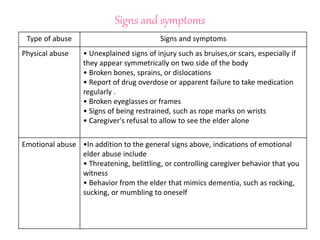
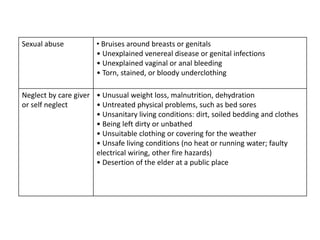
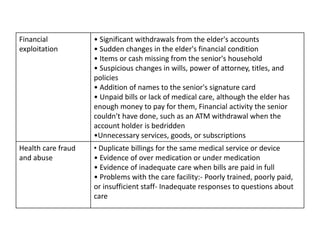
Elderly abuse is a significant problem as populations age around the world. Elder abuse can take several forms, including physical, emotional, sexual, financial abuse and neglect. Common signs of elder abuse include unexplained injuries, personality changes, and sudden financial changes. Community health nurses can help prevent elder abuse through public education, counseling families, identifying abuse cases, and ensuring proper care and support for abused elders.