Embed presentation
Downloaded 87 times






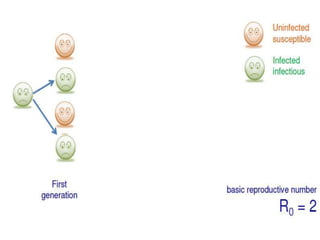
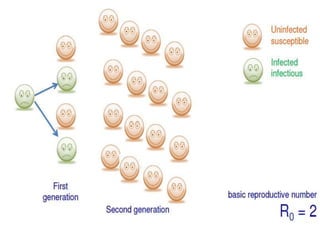
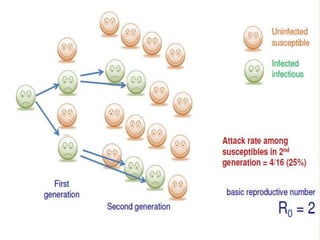
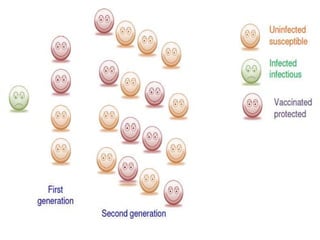
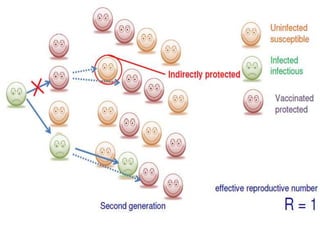
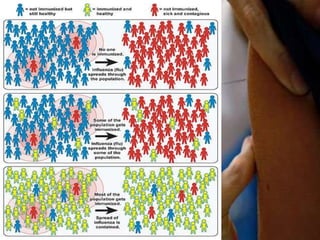
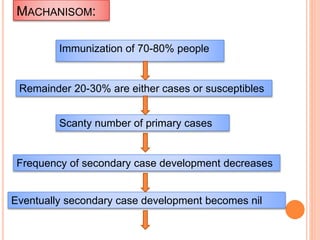





Herd immunity is achieved when a large percentage of a population is immune to an infectious disease, providing indirect protection to those who are not immune. It works by reducing opportunities for disease transmission, eventually eliminating the disease from the community. Herd immunity can be achieved through vaccination or natural infection and depends on factors like the human population size and density, presence of animal reservoirs or insect vectors, social interactions, and access to healthcare and nutrition.


















