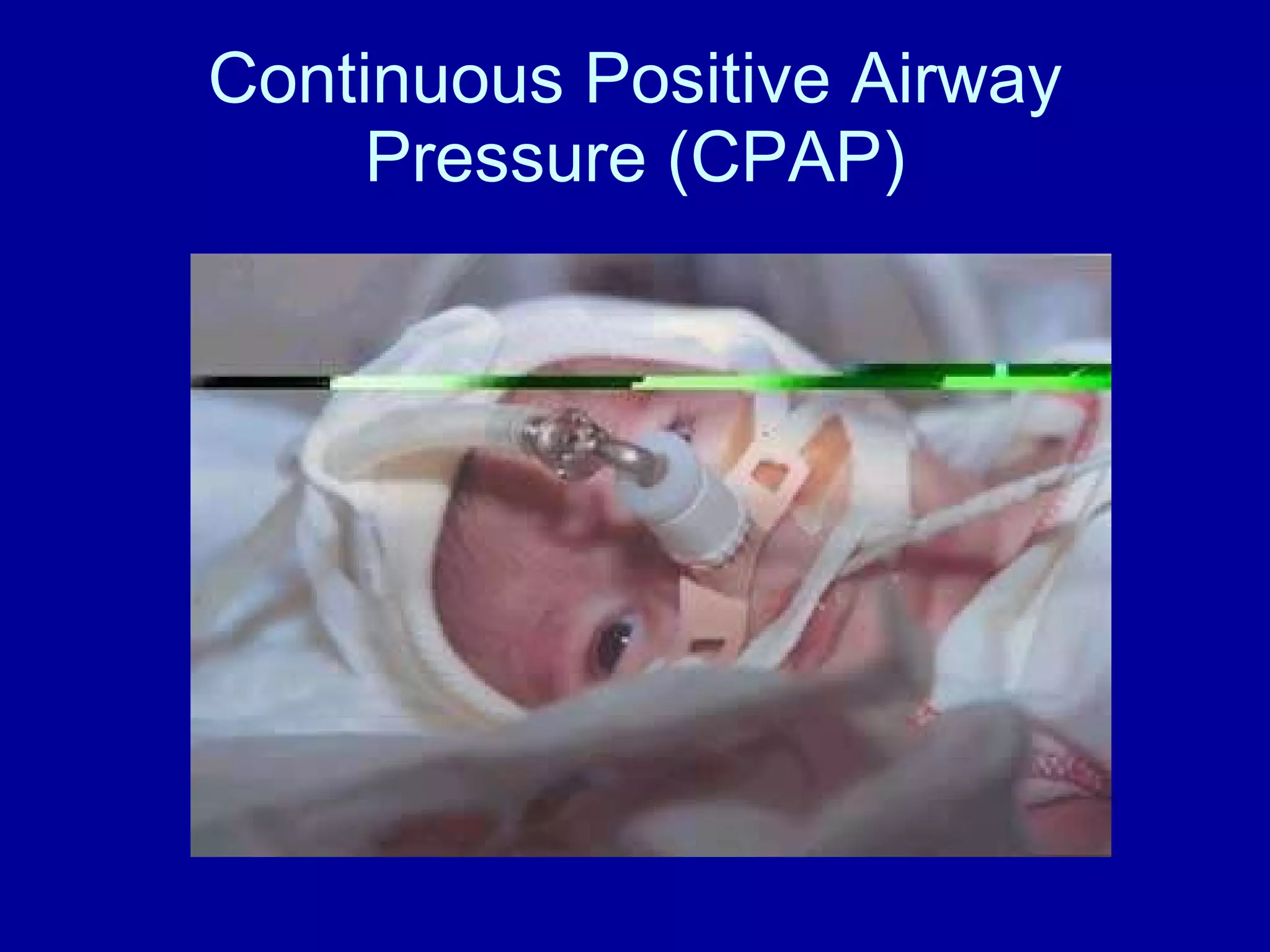
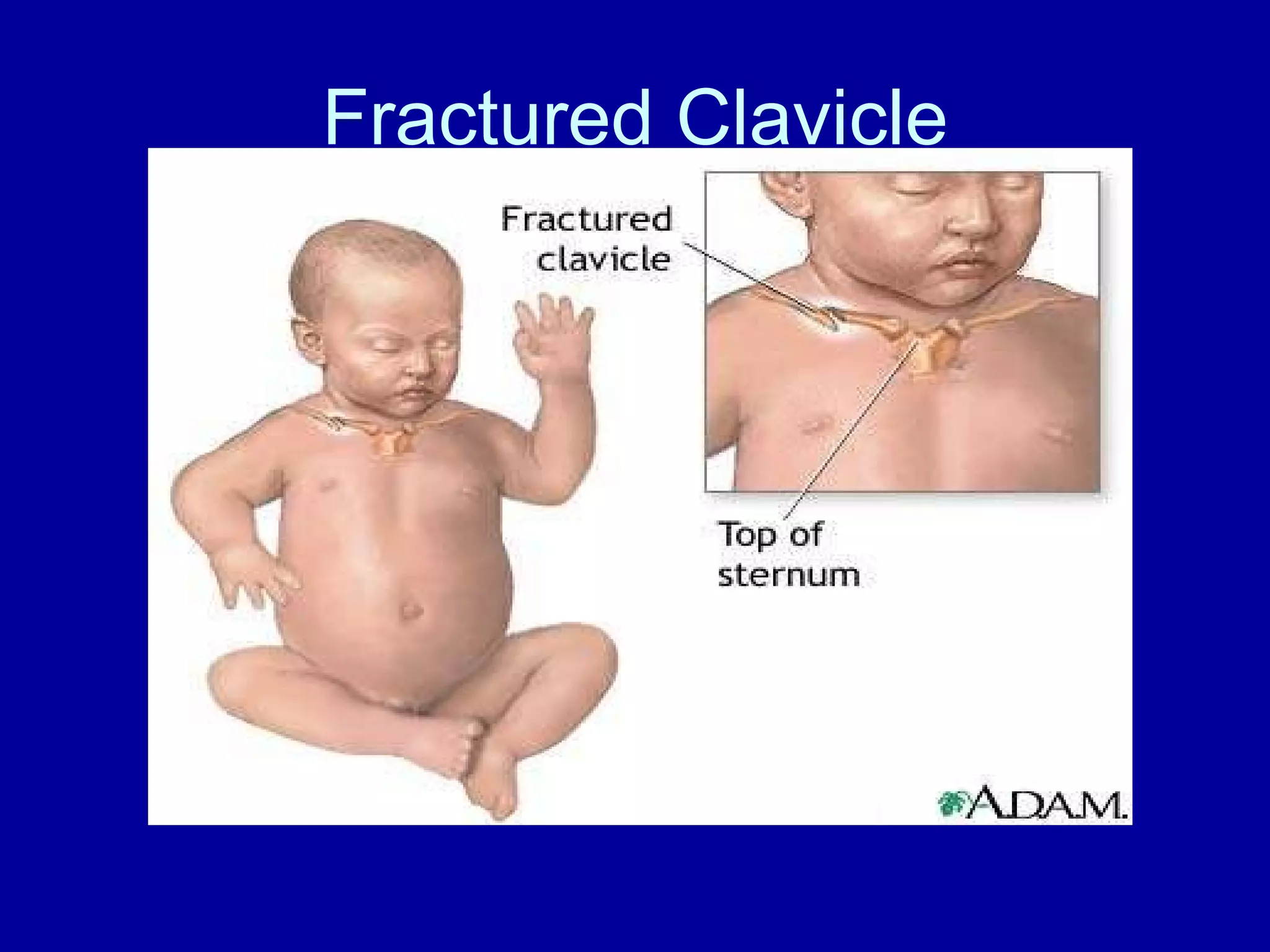
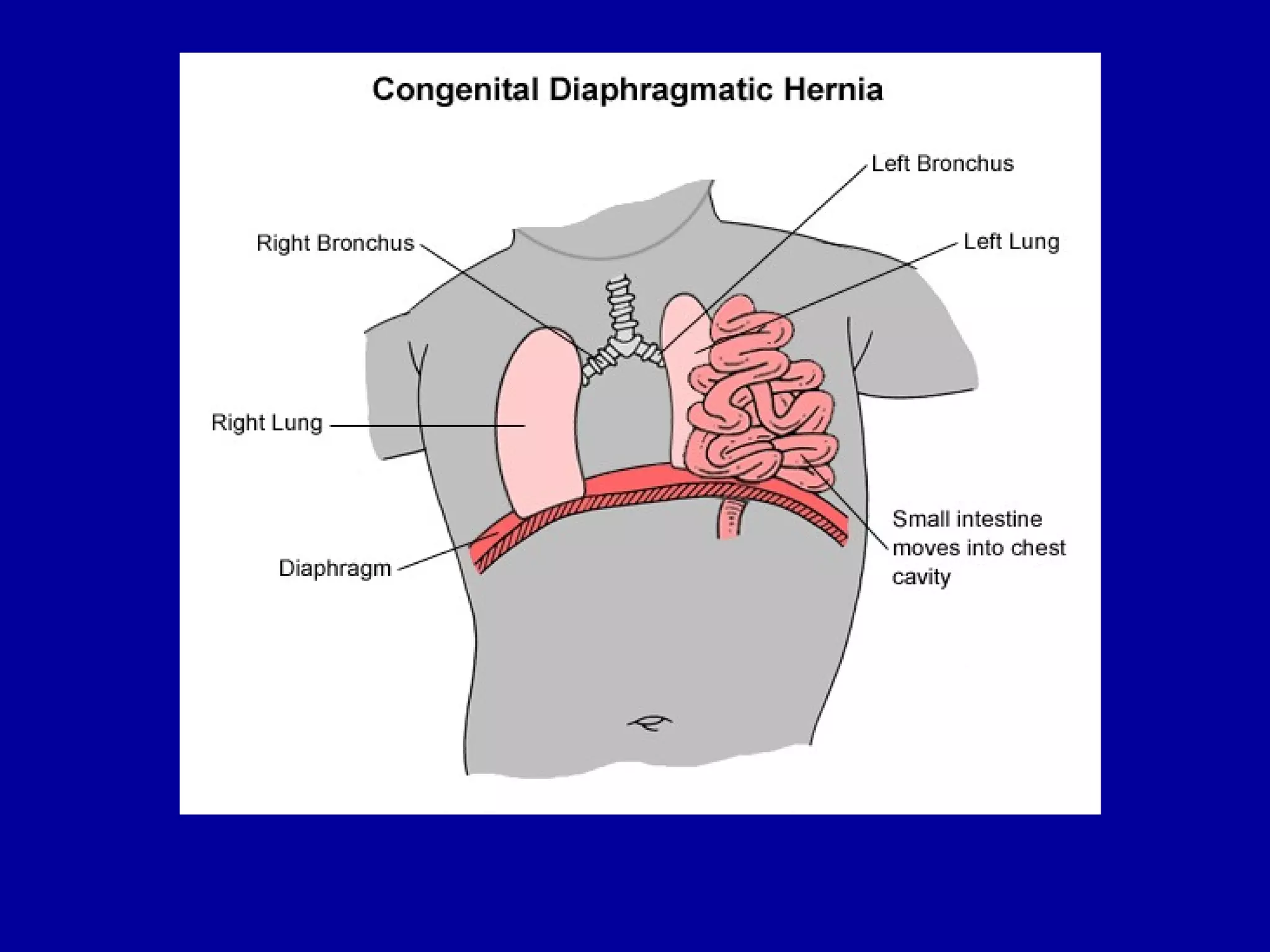
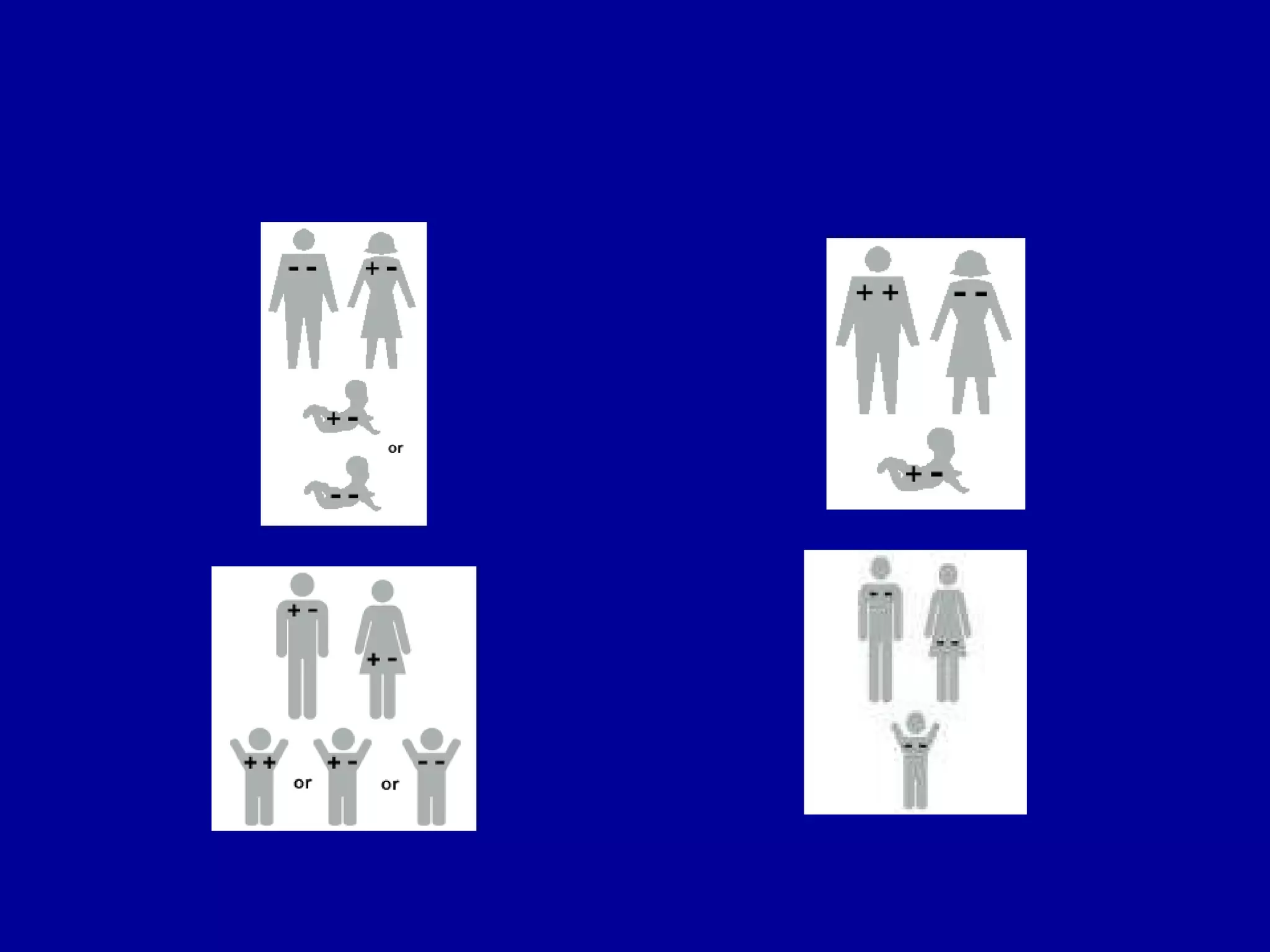
High risk neonates can experience various medical issues including respiratory distress syndrome, meconium aspiration syndrome, sepsis, and more. Nursing interventions focus on stabilizing vital functions like respiration and thermoregulation. Additional priorities include maintaining hydration and nutrition, facilitating development, and supporting the neonate-family bond. Risk factors span prematurity, growth abnormalities, and maternal health conditions that can endanger the fetus.