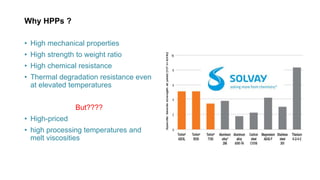
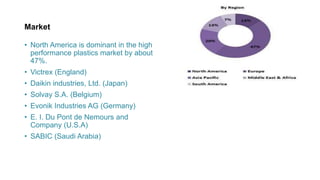
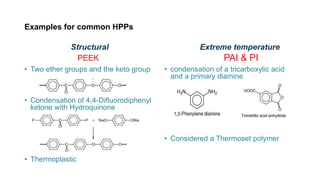
High performance polymers such as PEEK, PAI, and PI are used for their high strength, heat resistance, and chemical resistance. They are more expensive than traditional plastics but are lighter weight. The aerospace, medical, and coating industries are major users of high performance plastics to replace heavier materials like metal. Additives are used to improve processing and mechanical properties or provide other functions. The high performance plastics market is expected to grow to $35 billion by 2026 due to increasing demand in aerospace, medical, and other industries.