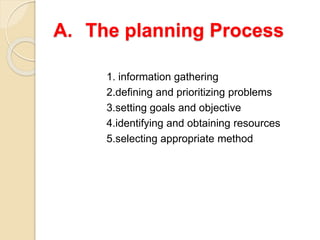
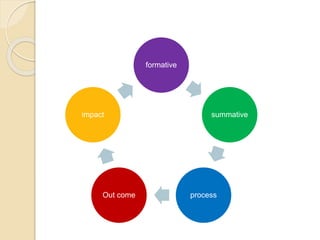
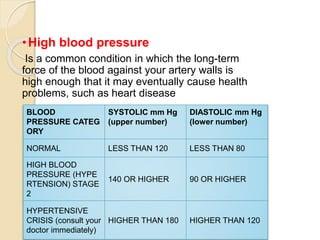
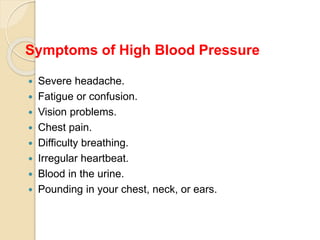
This document outlines the steps for planning and implementing a community health education program. It discusses gathering information about the community, defining health problems, setting goals and objectives, identifying resources, and selecting educational methods. The document also covers implementing the program, and evaluating it through formative, process, outcome, and impact assessments. It provides examples of existing national health programs in areas like family planning, immunizations, and disease control.