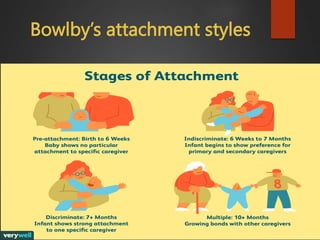
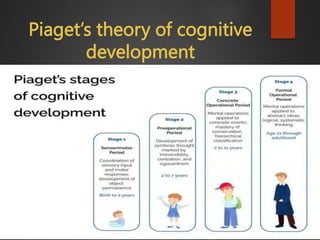
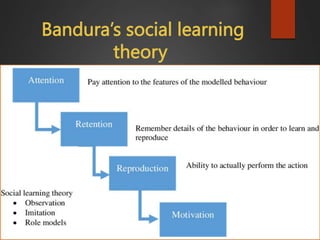
The document outlines the historical perspective of human development through the lens of developmental psychology, beginning in the late 19th century and initially focusing on child and adolescent development. It highlights key figures and their theories, such as Freud, Piaget, and Bandura, and notes the expansion of the field to include the entire lifespan and various aspects of development. Additionally, it discusses different research methods utilized in developmental psychology, each suited to specific study aims.