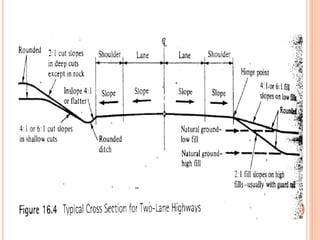
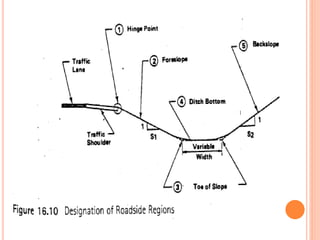
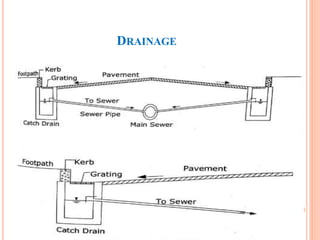
This document discusses various aspects of highway drainage facilities. It covers the importance of adequate drainage in highway design and construction. About 25% of highway funds are spent on erosion control and drainage structures like culverts and bridges. Inadequate drainage can damage pavements and cause accidents. The document describes different types of surface and subsurface drainage systems used in highways. These include ditches, culverts, bridges, inlets, catch basins and manholes to direct water flow. It emphasizes the role of drainage in protecting highways and ensuring safety.