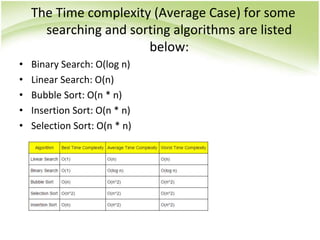
Linear search is a sequential search algorithm that checks each element of an array until the target element is found. It has a worst-case time complexity of O(n) where n is the number of elements. Binary search is a divide and conquer algorithm that compares the target to the middle element of a sorted array, eliminating half of the remaining elements with each comparison. It has a time complexity of O(log n). Common sorting algorithms like bubble sort, insertion sort, and selection sort have a time complexity of O(n^2) as they may require up to n^2 comparisons in the worst case.


![Linear Search
• Check every element in the list, until the
target is found
• For example, our target is 38:
i 0 1 2 3 4 5
a[i] 25 14 9 38 77 45
If item to search=38 ,then it tells found at
location 4
If item to search=55 ,then it tells Item Not found](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-3-320.jpg)
![Program to perform Linear Search
void linearsearch(int array[],item,n)
{
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
if (array[i] == item) /* If required element is found */
{
printf(“Found at location %d”, i+1);
flag=1
break;
}
}
if (flag==0)
printf(“Item not found”);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-4-320.jpg)
![Explanation
• Assume array of size n and item to search
• Assume initially flag=0
• First, we have to traverse the array elements using
a for loop.
• In each iteration of for loop, compare the search element
with the current array element,
– If array[i]==item, then it displays found at the position
of the corresponding array element and sets flag=1.
– If the element does not match, then move to the next
element.
• If flag==0 that means there is no match found in the given
array , then it displays not found](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-5-320.jpg)

![Binary Search
int BinarySearch(int key, int arr[], int n)
{
int low, high, mid;
low = 0;
high = n – 1;
while ( low <= high) {
mid = (low + high) / 2;
if ( key== arr[mid])
return mid; /*found match,return position where it is found*/
else if (key > arr[mid])
low = mid + 1; //search on right half by updating low
else
high = mid – 1; //search on left half by updating high
}
return –1; /*No match ,so return -1*/
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-7-320.jpg)
![Binary Search Explanation
• Assume key is element to search in array arr of size n
• Set two variables low=0 and high=n-1 pointing to start and
end of array
• Find the middle position of array ,mid=(low+high)/2
• Compare the middle element of the array with the key to
search.
– If the key ==arr[mid], then process is terminated and display found at
middle location.
– If the key is not found at middle element, choose which half will be
used as the next search space.
• If the key > arr[mid], then the right side is used for next search.
• If the key < arr[mid], then the left side is used for next search.
• This process is continued until the key is found or the complete
array is exhausted.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-8-320.jpg)
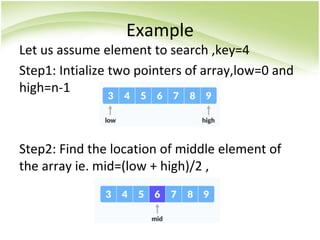
![Example
Step3: As key <arr[mid] so it has to search on
left of array.So it update,low=0 and high=mid-1
Step4:Now new middle position=(low+high)/2=1
Step5: Then,it compares key with middle
element .As key==arr[mid],so it displays found
at middle location 1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-10-320.jpg)



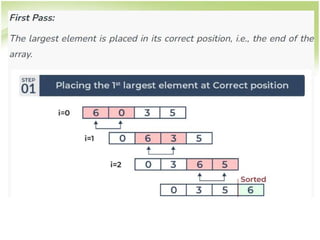
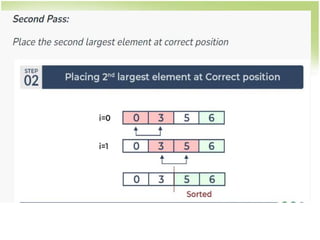
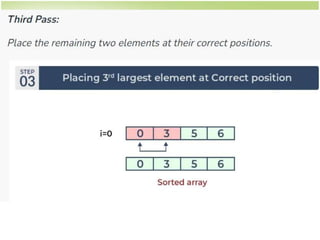
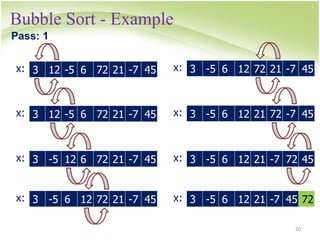
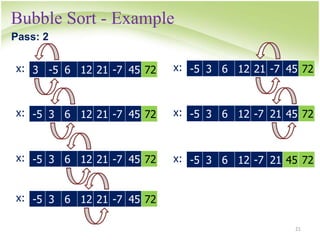
![Bubble Sort
for i -> 1 to n-1
for j -> 1 to n-i
if a[j]>a[j+1], swap them
• How to swap?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-15-320.jpg)

![Bubble Sort
void bubbleSort (int a[ ] , int size)
{
int i, j, temp;
for ( i = 0; i < size; i++ ) /* controls passes through the list */
{
for ( j = 0; j < size - 1; j++ ) /* performs adjacent comparisons */
{
if ( a[ j ] > a[ j+1 ] ) /* determines if a swap should occur */
{
temp = a[ j ]; /* swap is performed */
a[ j ] = a[ j + 1 ];
a[ j+1 ] = temp;
}
}
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-22-320.jpg)
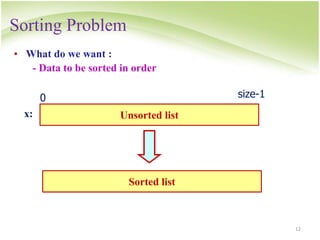
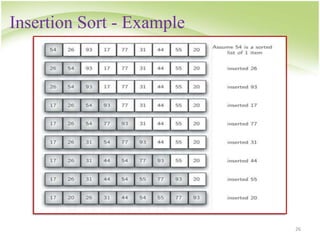
![Insertion Sort
23
General situation :
0 size-1
i
remainder, unsorted
smallest elements, sorted
0 size-1
i
x:
i
j
Compare and
Shift till x[i] is
larger.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-23-320.jpg)
![Insertion Sort
25
void insertionSort (int list[], int size)
{
int i,j,item;
for (i=1; i<size; i++)
{
item = list[i] ;
/* Move elements of list[0..i-1], that are greater than
item, to one position ahead of their current position */
for (j=i-1; (j>=0)&& (list[j] > item); j--)
list[j+1] = list[j];
list[j+1] = item ;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-25-320.jpg)
![Insertion Sort
void insertionSort(int numbers[], int array_size)
{
int i, j, index;
for (i=1; i < array_size; i++) {
index = numbers[i];
j = i;
while ((j > 0) && (numbers[j-1] > index)) {
numbers[j] = numbers[j-1];
j = j - 1;
}
numbers[j] = index;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-27-320.jpg)
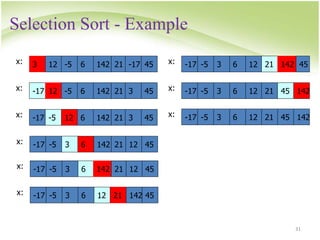
![Selection Sort
28
General situation :
remainder, unsorted
smallest elements, sorted
0 size-1
k
x:
Steps :
• Find smallest element, mval, in x[k…size-1]
• Swap smallest element with x[k], then increase k.
0 k size-1
mval
swap
x:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-28-320.jpg)
![Selection Sort
29
/* Yield location of smallest element in
x[k .. size-1];*/
int findMinLloc (int x[ ], int k, int size)
{
int j, pos; /* x[pos] is the smallest
element found so far */
pos = k;
for (j=k+1; j<size; j++)
if (x[j] < x[pos])
pos = j;
return pos;
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-29-320.jpg)
![Selection Sort
30
/* The main sorting function */
/* Sort x[0..size-1] in non-decreasing order */
int selectionSort (int x[], int size)
{ int k, m;
for (k=0; k<size-1; k++)
{
m = findMinLoc(x, k, size);
temp = a[k];
a[k] = a[m];
a[m] = temp;
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/searchsort-231105054446-2f9b5a9c/85/search_sort-ppt-30-320.jpg)