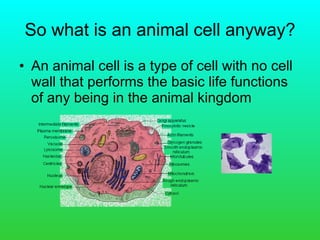
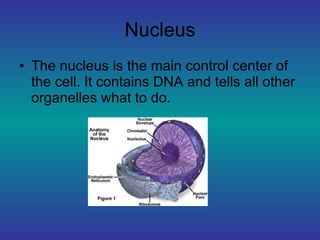
An animal cell contains several organelles that perform essential life functions. The nucleus contains DNA and directs the cell's activities. The mitochondria produces energy for the cell through cellular respiration. Other organelles like the endoplasmic reticulum, golgi bodies, and lysosomes help transport nutrients and waste within and out of the cell. Together these organelles allow the cell to survive and function as the basic unit of life.