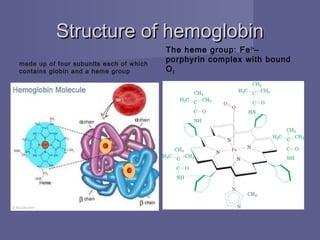
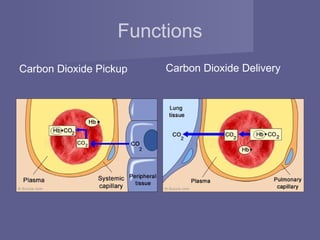
Haemoglobin is the protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen and carbon dioxide throughout the body. It is composed of four globin protein subunits, each containing an iron-containing heme group. Haemoglobin's ability to bind and release oxygen and carbon dioxide allows it to deliver oxygen from the lungs to tissues and remove carbon dioxide from tissues back to the lungs. Several factors regulate haemoglobin's affinity for oxygen, including partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide, pH, and levels of 2,3-bisphosphoglycerate in the blood. This complex regulation allows haemoglobin to efficiently load and unload gases where they are needed.