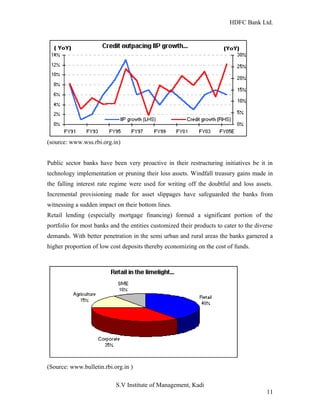
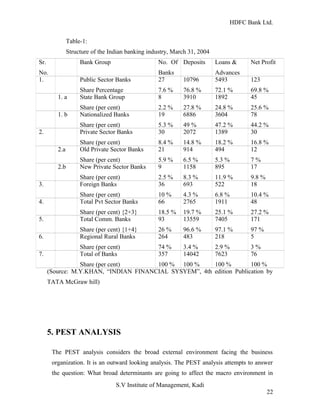
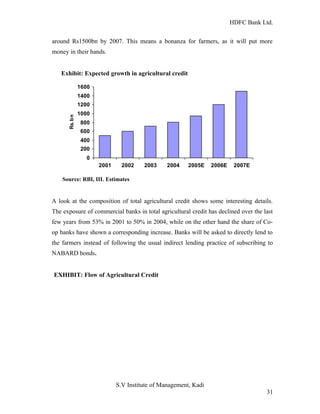
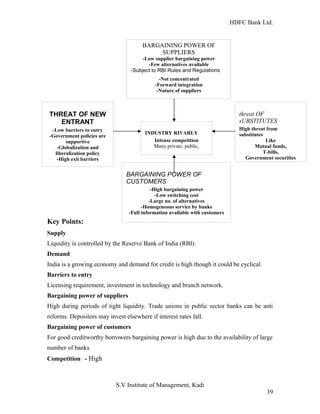
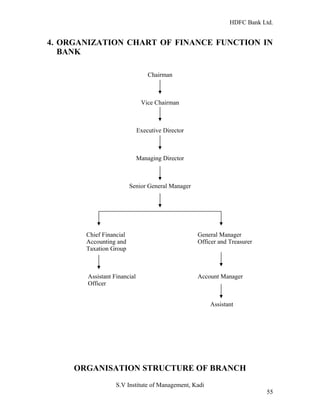
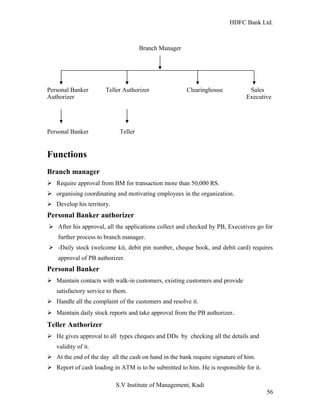
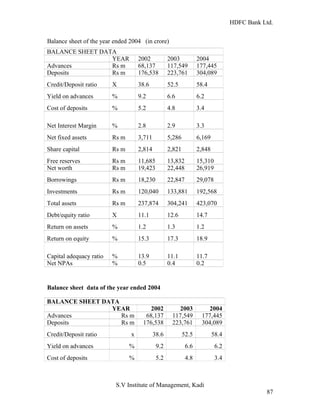
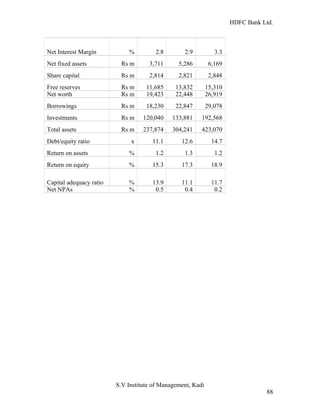
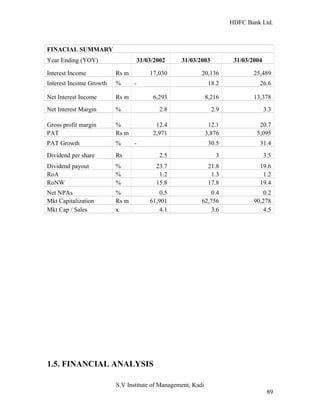
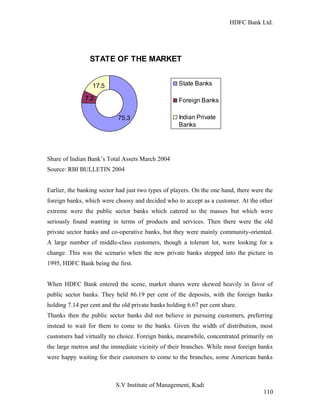
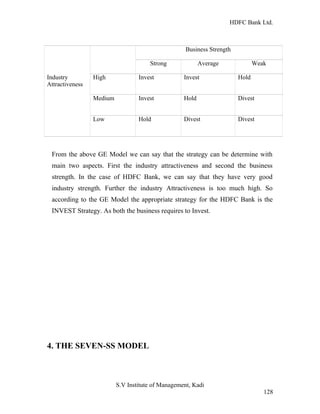
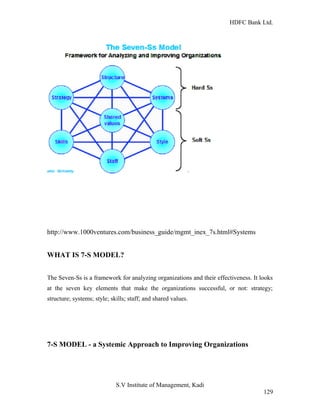
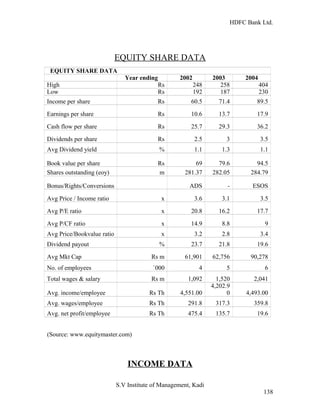
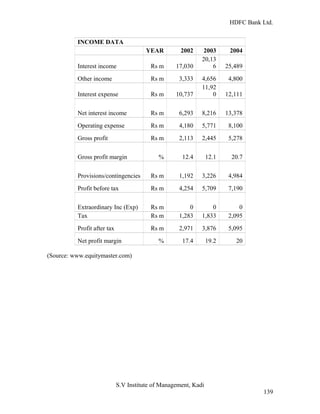
HDFC Bank Ltd. conducted research on its functional areas and performance. The objectives were to understand functions, evaluate industry performance, and measure individual area performance. Primary and secondary data was collected through employee interviews. Department heads and managers were interviewed as a non-probability sample. The history of banking in India dates back to Vedic times, with early indigenous bankers and agency houses. Major developments included the establishment of presidency banks, the Reserve Bank of India, nationalization of banks, and reforms allowing private banks. Banking sector reforms have improved profitability, productivity and efficiency.