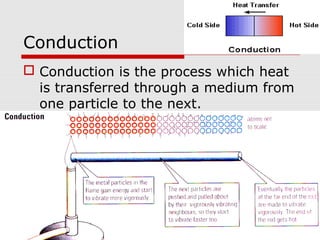
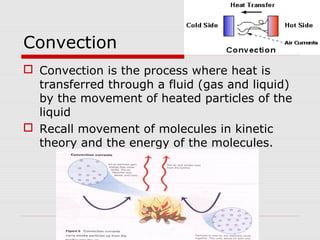
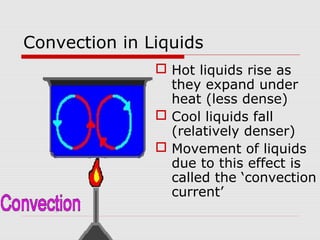
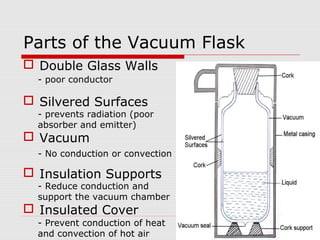
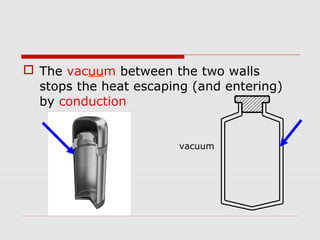
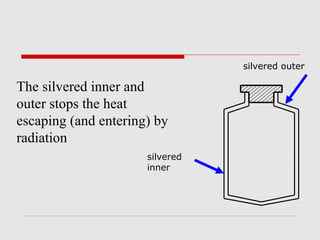
Heat can be transferred through three processes: conduction, convection, and radiation. Conduction involves the transfer of heat between particles in direct contact. Convection refers to the transfer of heat by the movement of fluids like gases and liquids. Radiation involves the transfer of heat by electromagnetic waves and does not require a medium. The vacuum flask harnesses these principles of heat transfer to keep liquids hot or cold by using double walls, a vacuum between the walls, and silvered surfaces to minimize conduction, convection, and radiation between the interior and exterior.