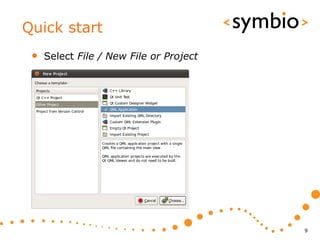
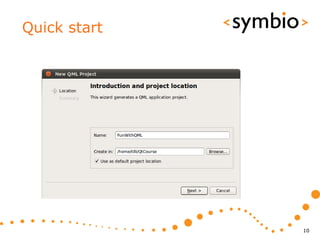
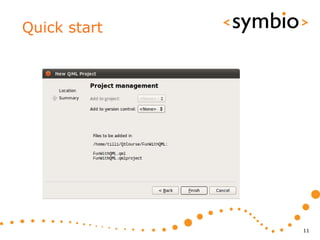
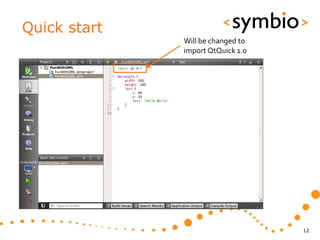
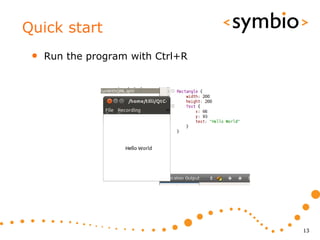
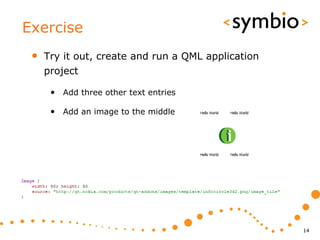
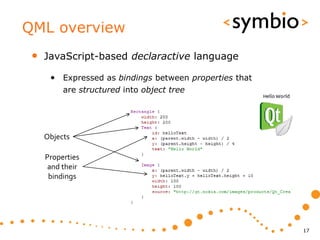
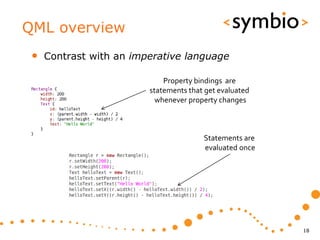
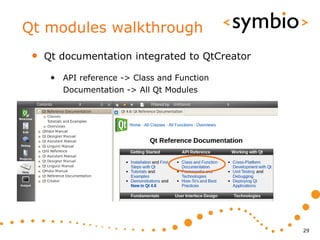
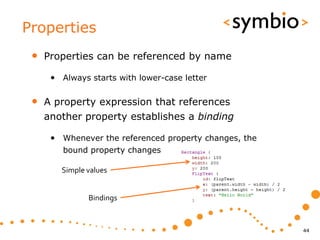
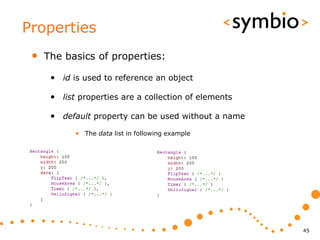
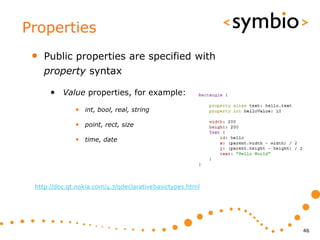
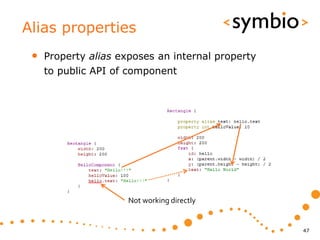
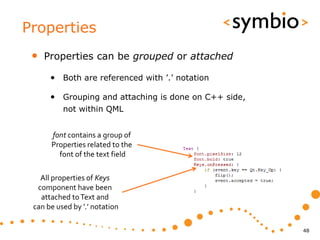
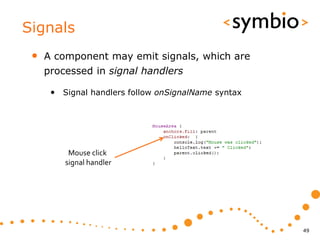
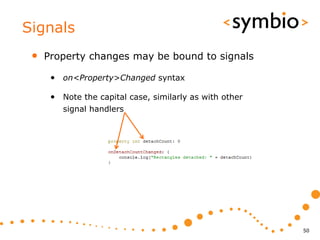
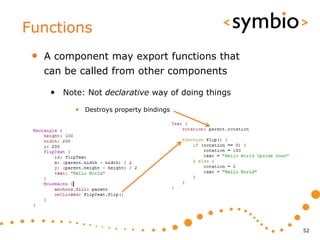
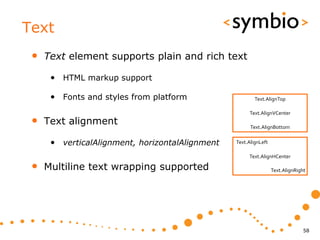
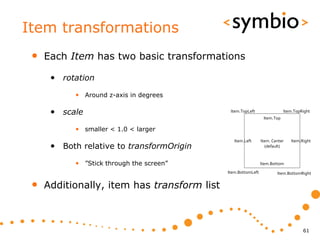
The document provides an overview of Qt Quick, focusing on environment installation, QML language, and GUI component development using Qt Creator. It covers concepts like property bindings, signals, and basic GUI elements, alongside instruction for creating a Hello World project. Additionally, various Qt modules, including core, GUI, network, and multimedia, are discussed, highlighting their functionalities and applications in mobile development.