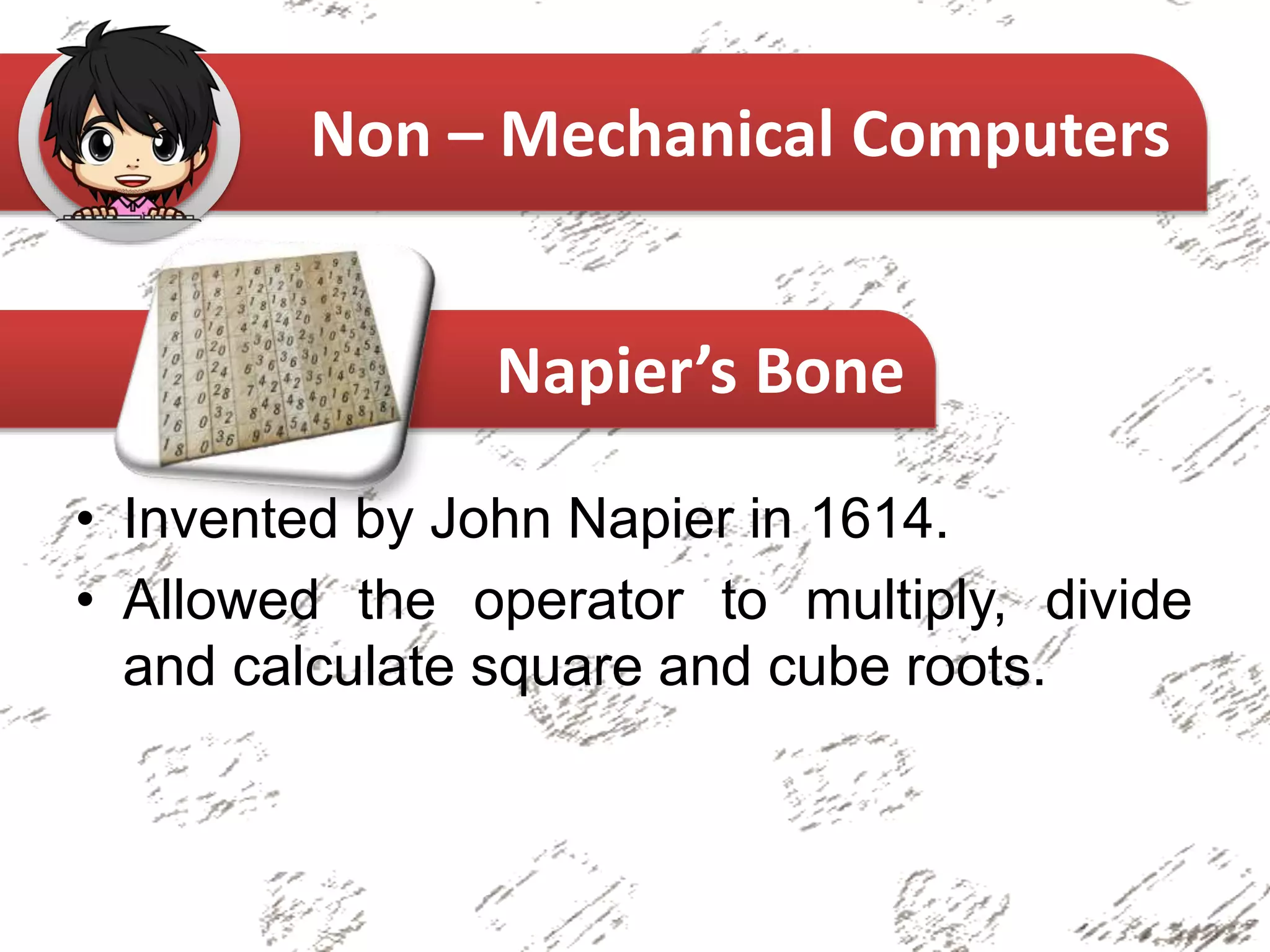
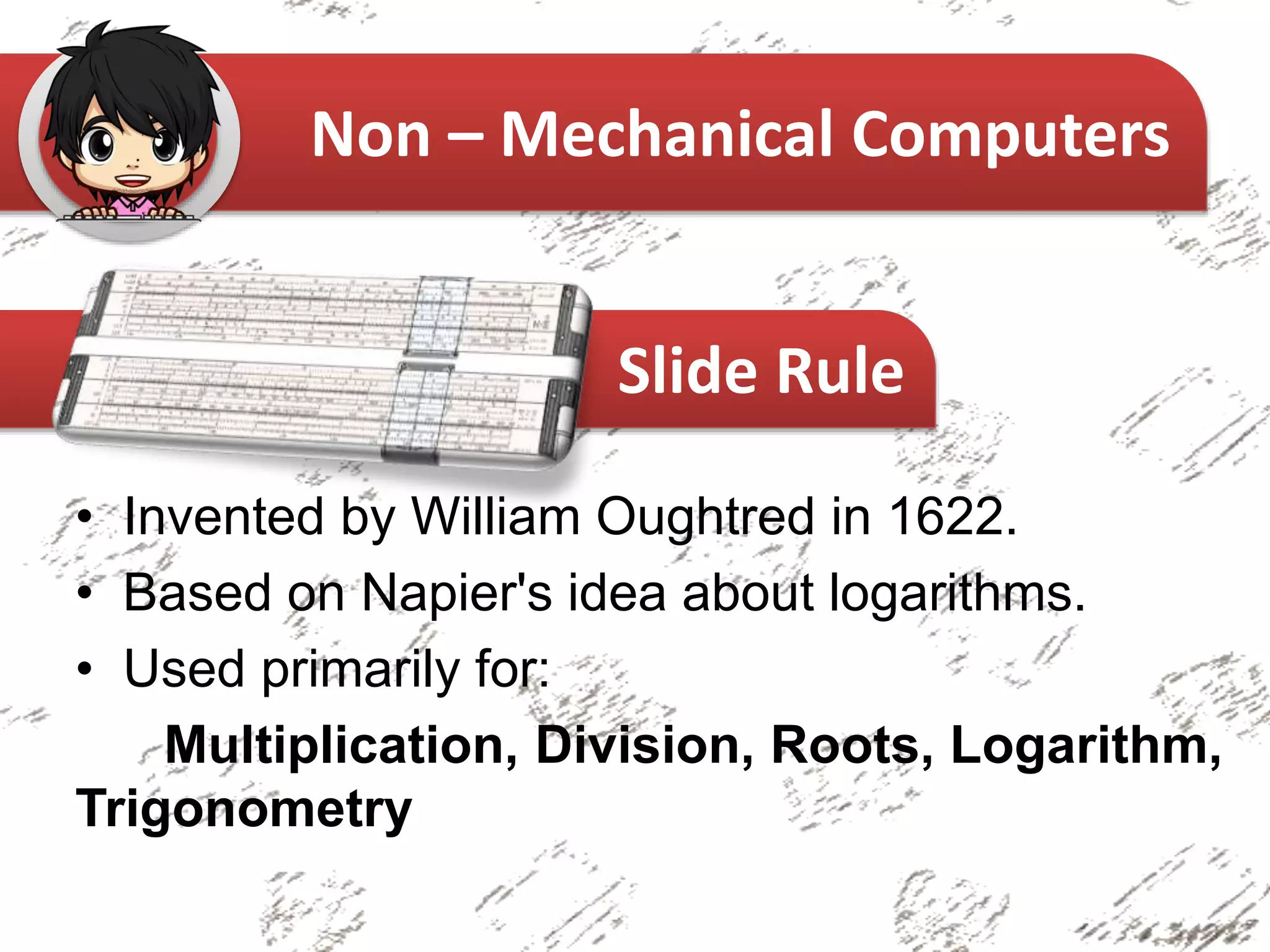
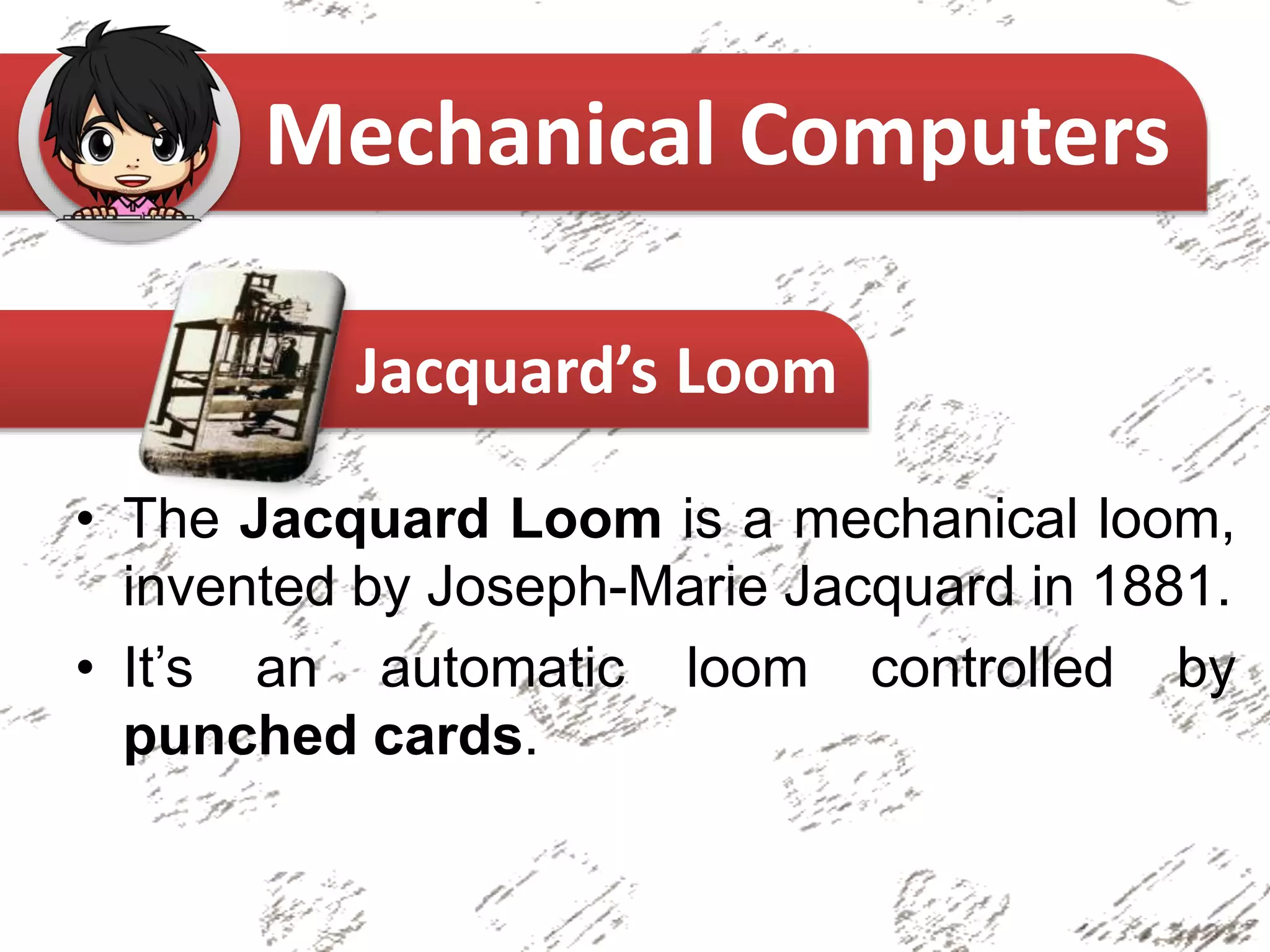
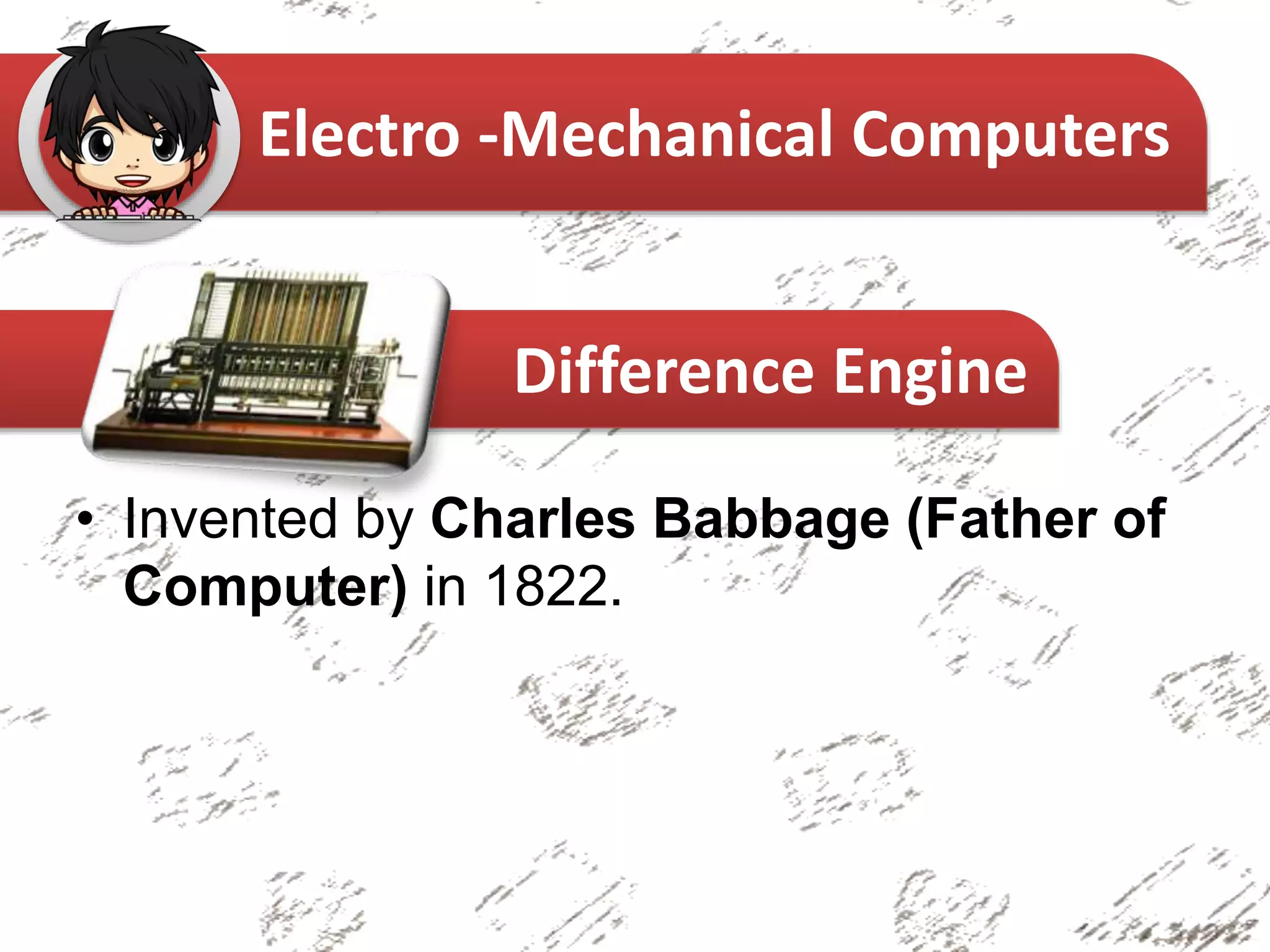
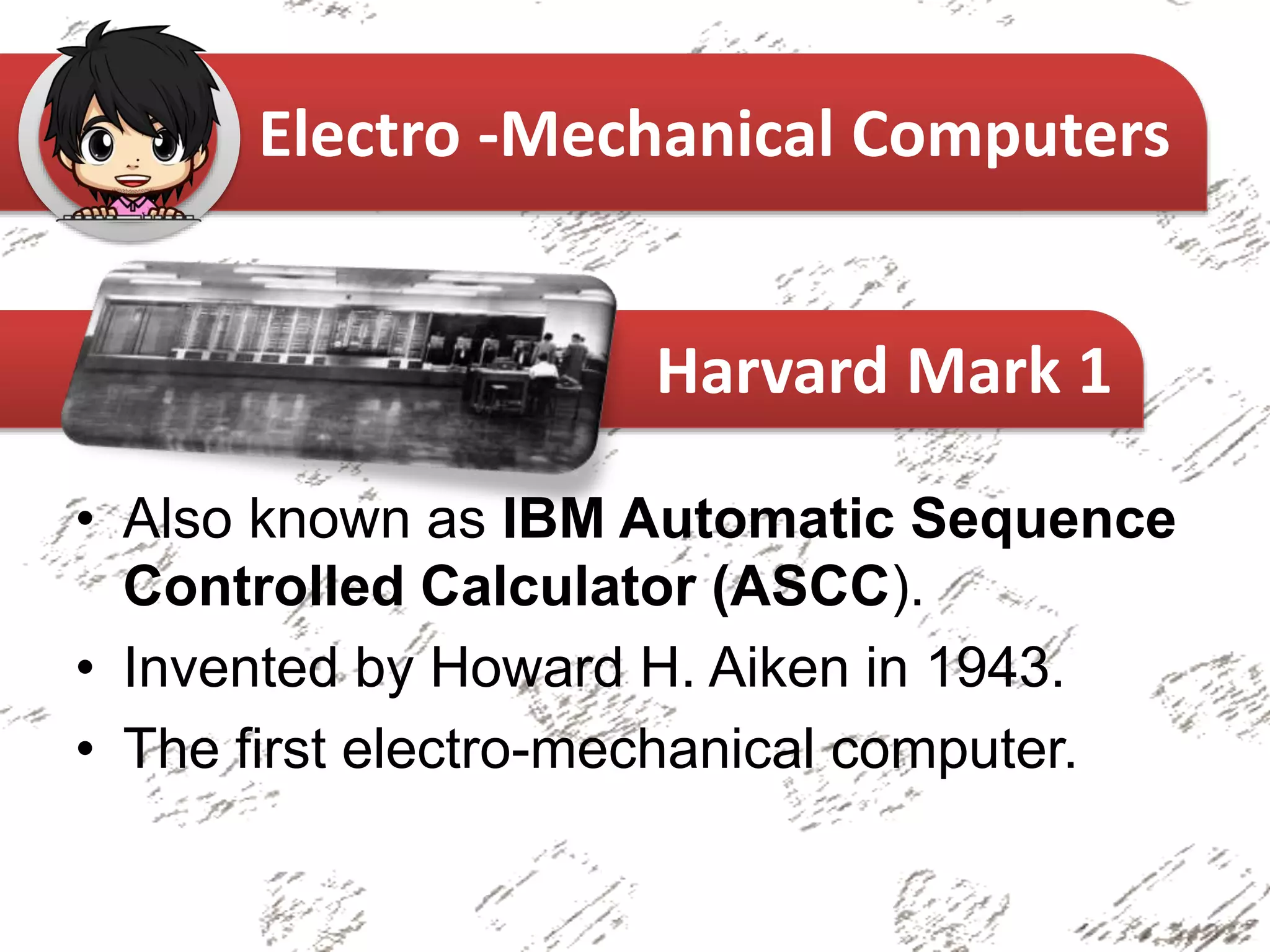
The document provides an overview of the history of computers, categorizing them into non-mechanical, mechanical, and electro-mechanical types. It highlights significant inventions such as the abacus, Pascaline, and the Analytical Engine, along with their inventors and primary functions. Key figures in the evolution of computing, including Charles Babbage and Ada Lovelace, are also mentioned.