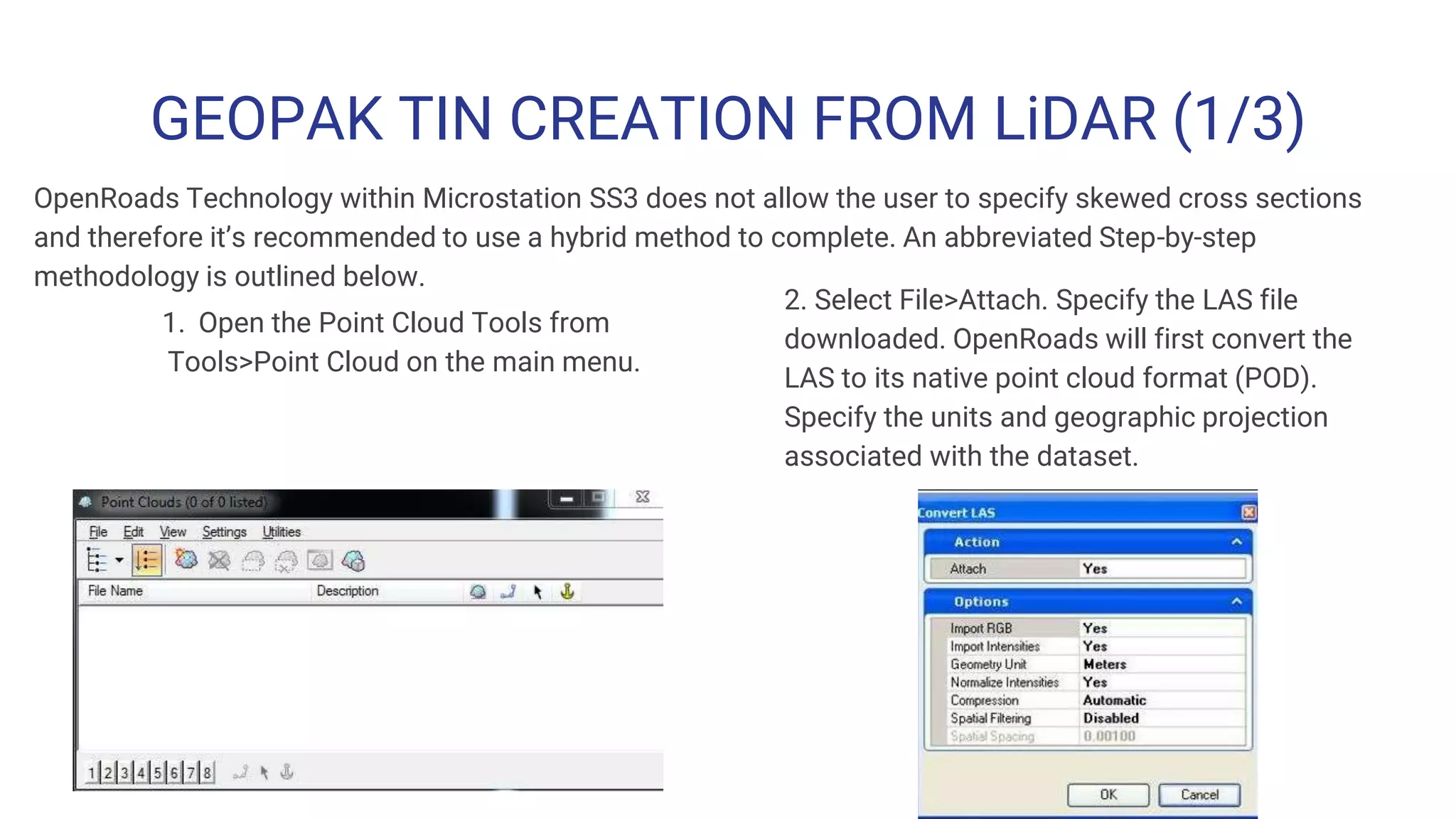
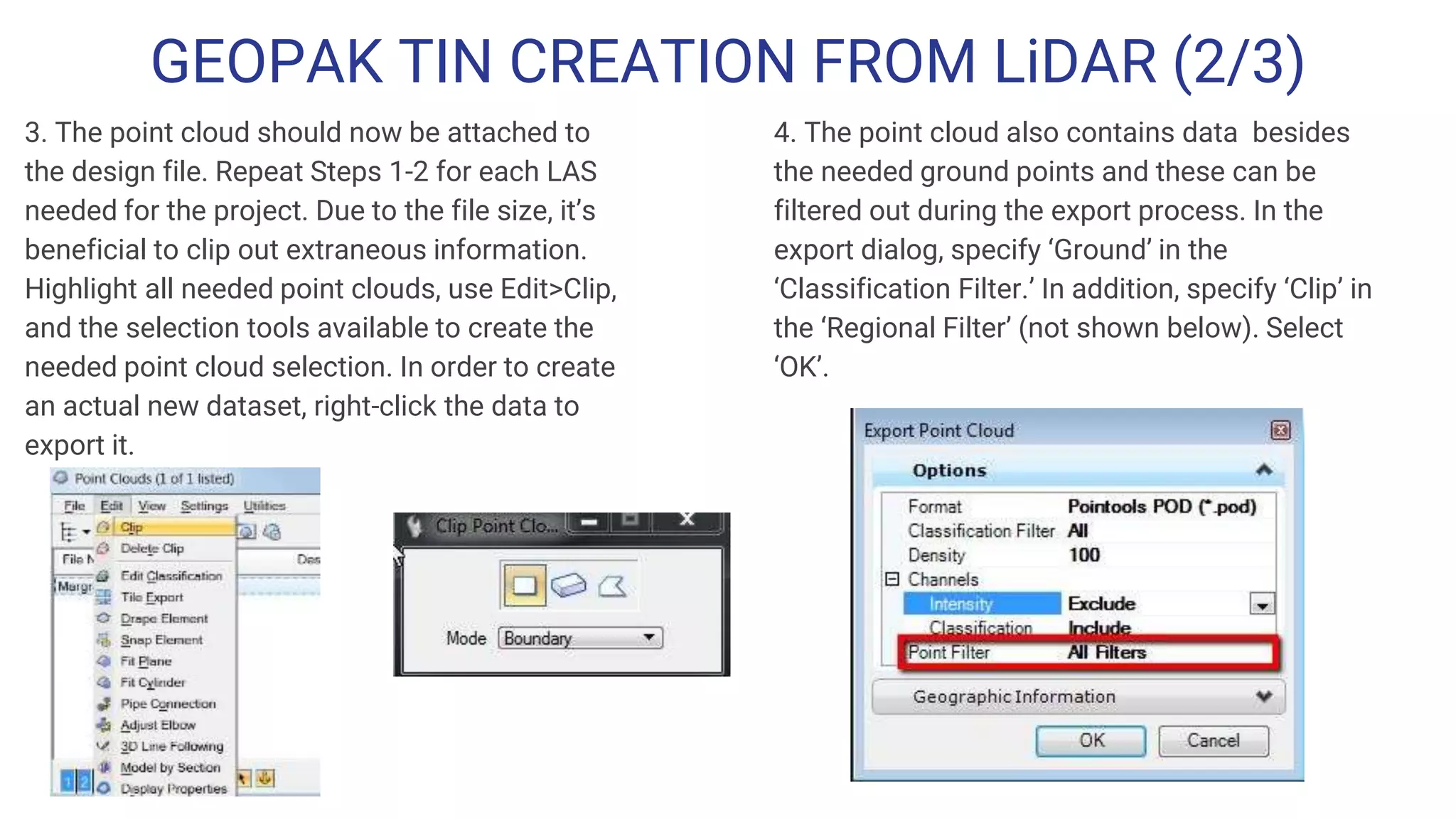
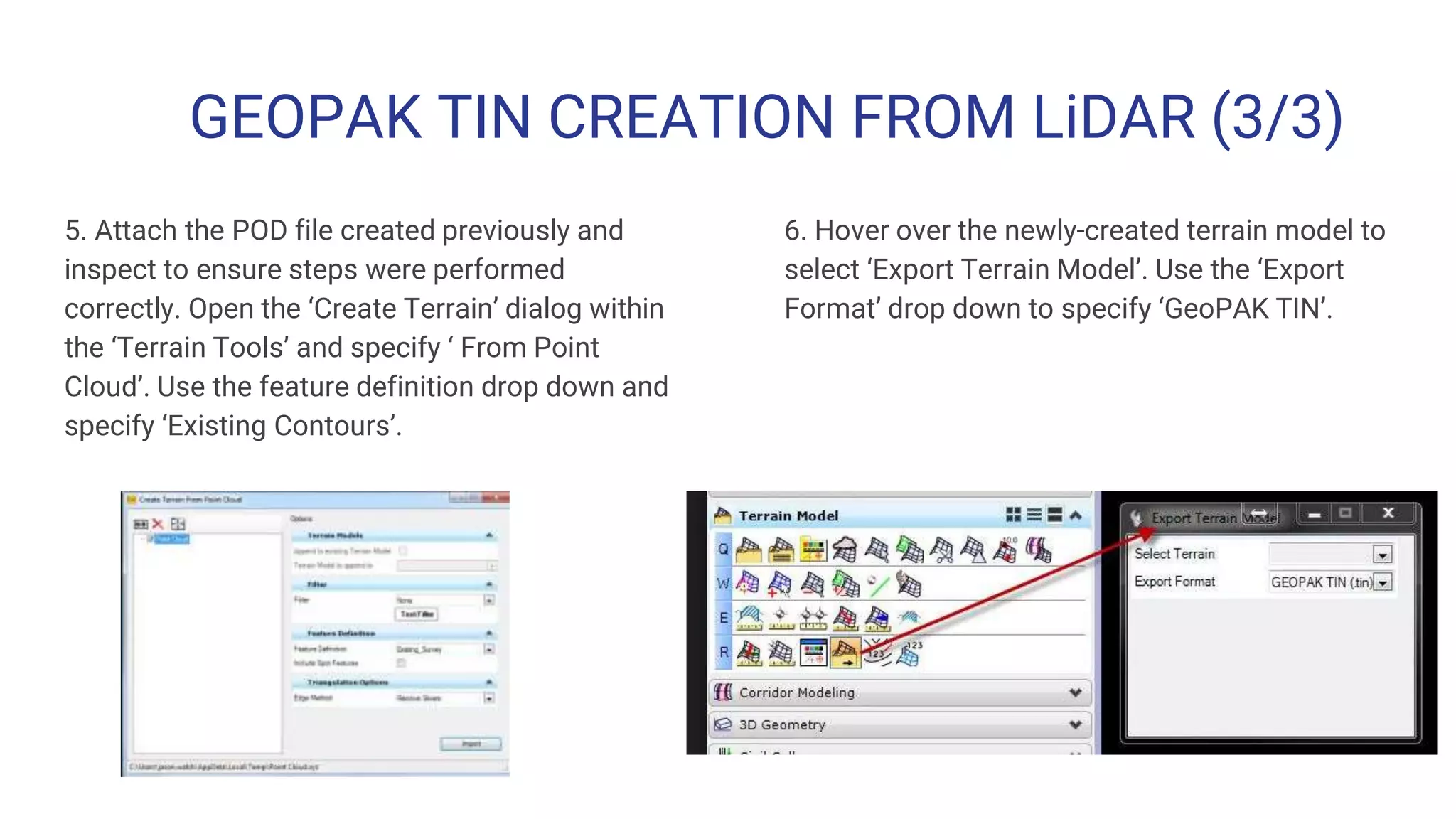
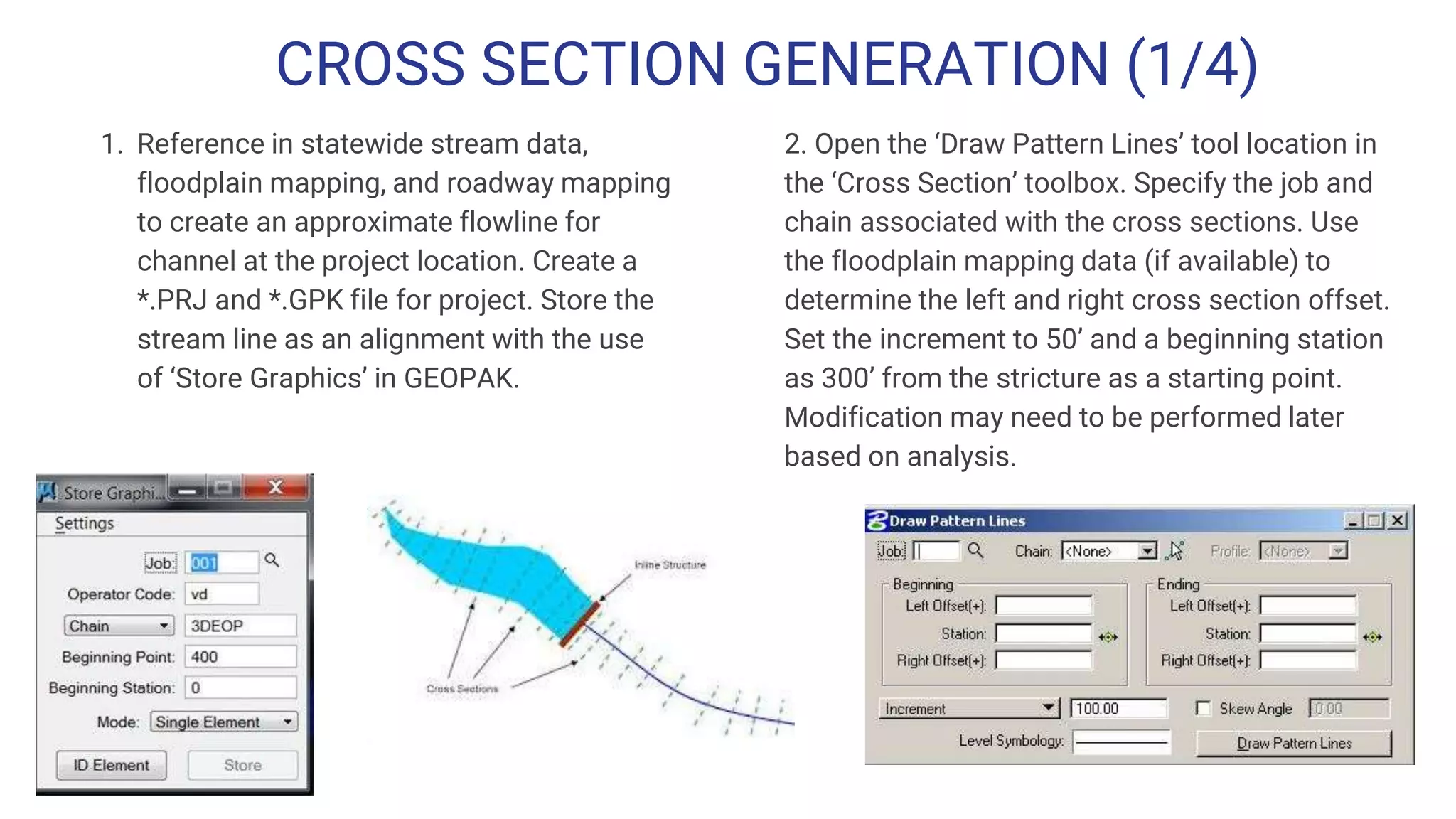
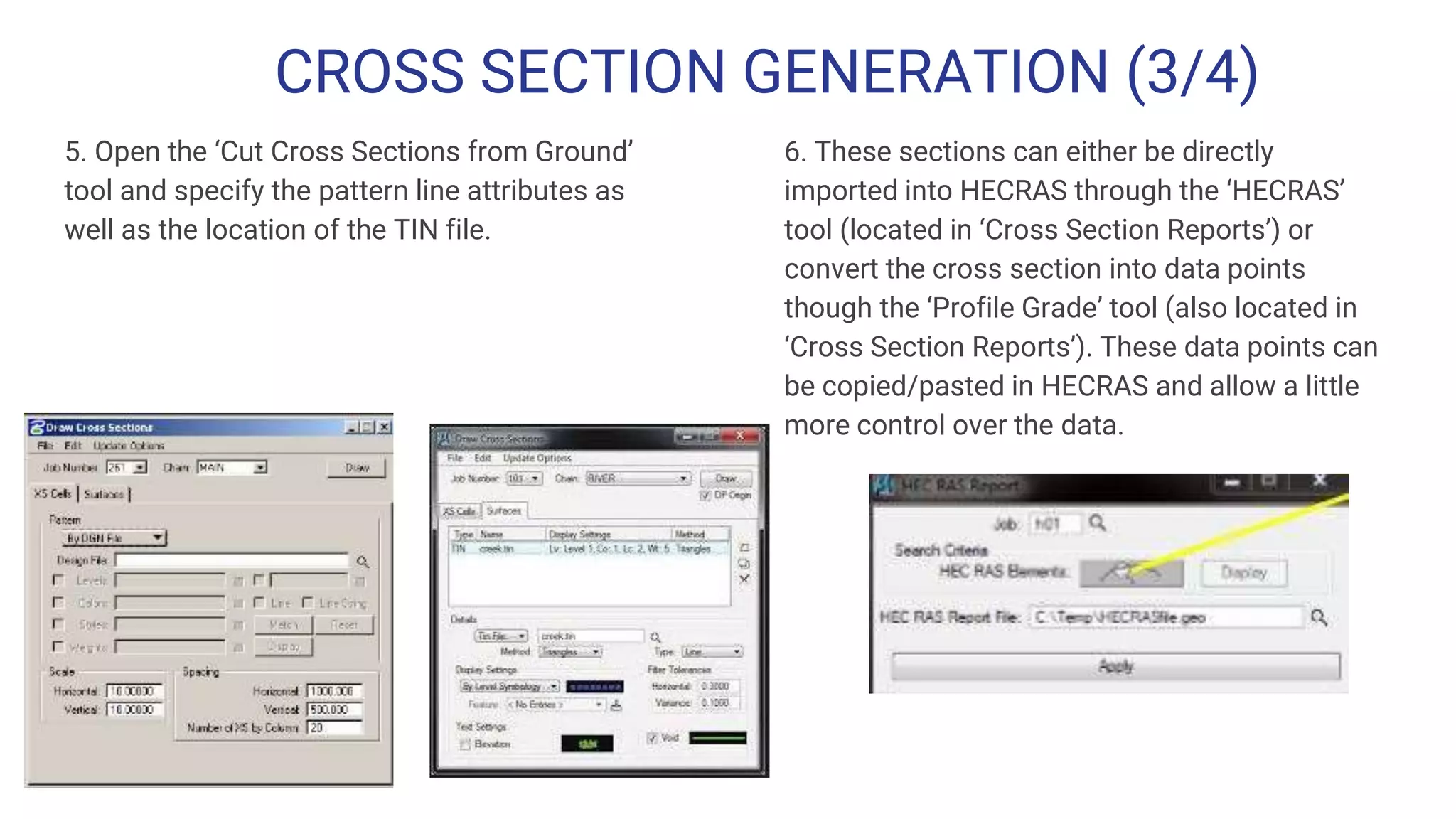
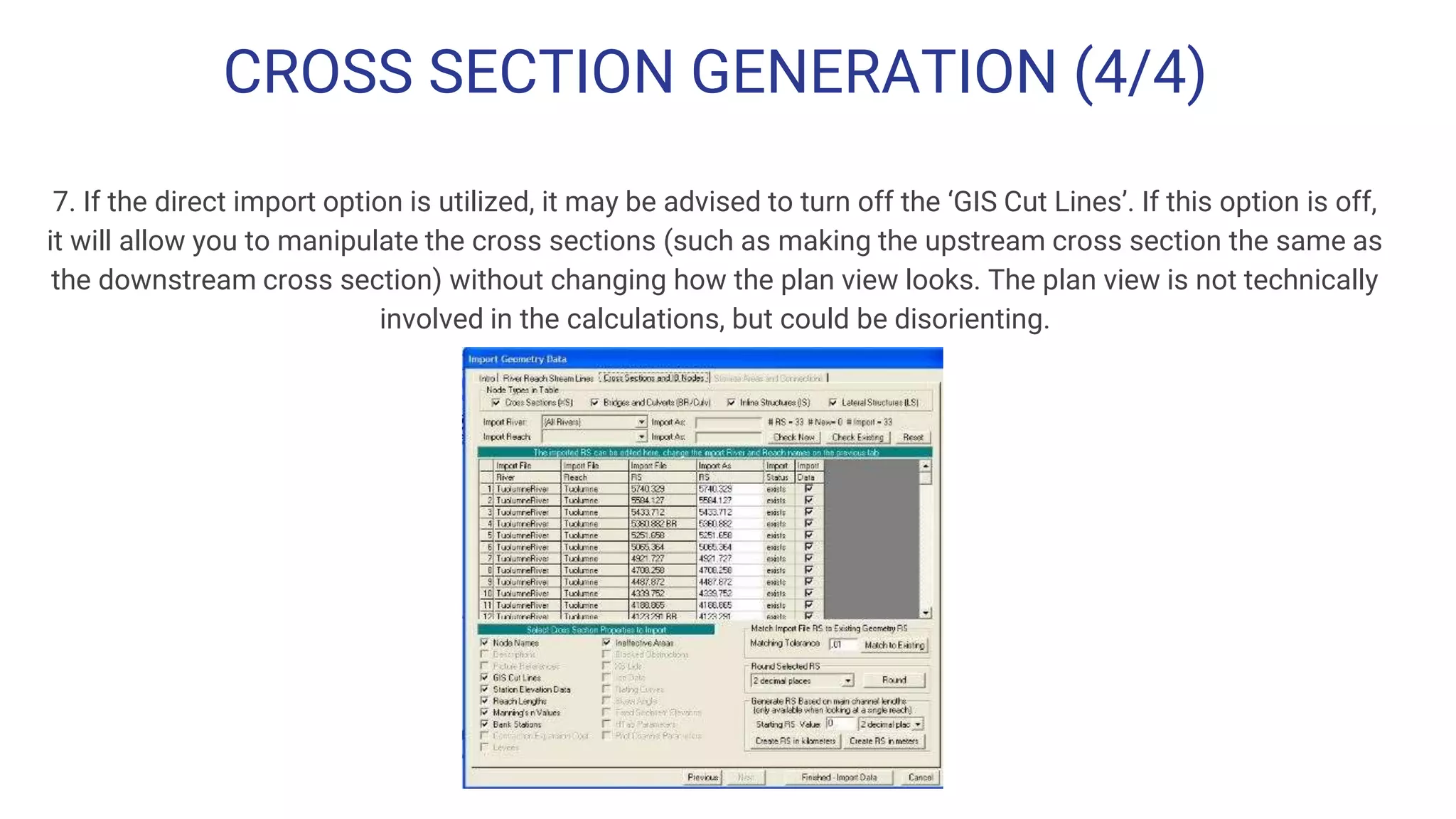
The document outlines the steps for creating HEC-RAS cross-sections using LIDAR data within Open Roads/MicroStation SS3, emphasizing the importance of data quality and suitability for hydraulic risk assessment. It details the process of generating Geopak TIN from LIDAR data, importing point clouds, and producing cross-sections with various adjustments. Resources and techniques for efficiently navigating the software and managing data classifications are also provided.