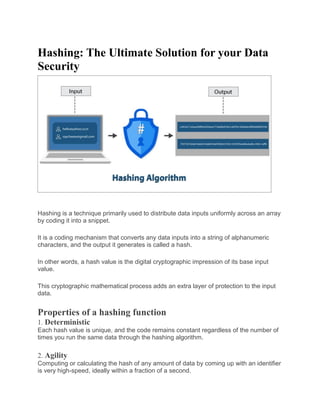
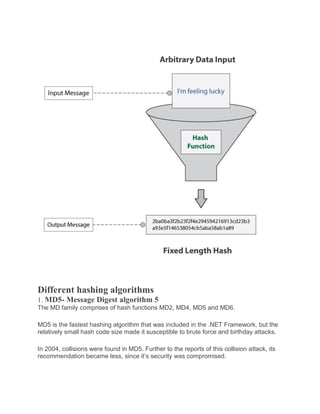
Hashing is a technique that converts data inputs into a unique alphanumeric string called a hash value. It adds an extra layer of security by making the data unreadable and hiding information about the original input. Some key properties of hashing include being deterministic, agile, providing avalanche effects and collision resistance. Common hashing algorithms include MD5, SHA-1, SHA-256, and Tiger, with longer hashes providing better security. Hashing is widely used to check file integrity, encrypt signatures, store passwords, detect duplicates, and anonymize data while maintaining privacy.