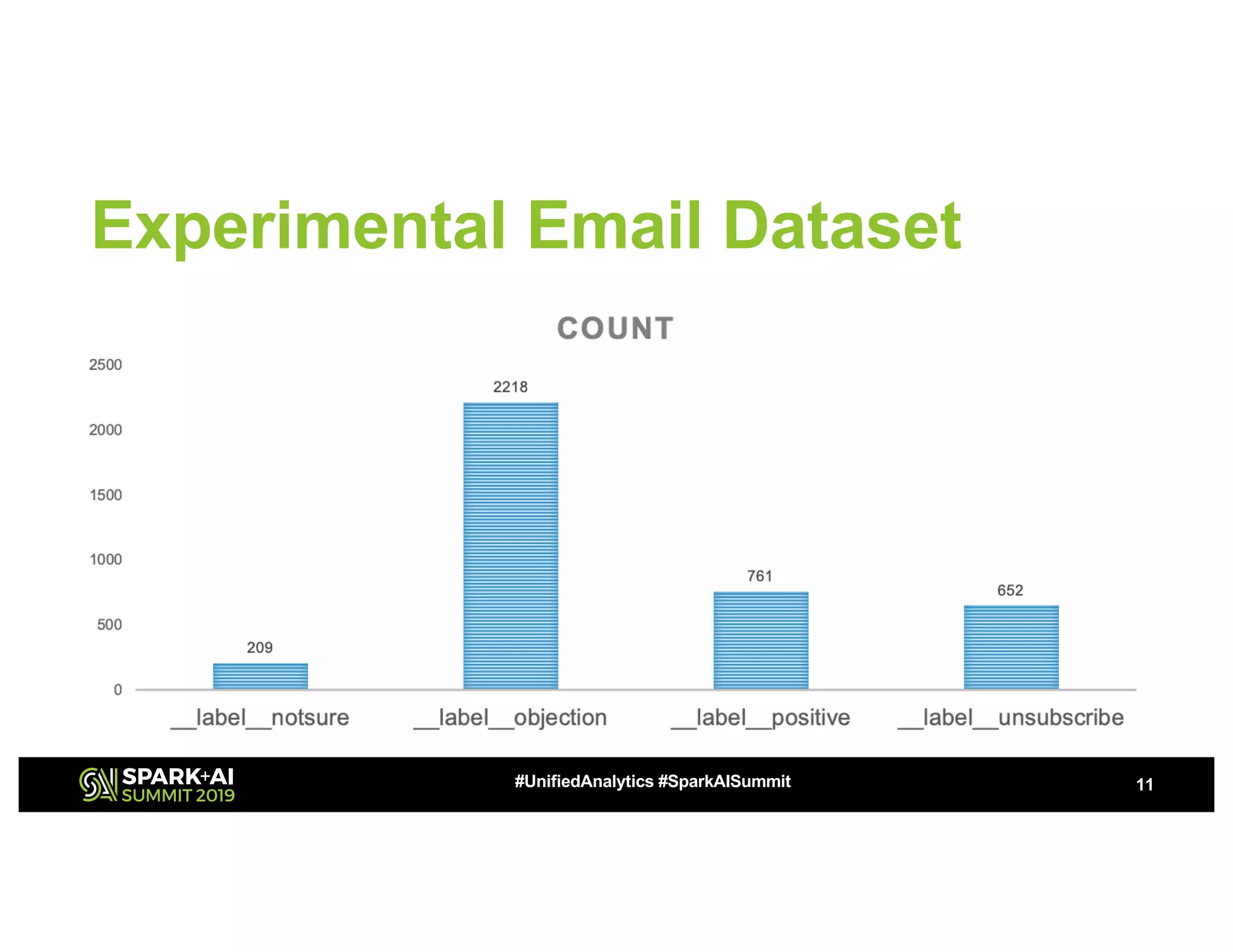
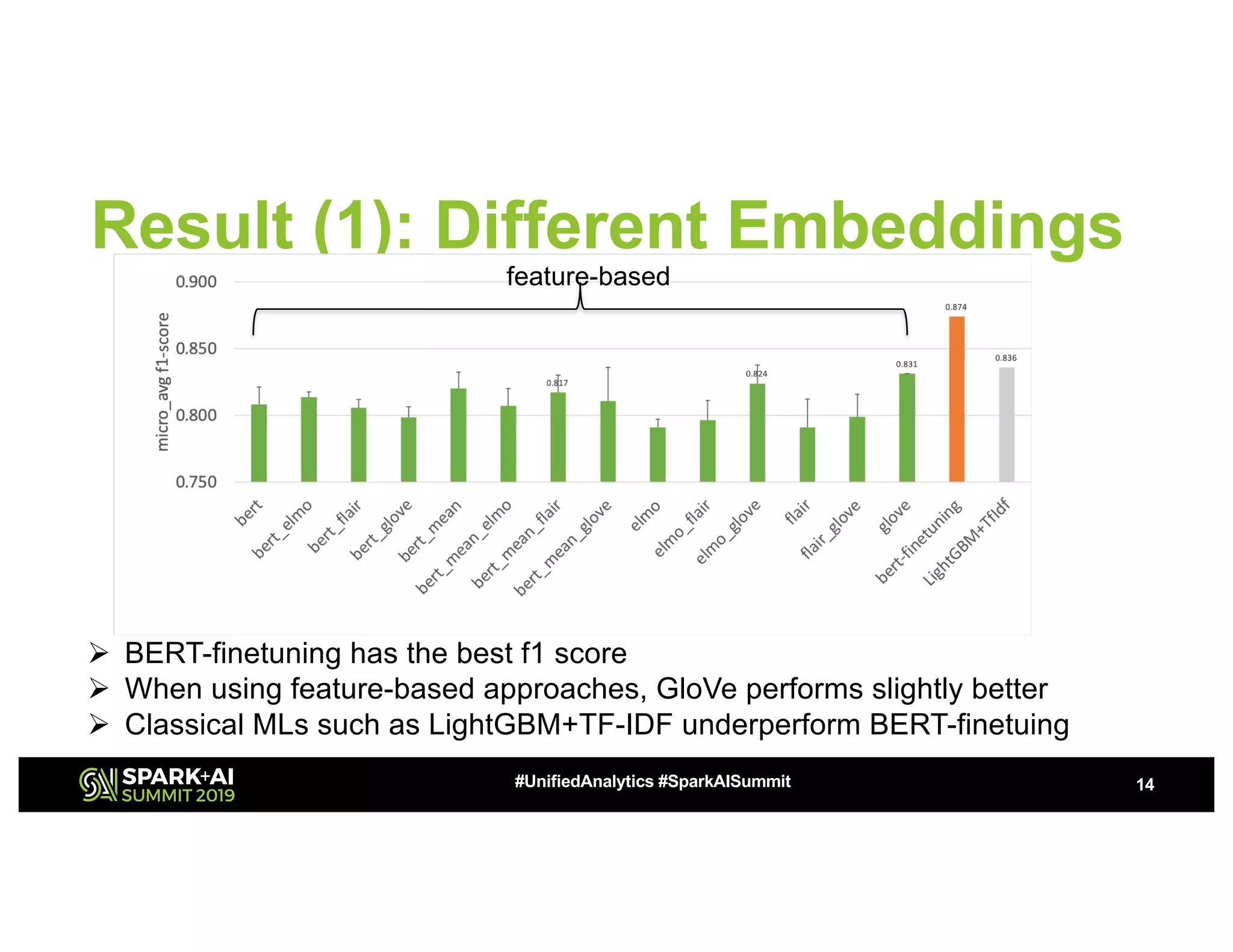
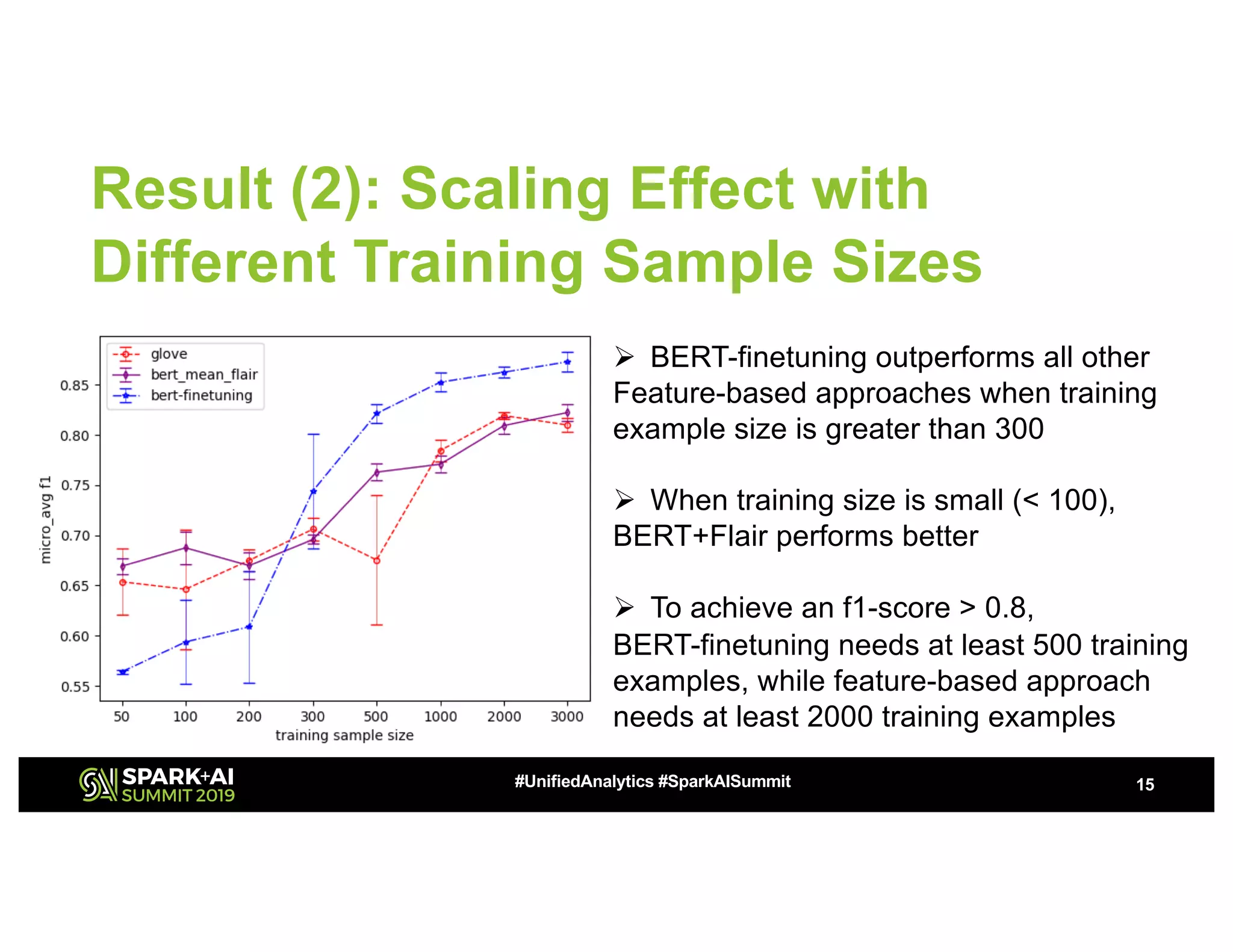
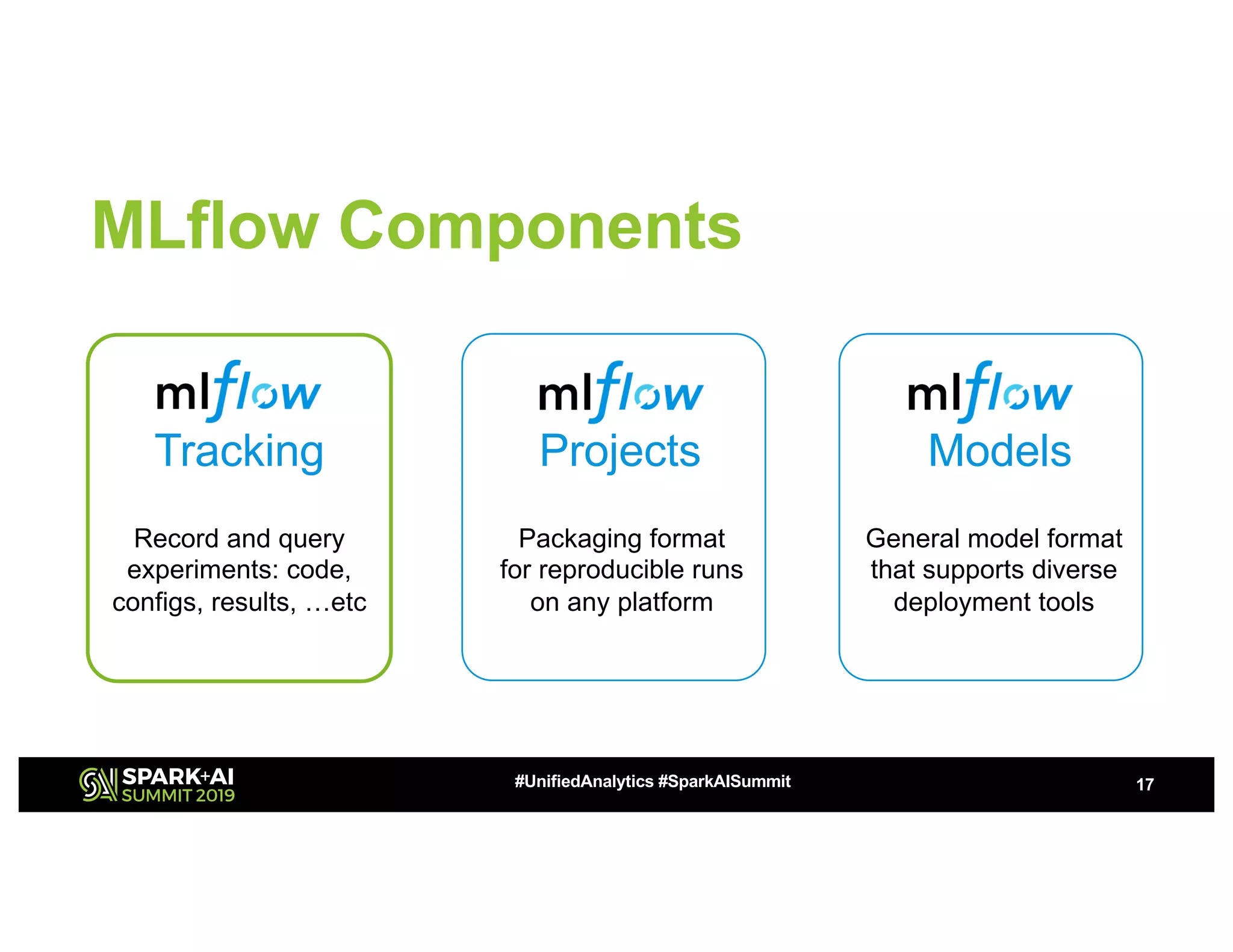
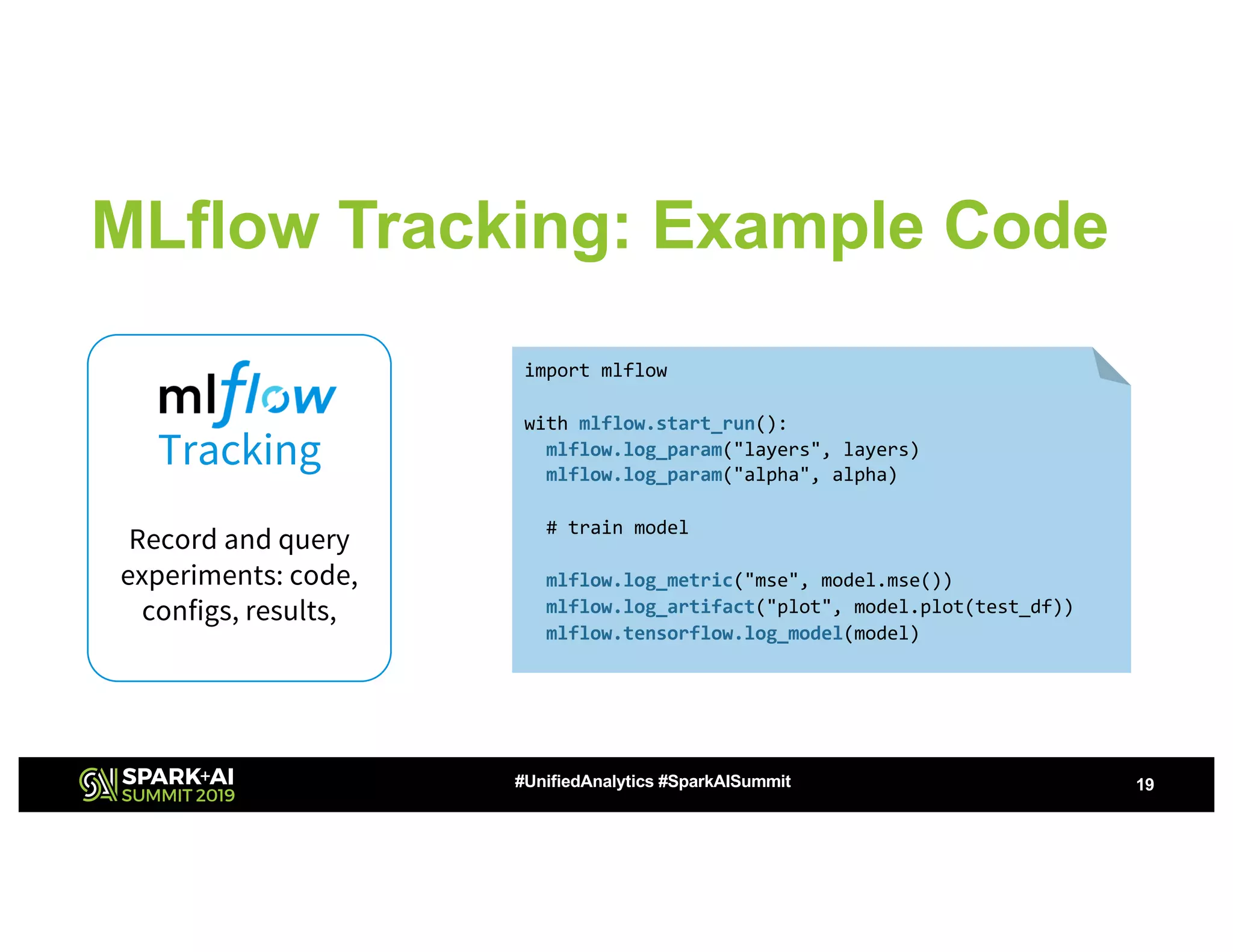
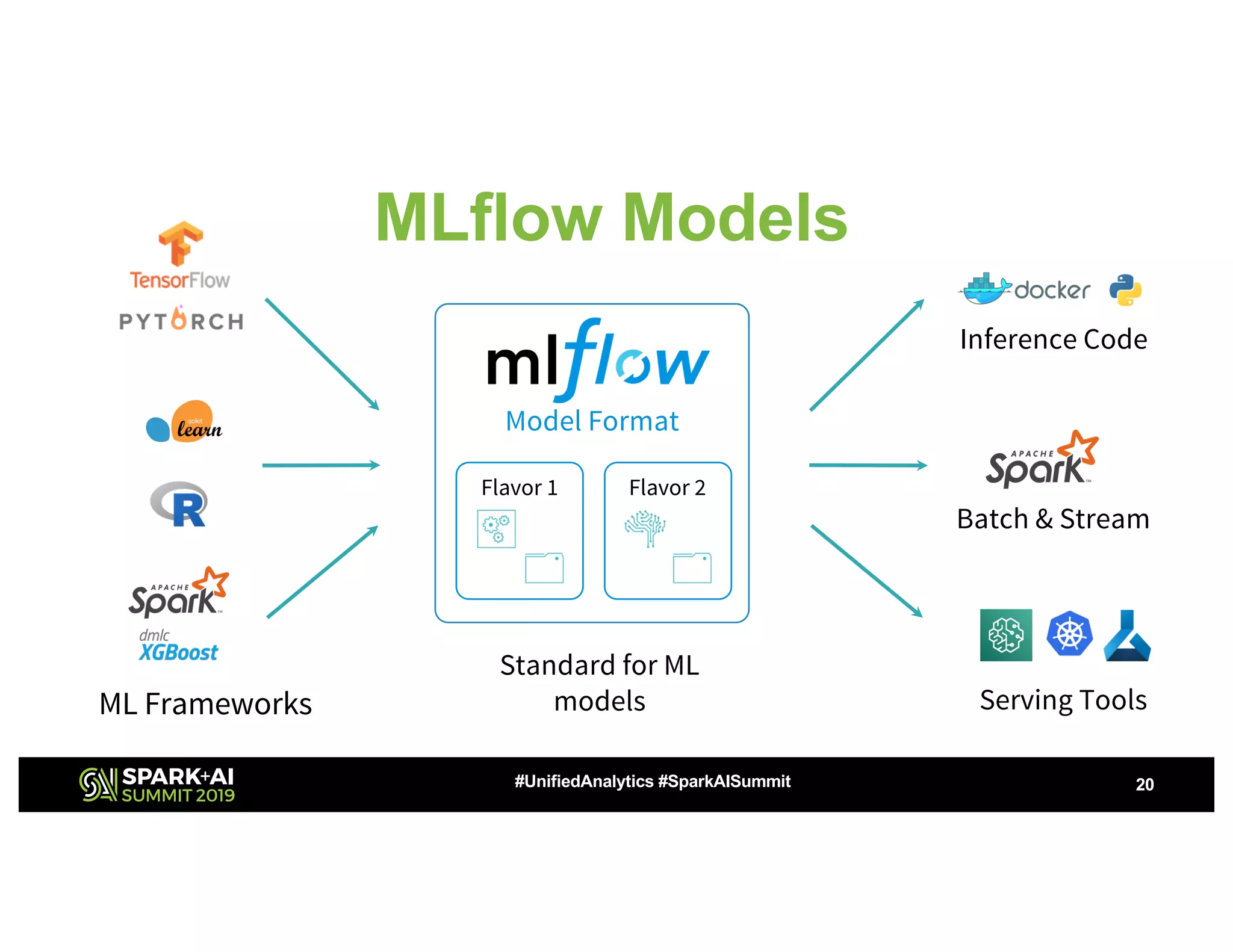
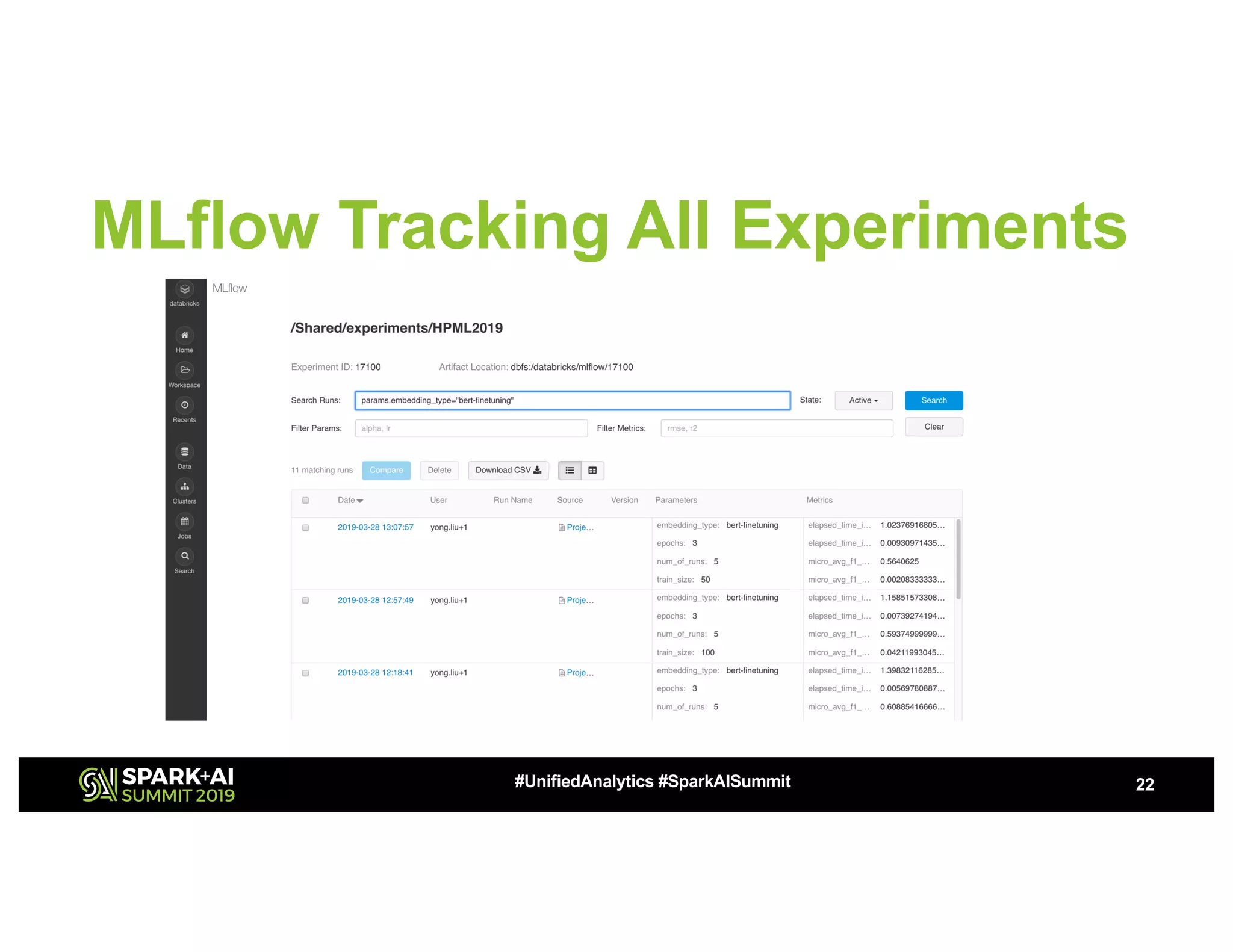
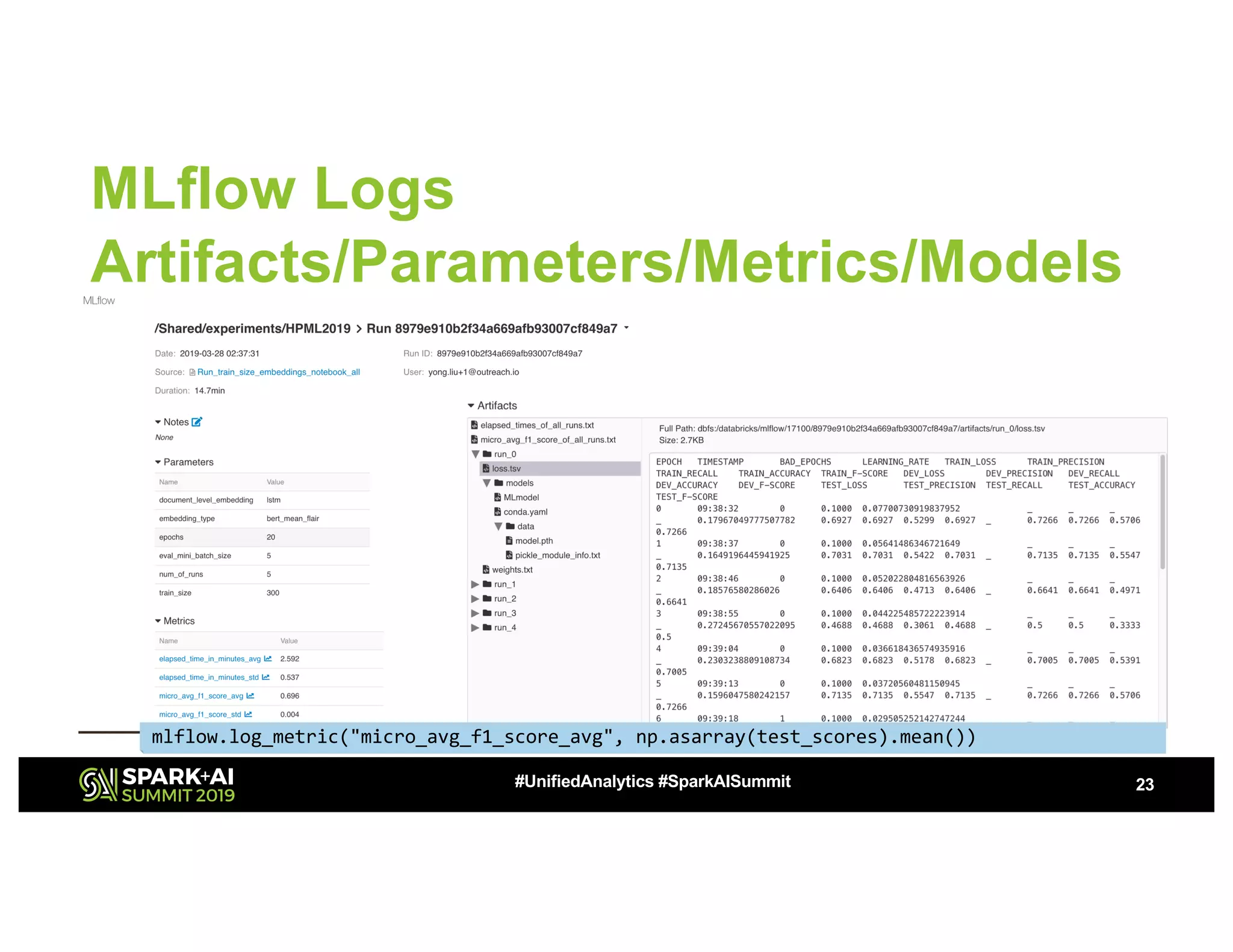
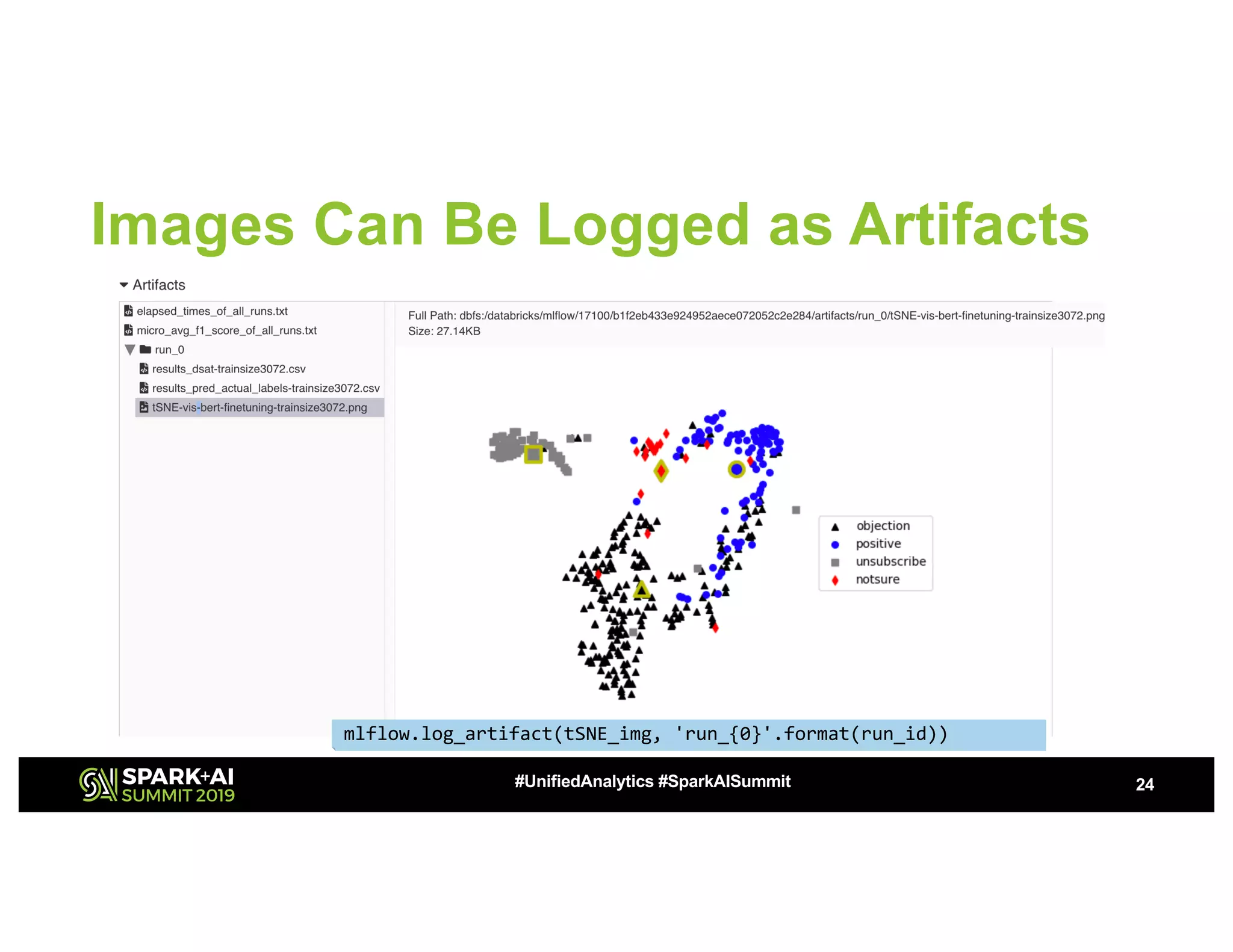
The document presents a study on high-performance transfer learning for classifying intent in sales engagement emails, focusing on objectives, challenges, and experimental results. It outlines the significance of effective email intent classification, the use of pretrained language models, and the integration of MLflow for tracking experiments. Key findings indicate that fine-tuning BERT with sufficient training examples yields superior performance over feature-based approaches.