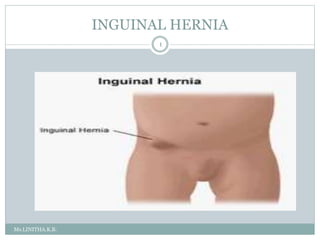
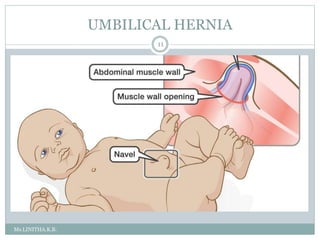
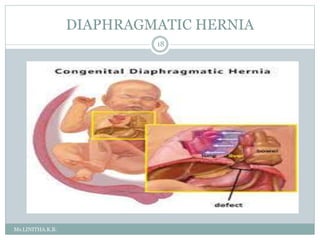
Inguinal hernia is an abnormal protrusion of abdominal organs through the groin region. It most commonly occurs in infants and boys. It is caused by a failure of the processus vaginalis to close after testicular descent. Types include direct and indirect hernias. Clinical features include a painless swelling in the groin that reduces with crying. Management involves early elective surgery to repair the defect. Umbilical hernia involves a weakness at the umbilical ring allowing intestinal contents to protrude. It often closes spontaneously by age 5 without surgery. Diaphragmatic hernia is a congenital defect where abdominal organs protrude into the chest cavity through an opening in the diaphragm.