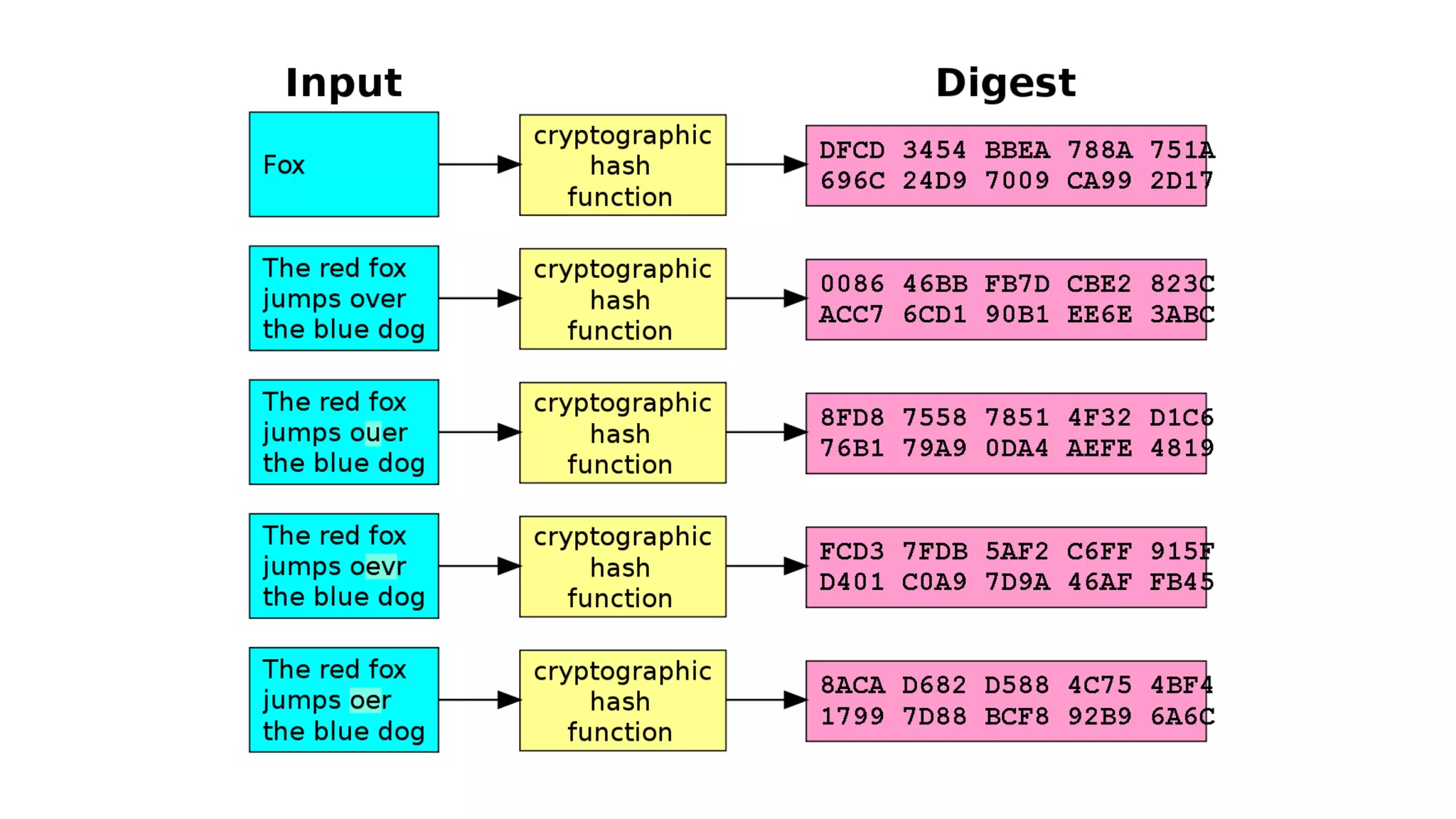
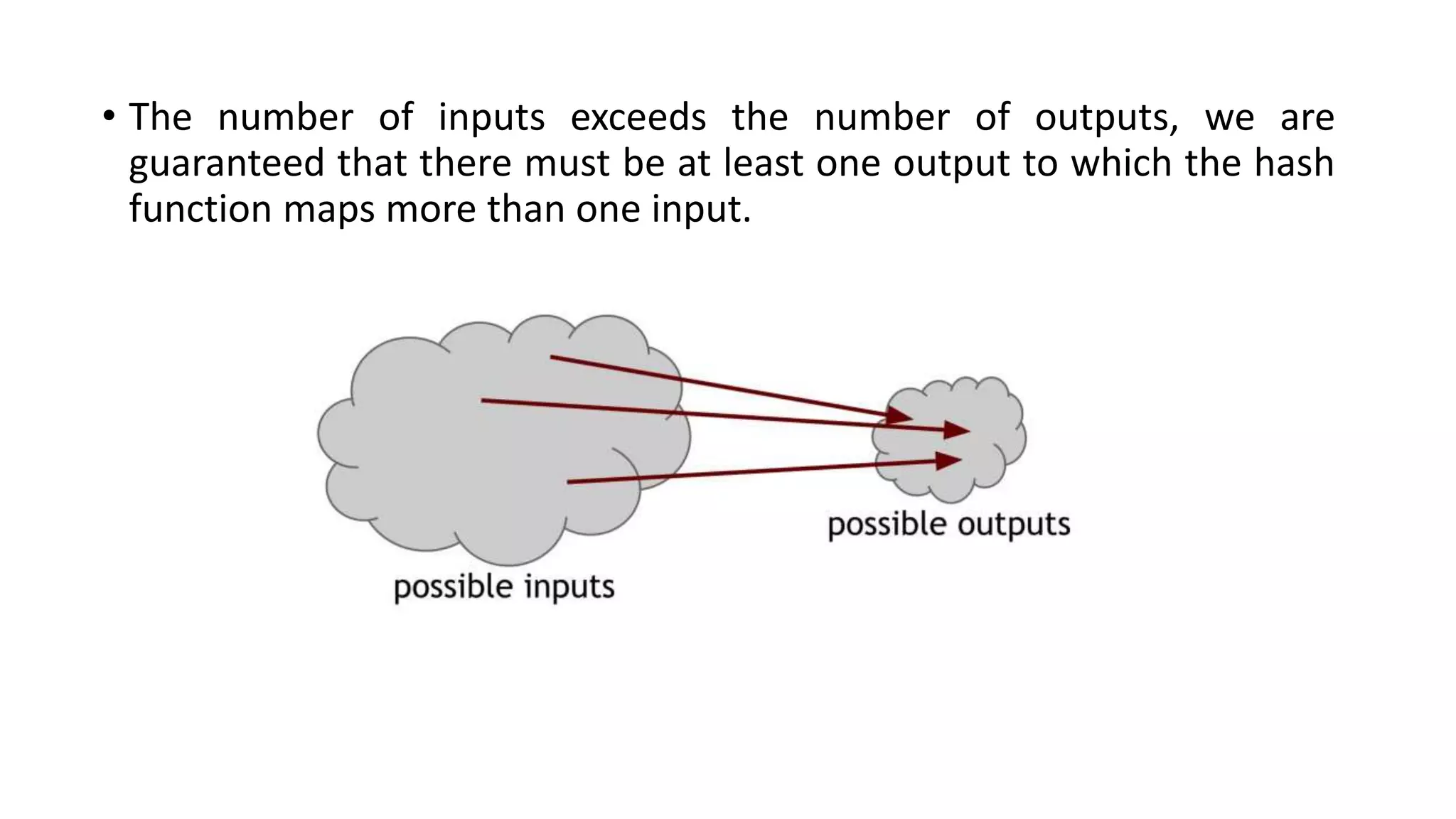
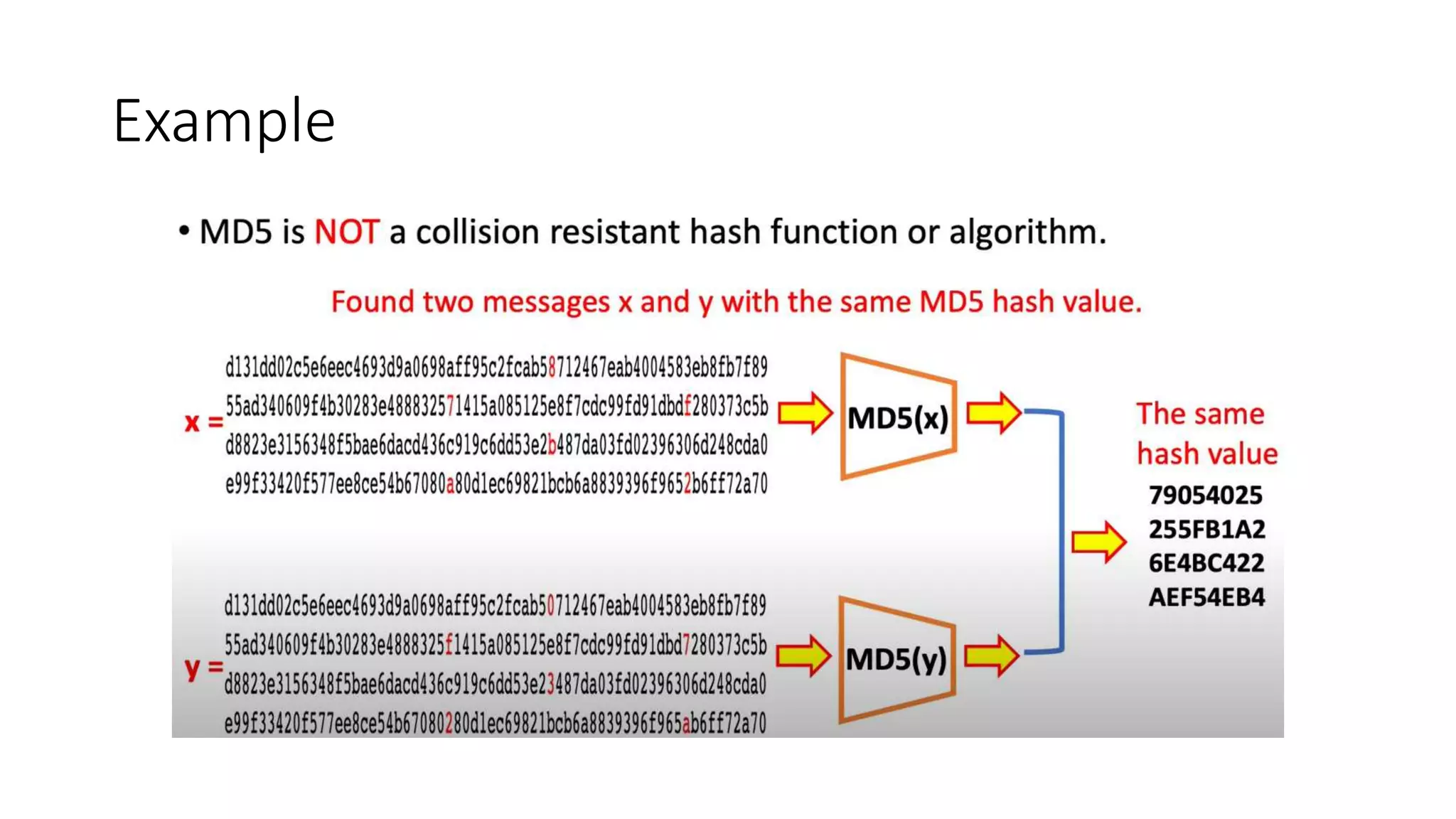
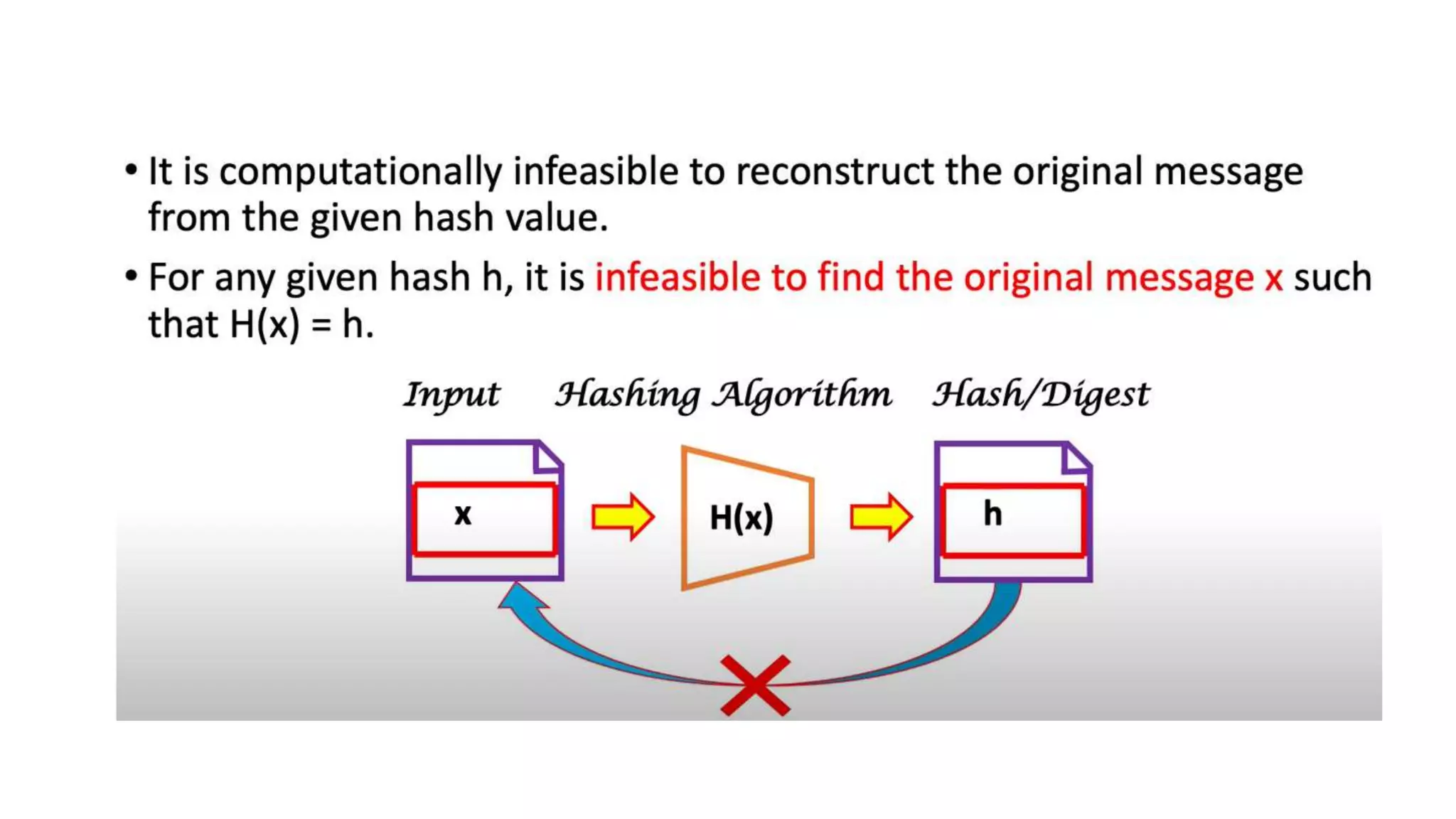
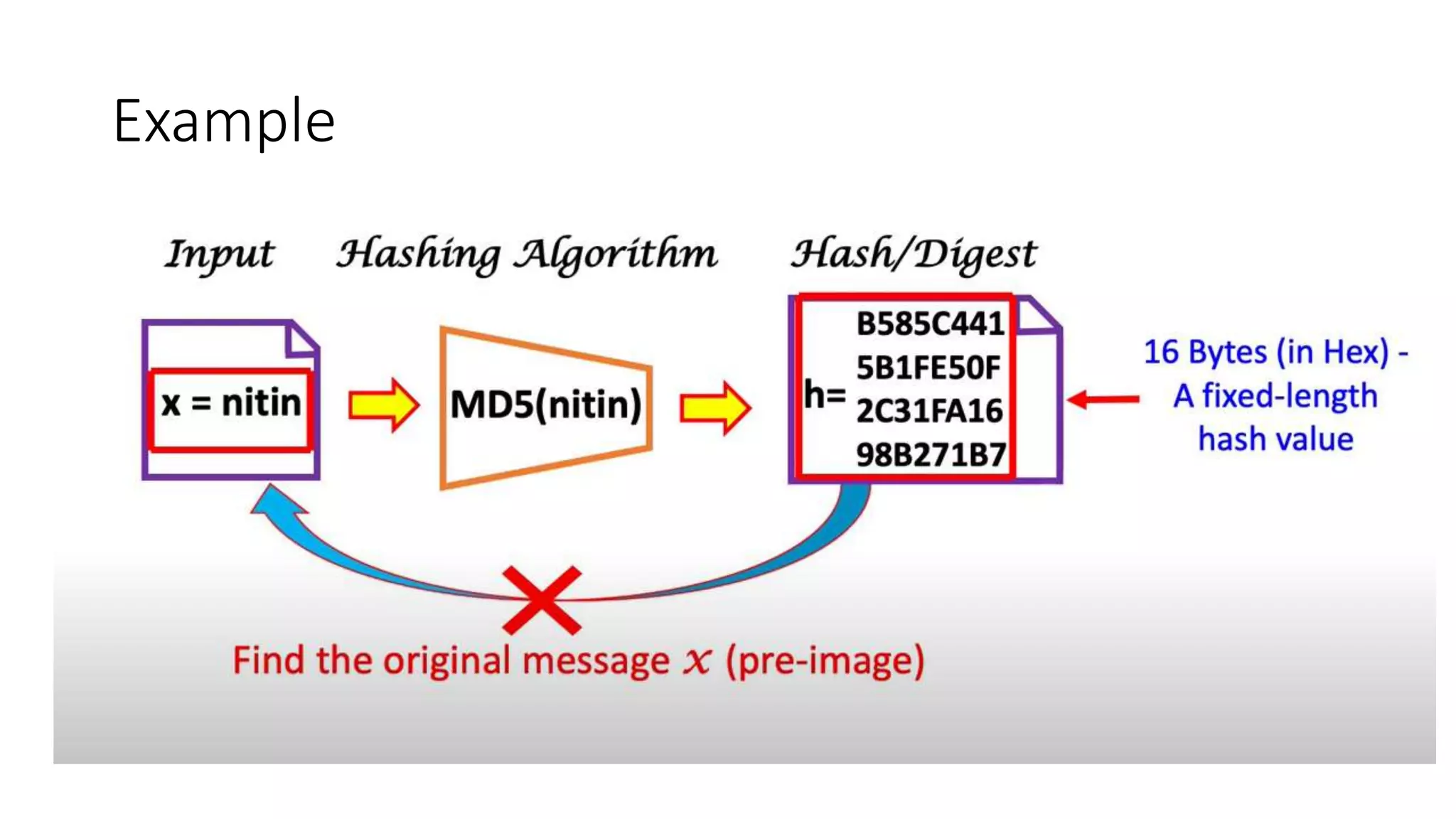
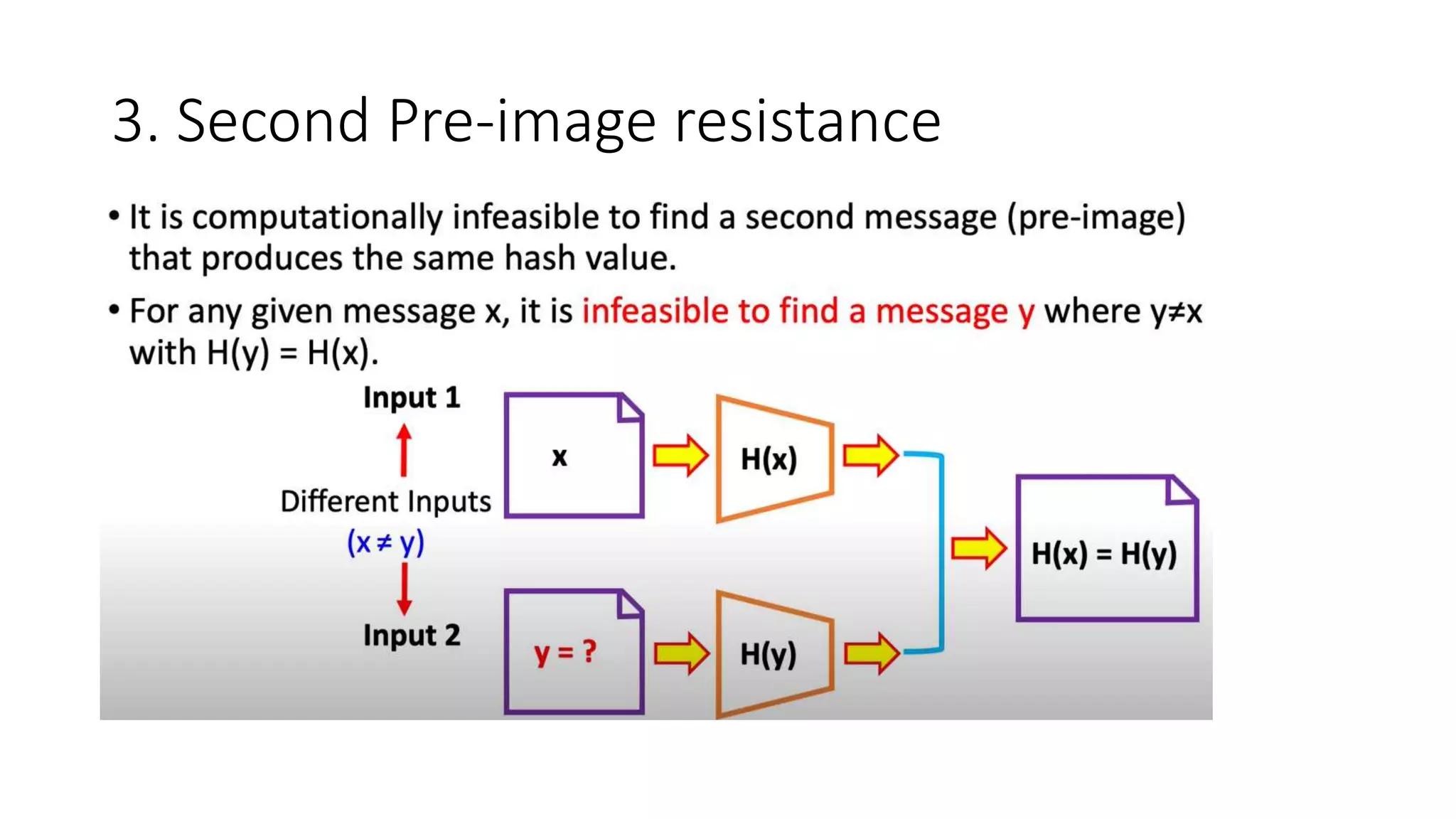
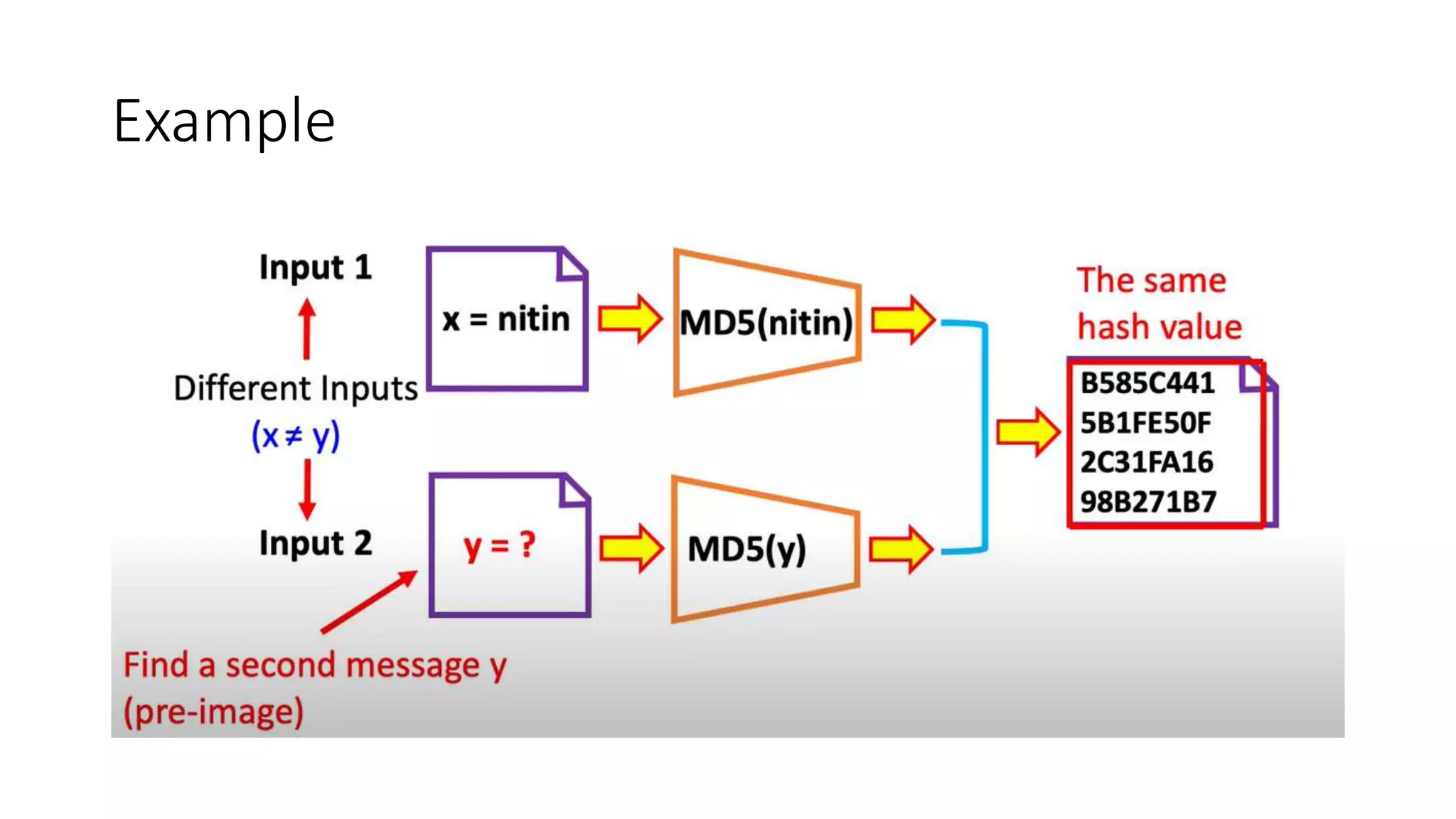
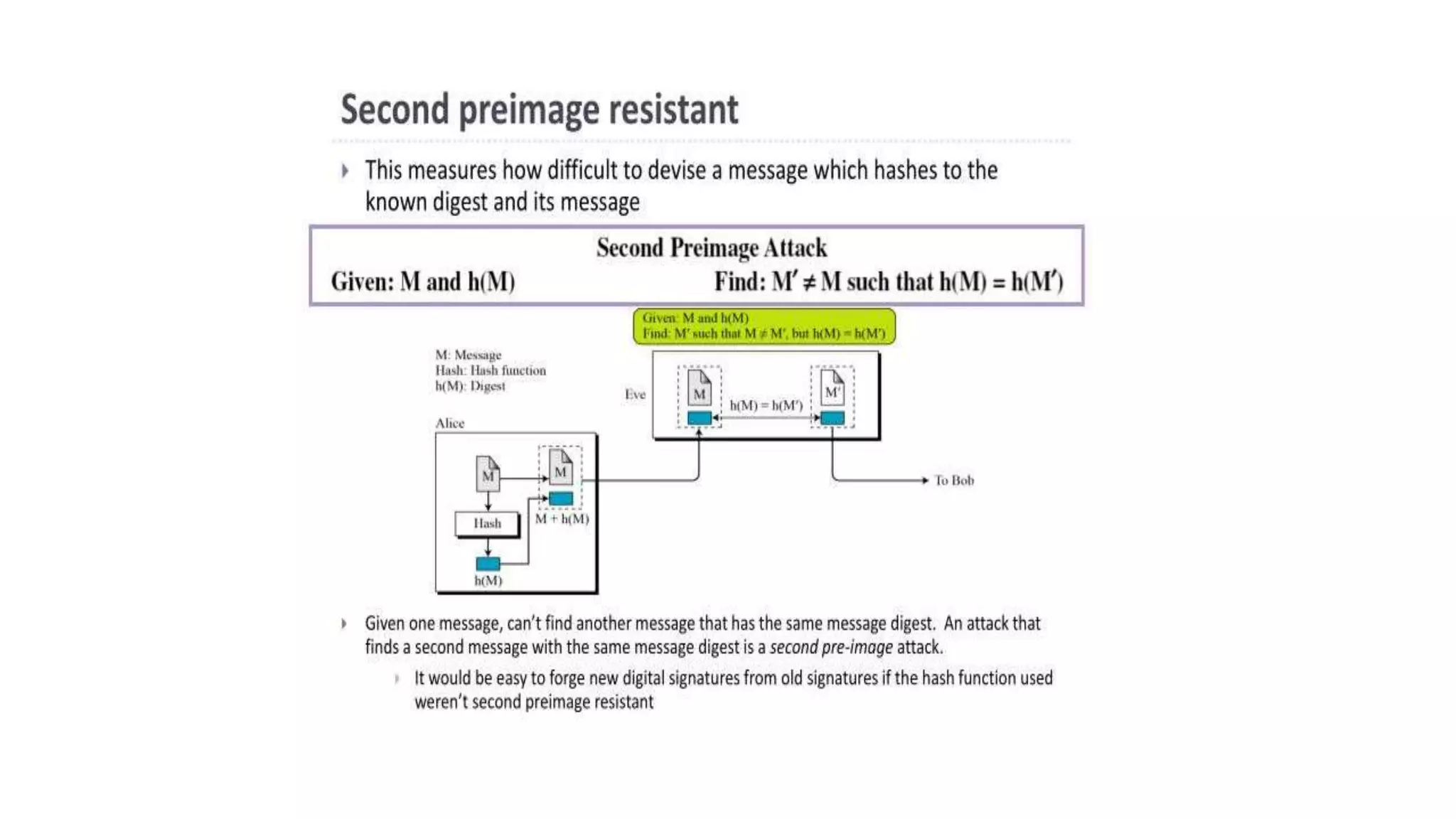
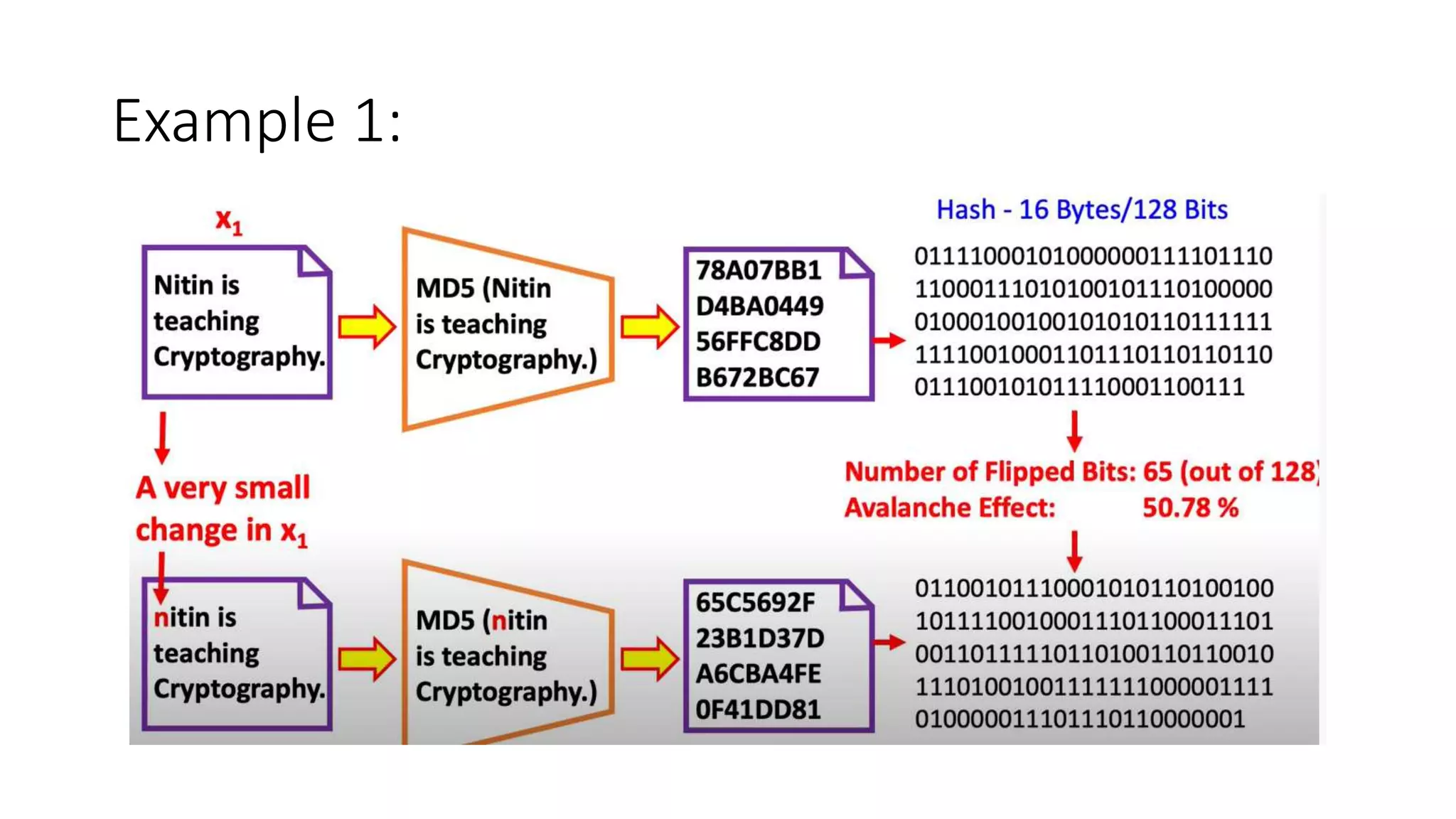
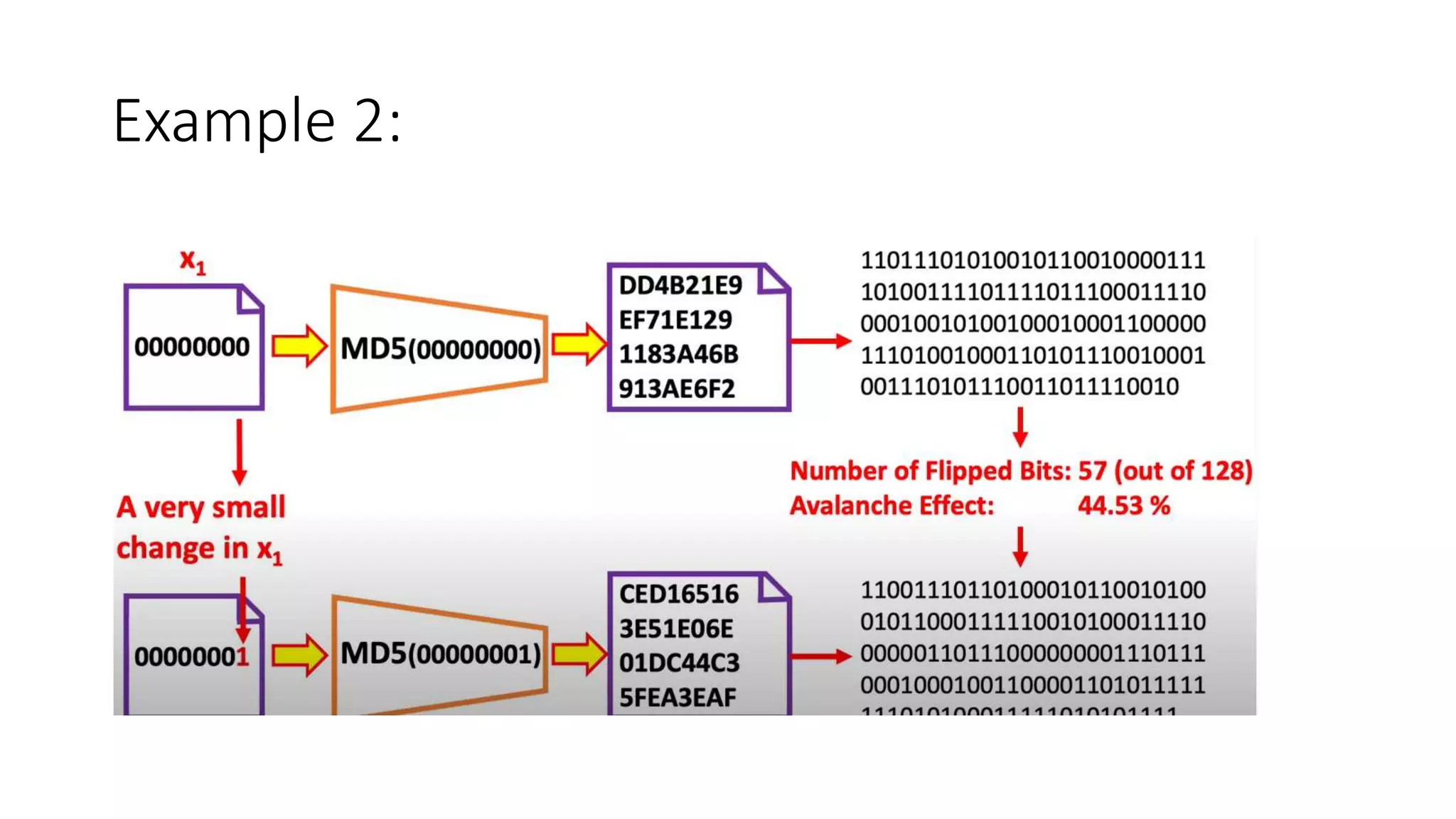
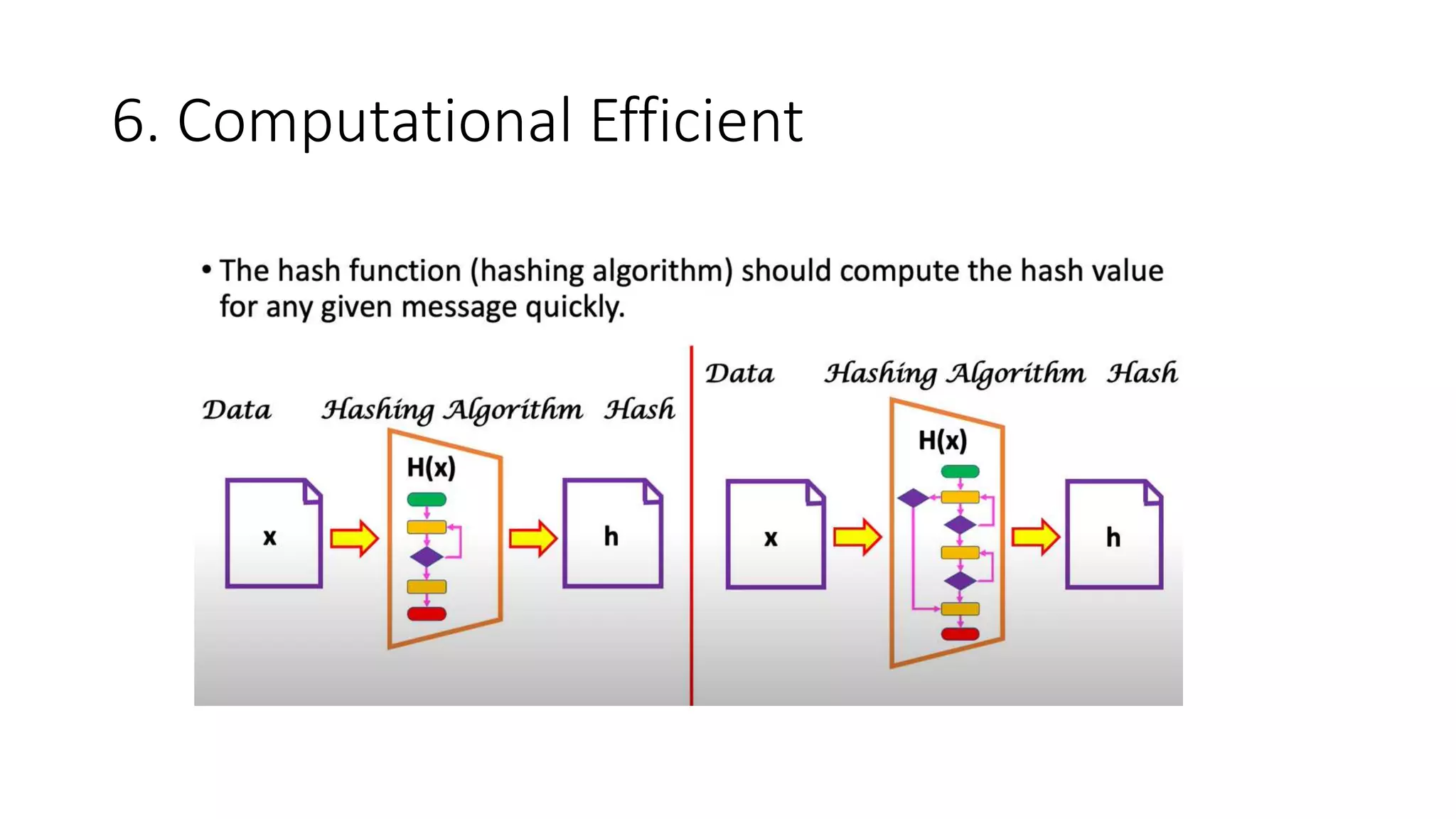
Cryptographic hash functions are used in blockchains to protect user privacy, transaction information, and ensure data consistency. They encode rules for currency creation into a mathematical protocol and utilize advanced cryptographic techniques. A hash function generates a fixed-length hash value from variable-length input data, unlike encryption which is reversible. Common hashing algorithms include MD5, SHA-2, and CRC32. Hash functions have properties like collision resistance, pre-image resistance, second pre-image resistance, avalanche effect, determinism, and computational efficiency.