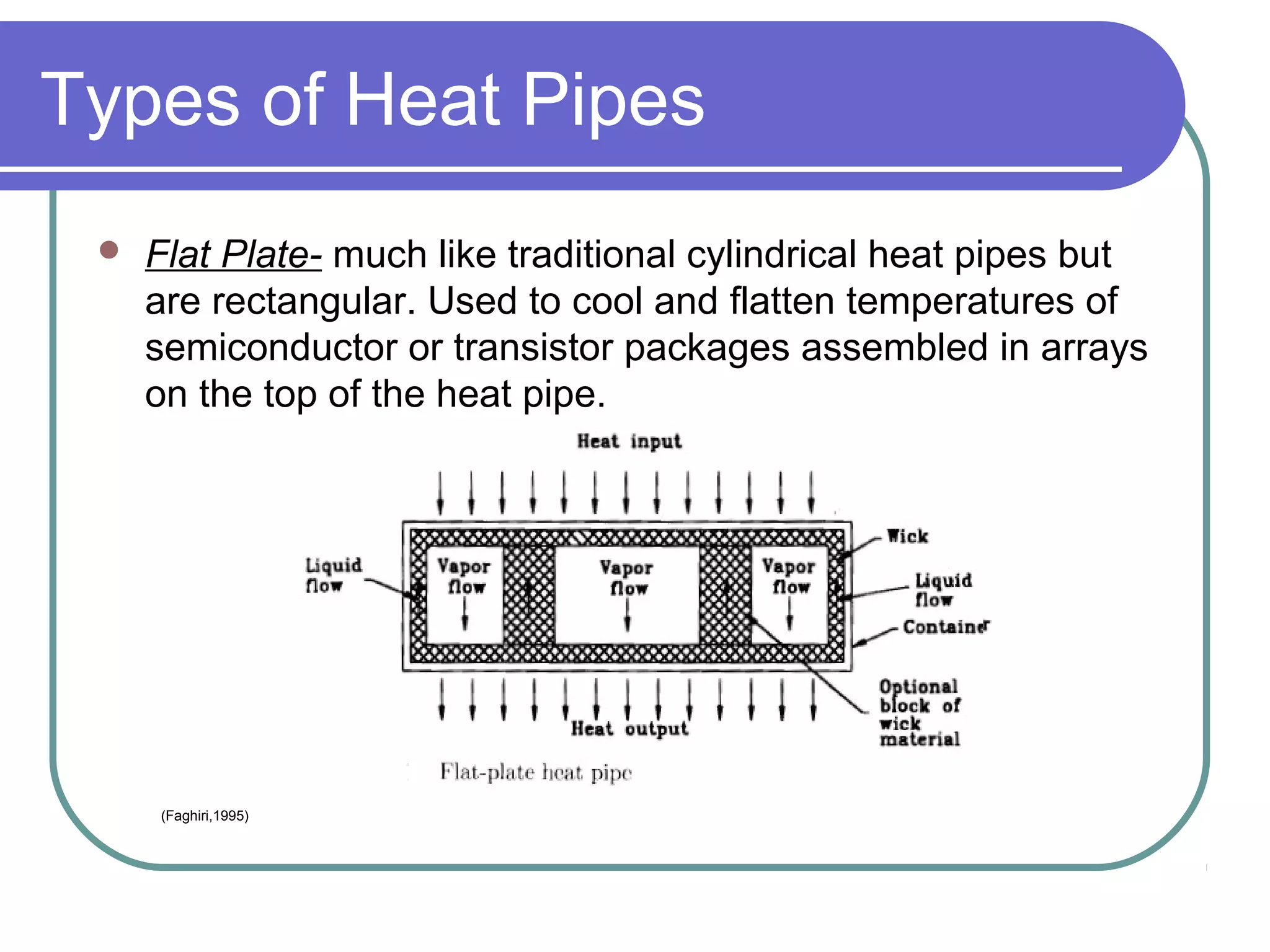
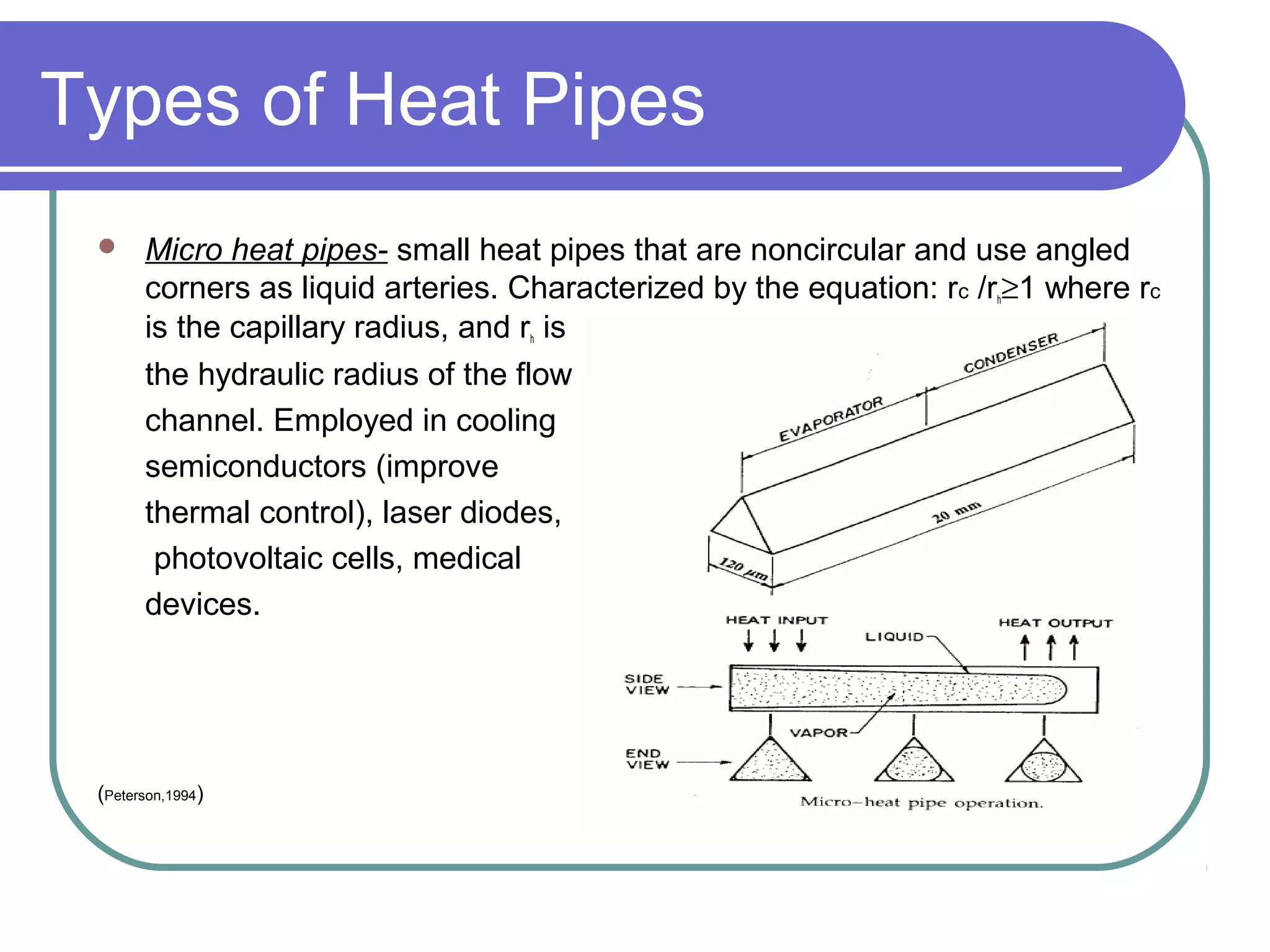
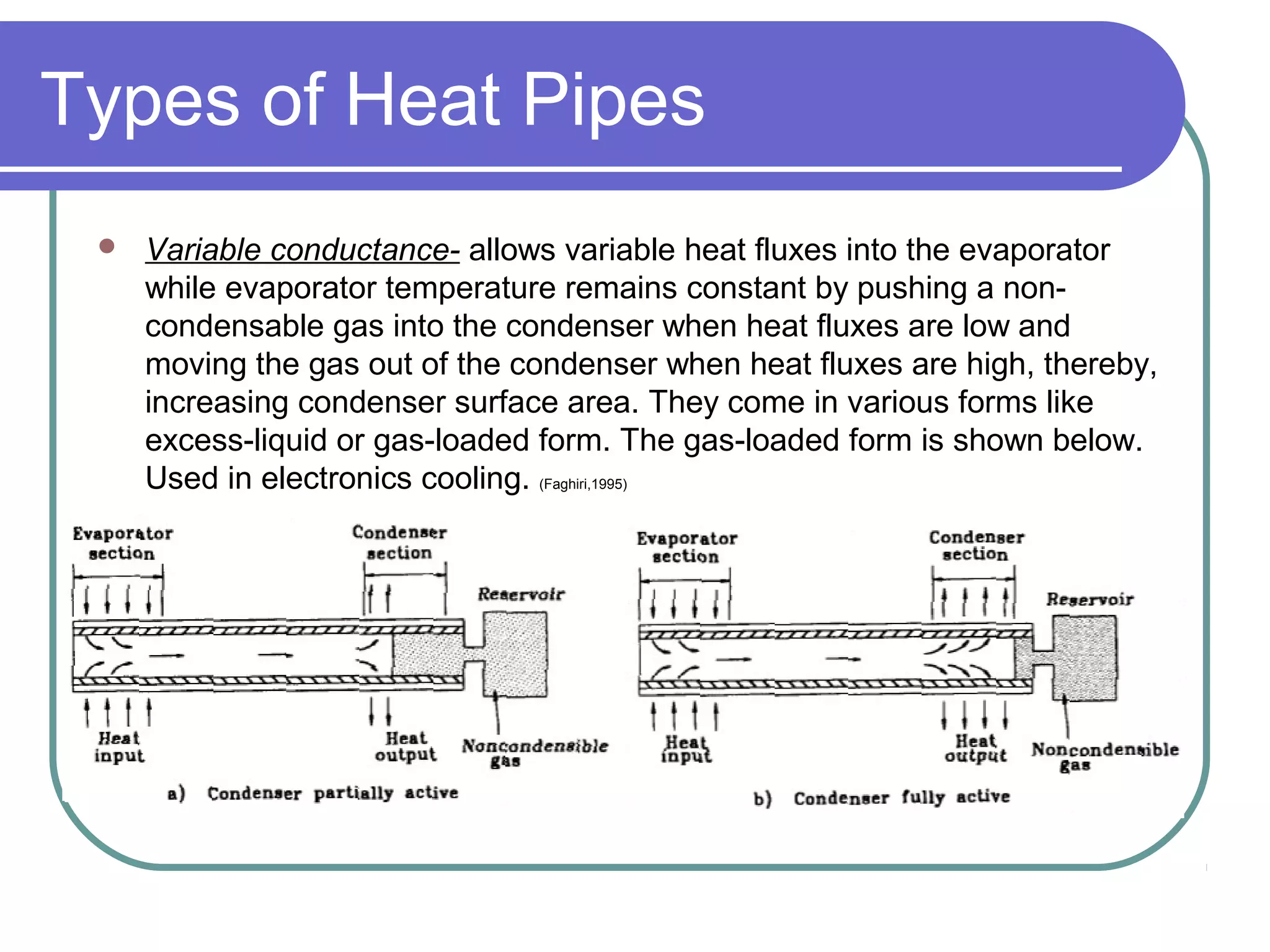
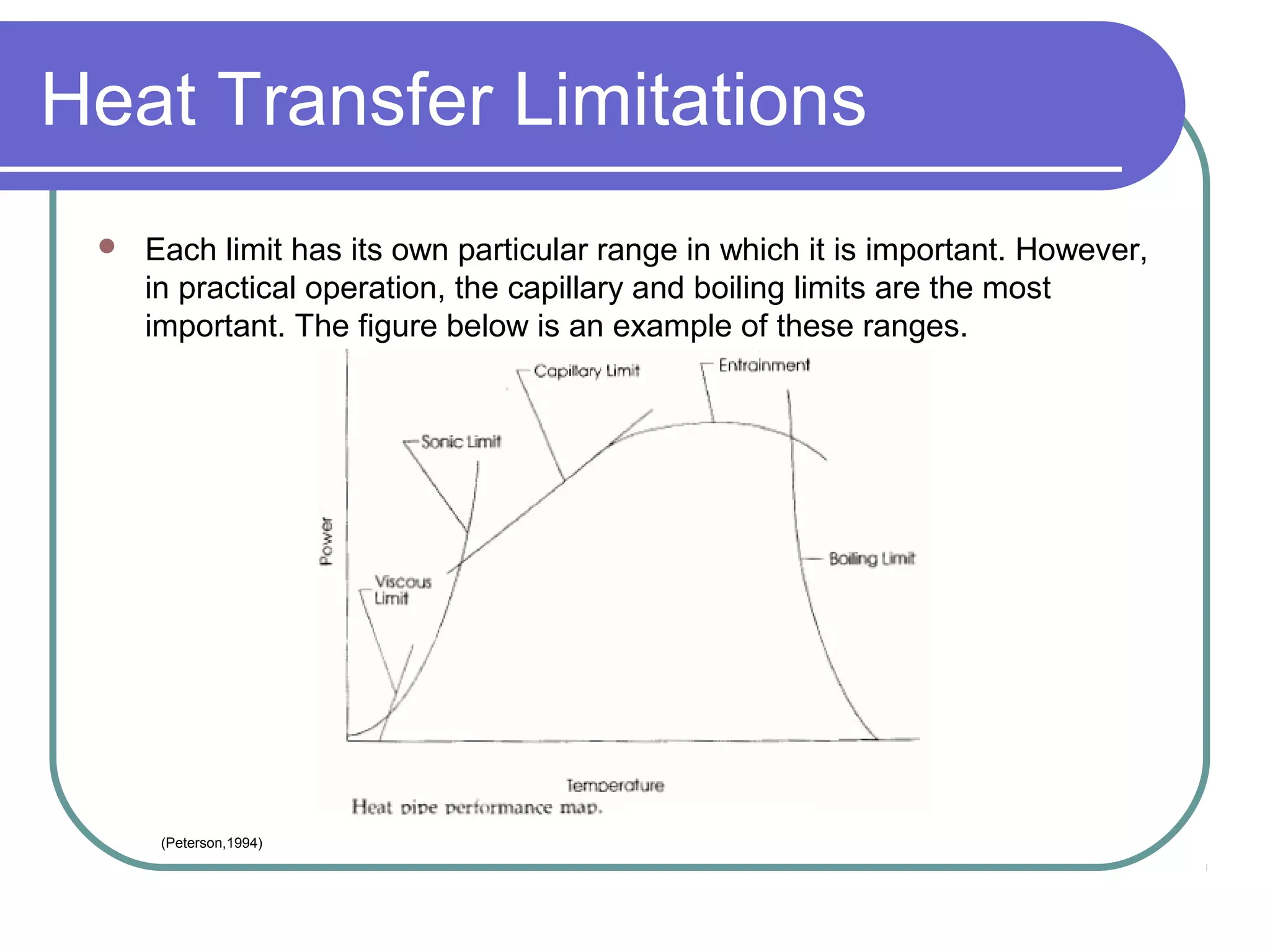
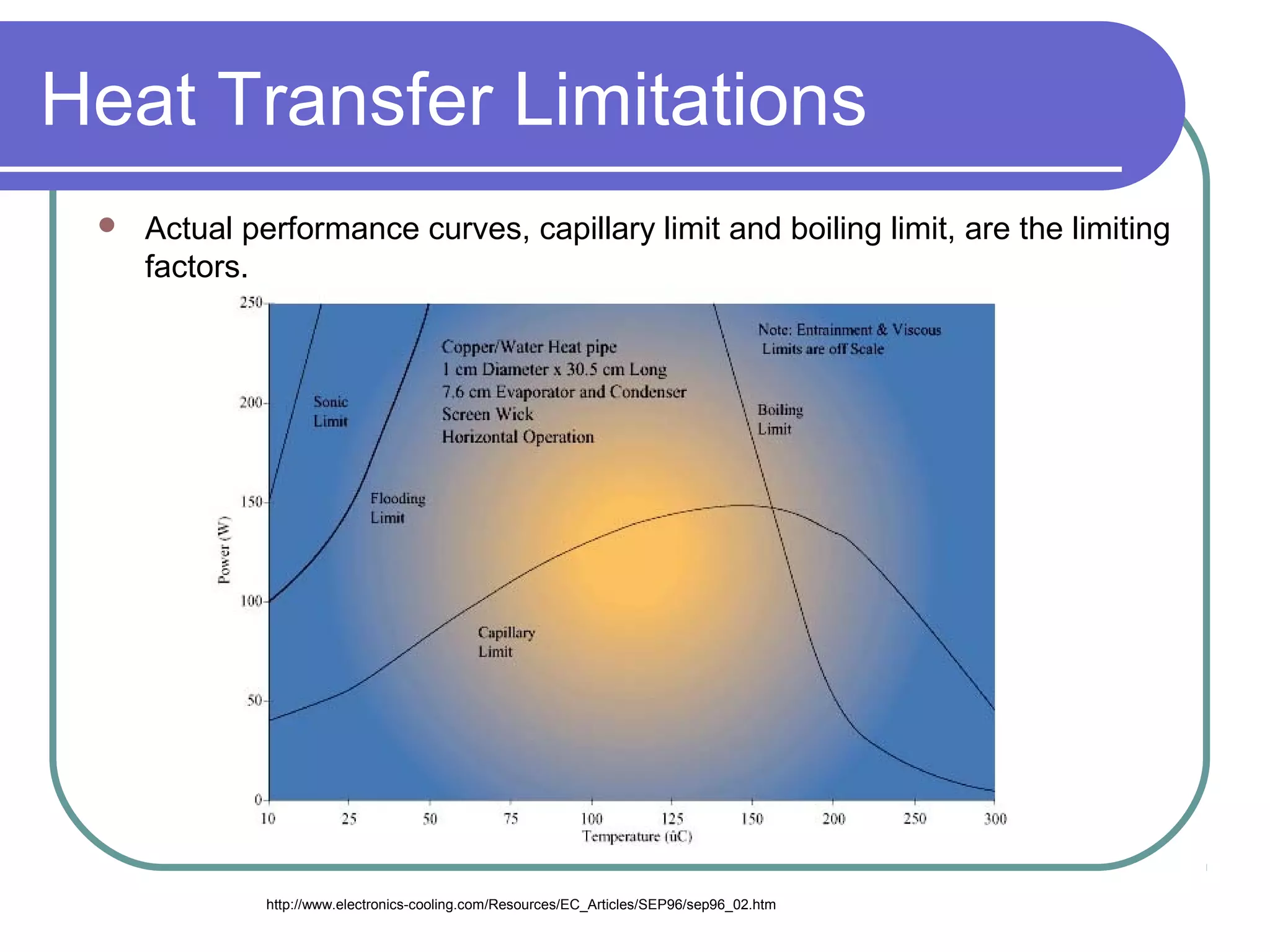
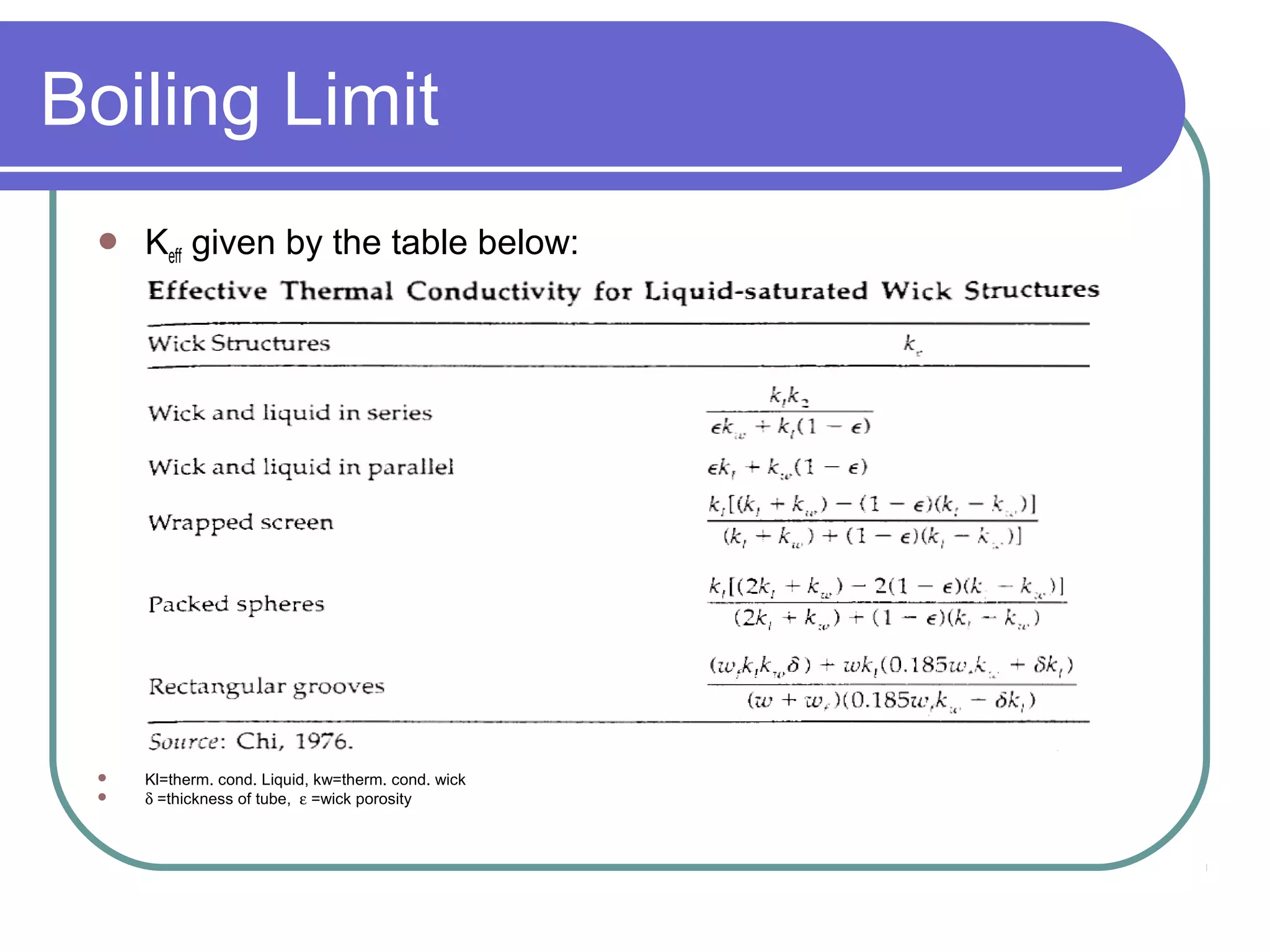
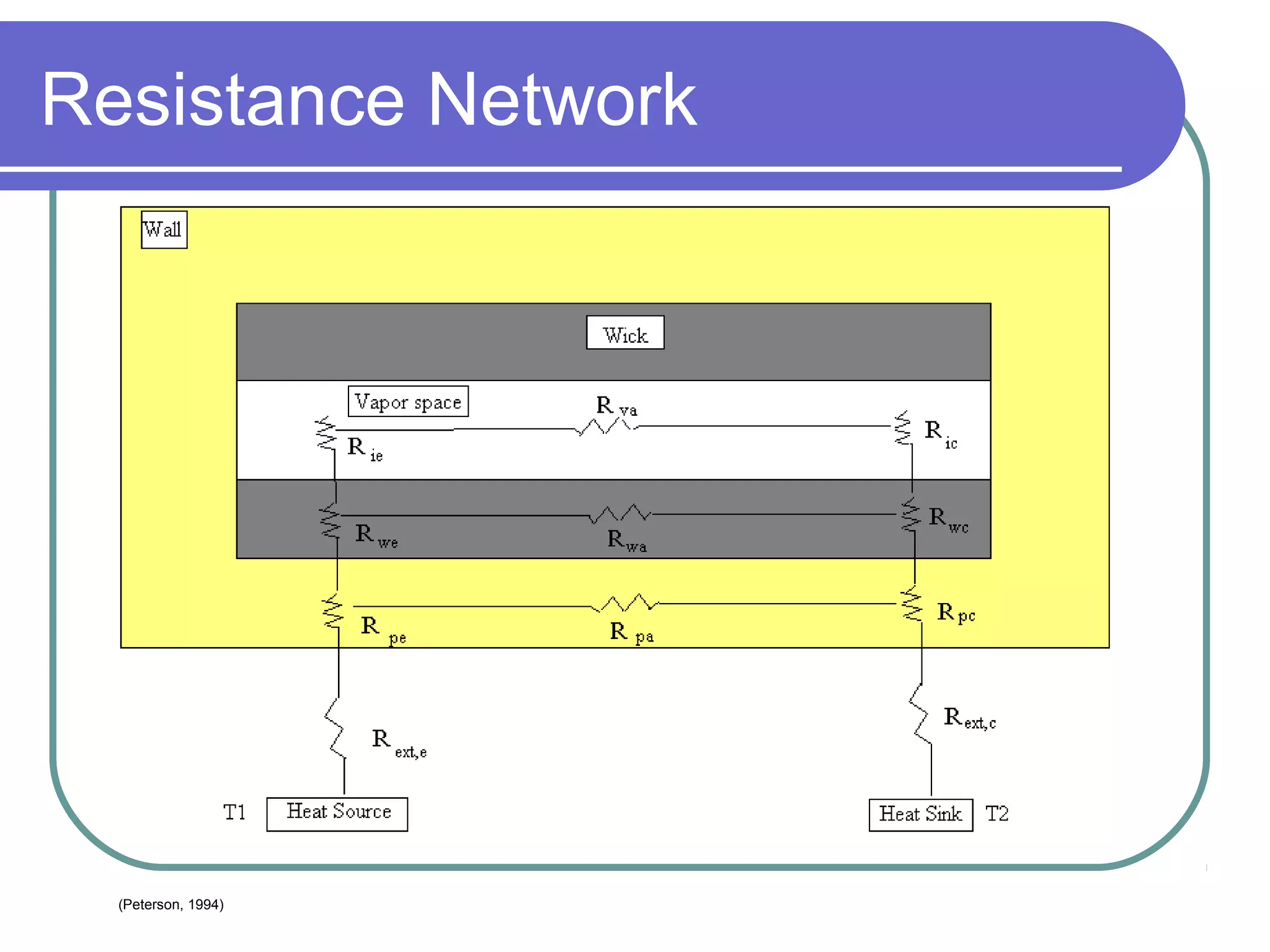
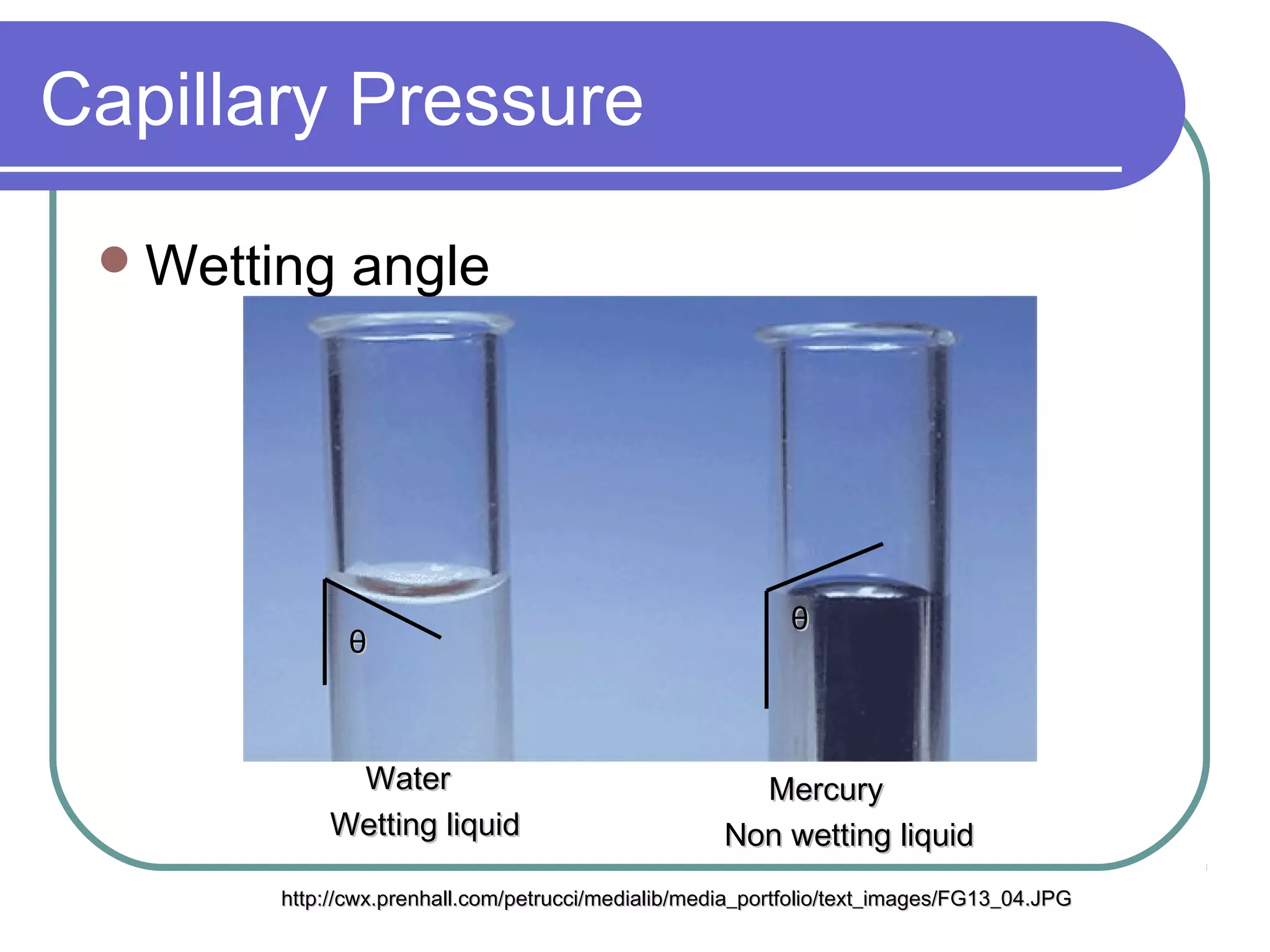
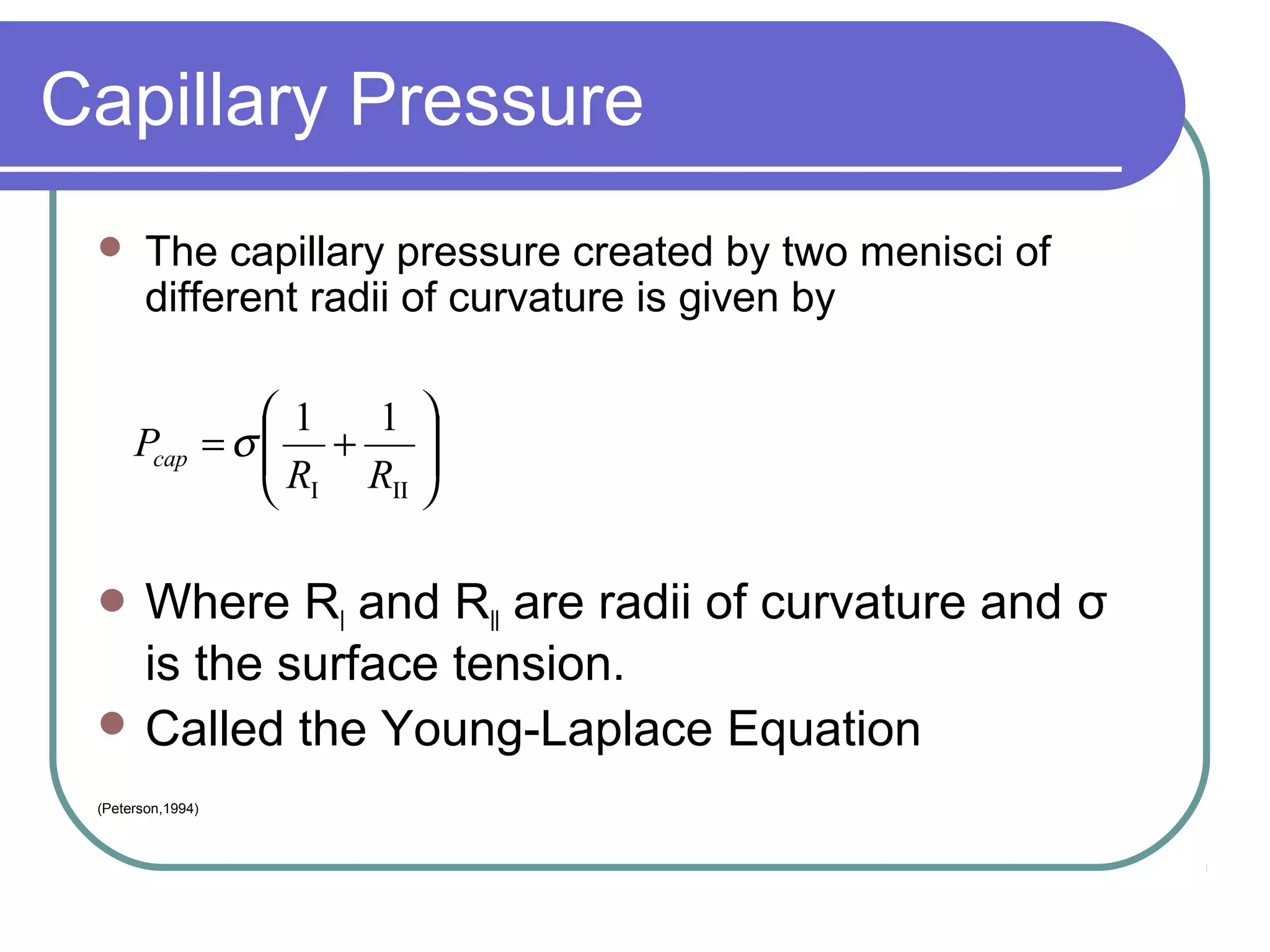
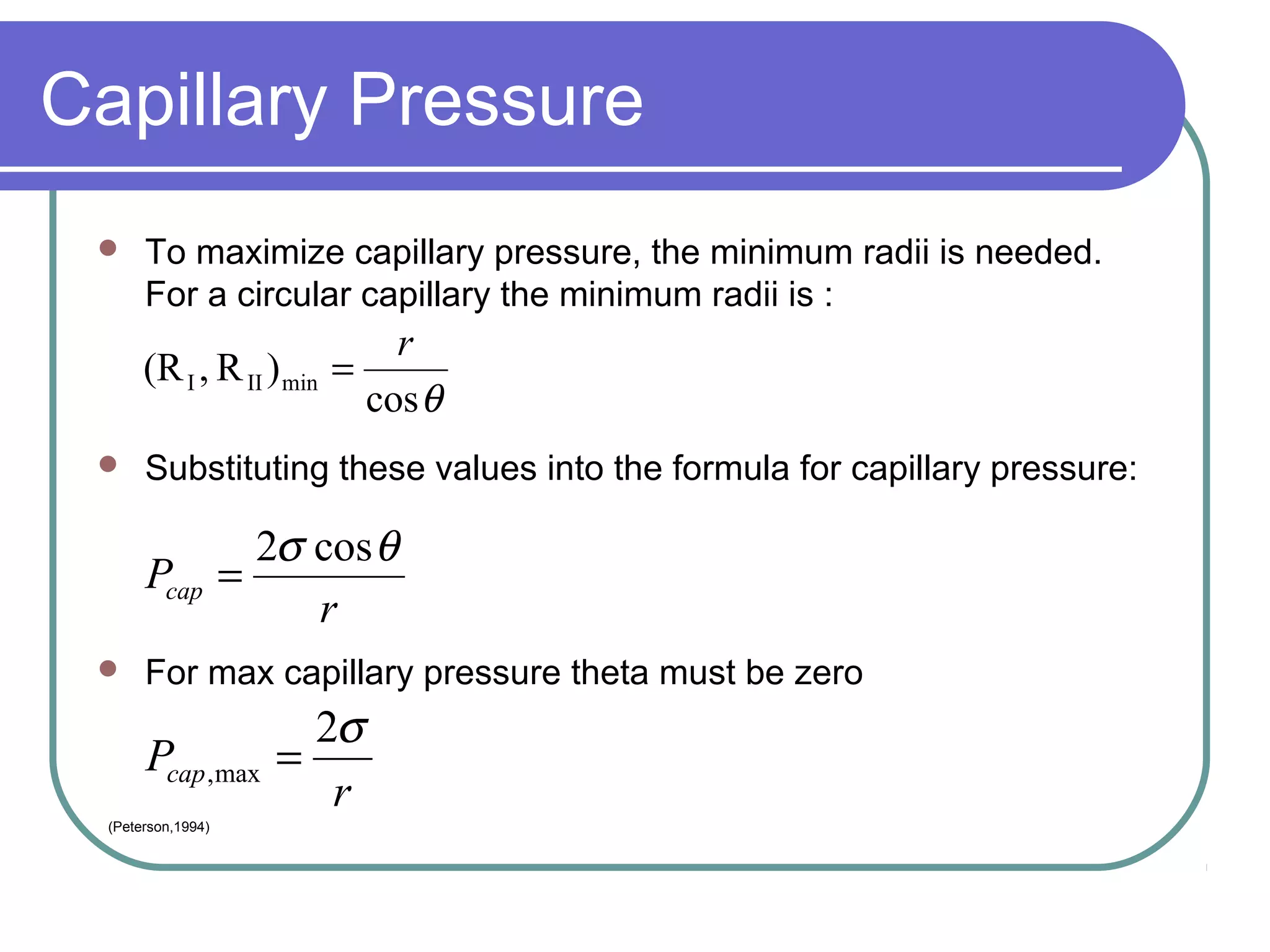
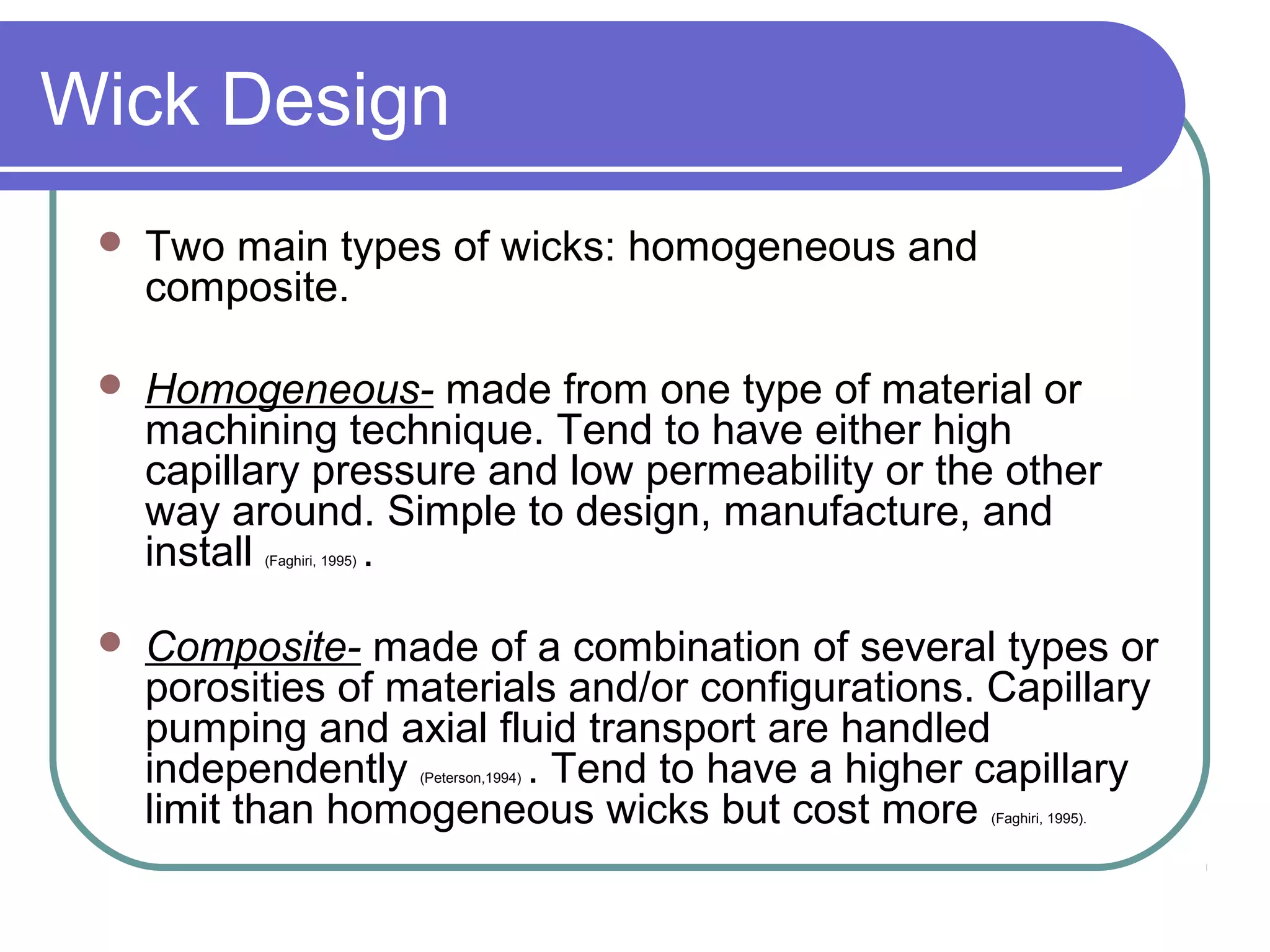
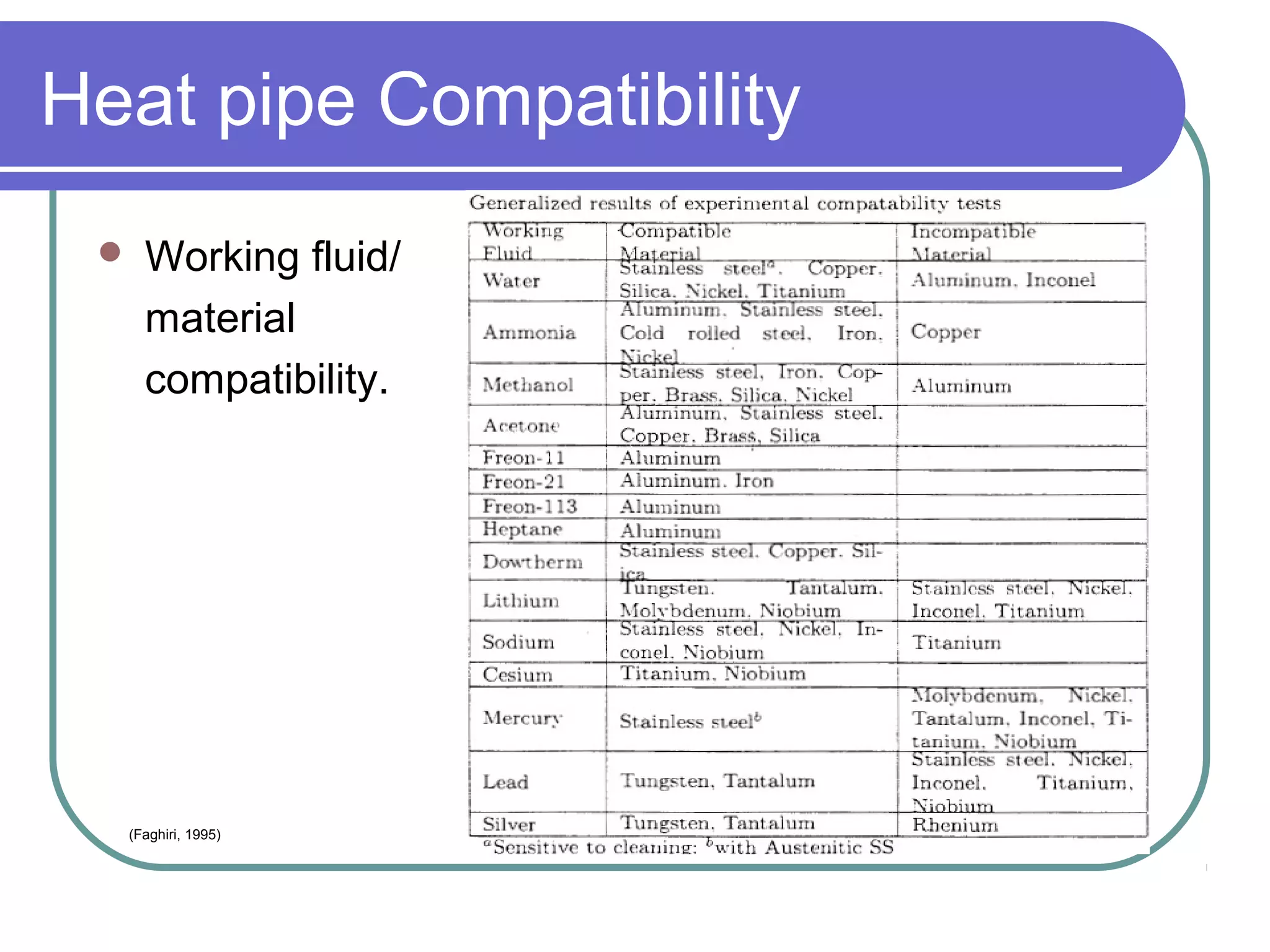
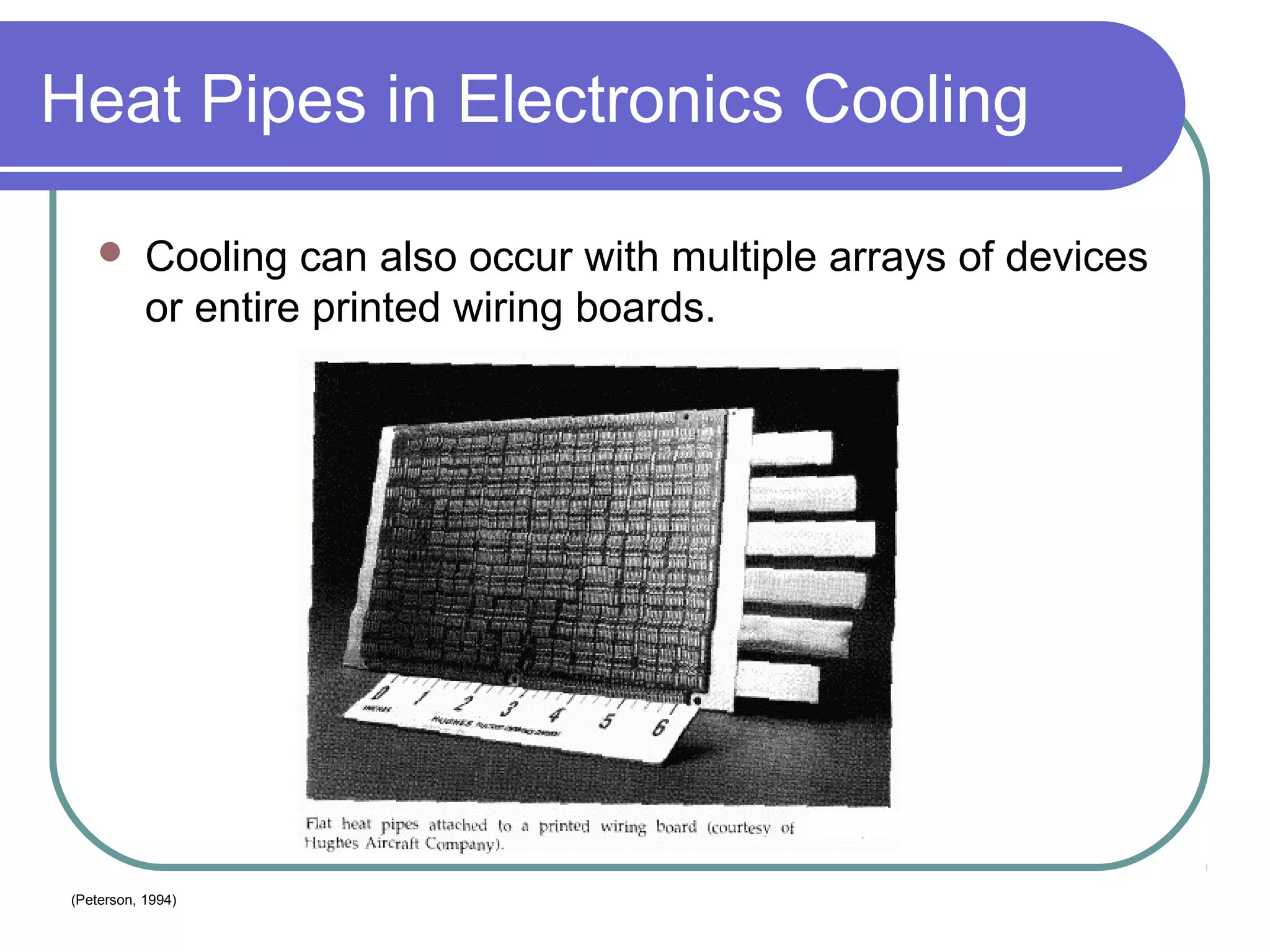
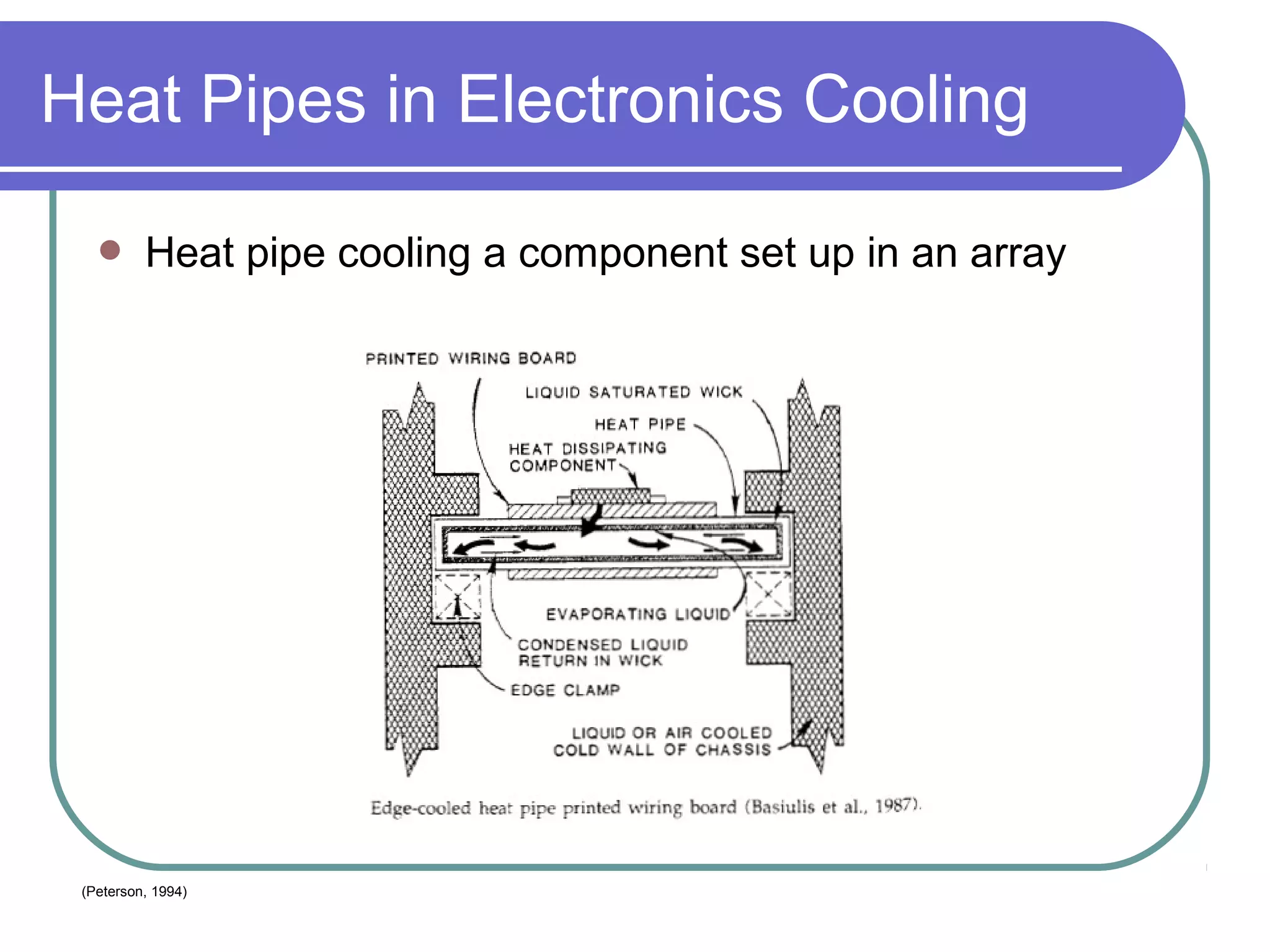
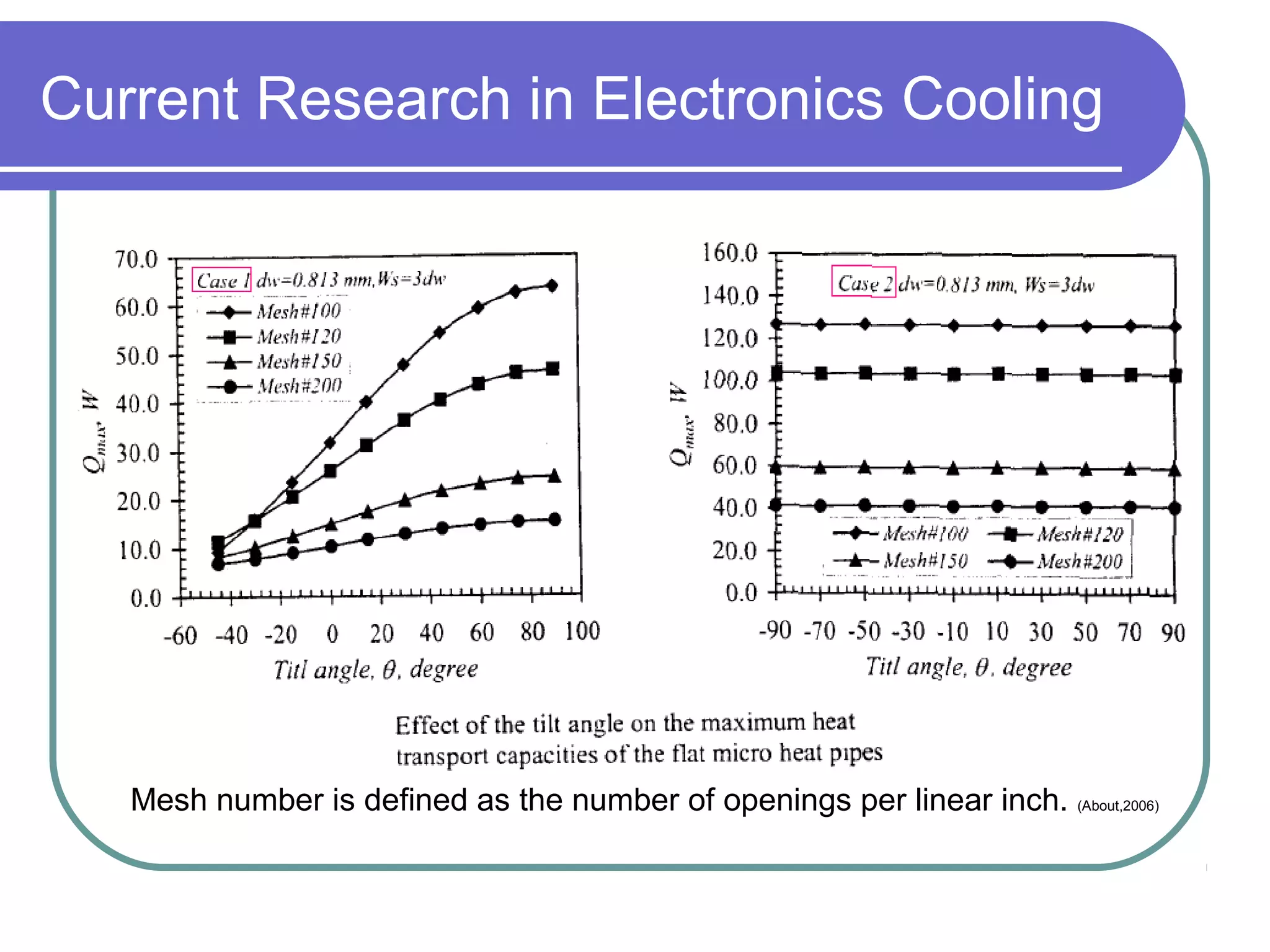
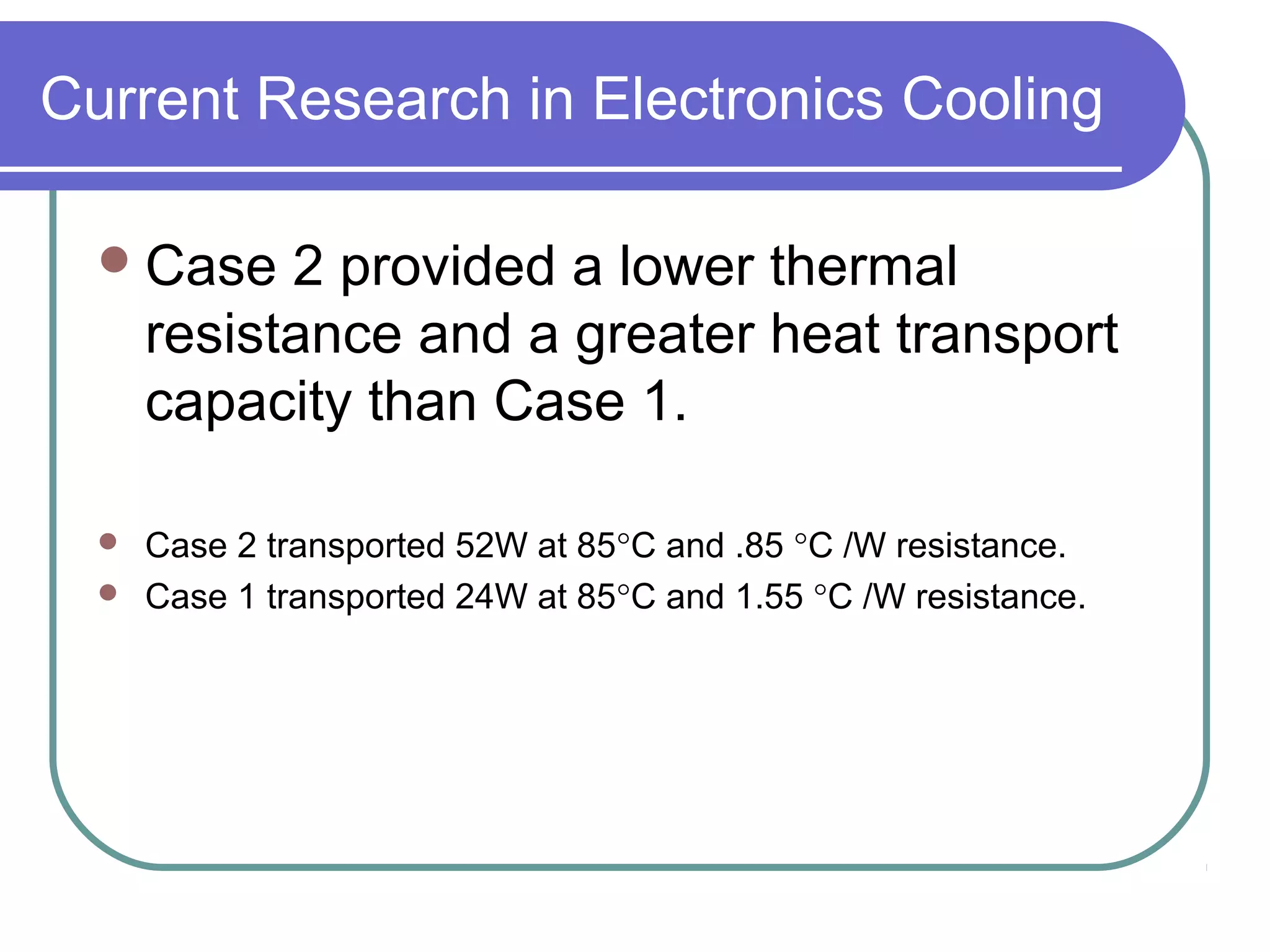
This document discusses heat pipes and their applications in electronics cooling. It describes the basic components of a heat pipe including an evaporator, condenser, wick, and adiabatic section. Heat pipes offer very high thermal conductivity and can efficiently transport heat. Their ideal thermodynamic cycle involves heat being absorbed in the evaporator, vapor moving through the adiabatic section to the condenser, and liquid being returned via capillary action in the wick. Heat pipes are well-suited to electronics cooling due to their ability to handle high heat fluxes and maintain uniform temperatures.