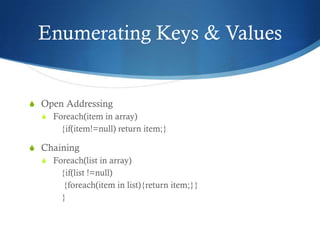
The document provides an overview of hash tables, including how they store key-value pairs using hashing to map keys to indexes. It discusses hashing functions and how they should be stable, uniform, efficient and possibly secure. It describes how hash tables handle collisions through open addressing or chaining and how items can be added, removed, searched for and enumerated from a hash table.




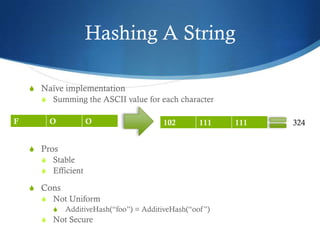


![Hash Table Overview
S Adding Jane
S int index = GetIndex(Jane.Name);
S _array[index] = Jane;
S What does GetIndex() do? It hashes the string](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hashtables-130111134936-phpapp01/85/Hash-tables-8-320.jpg)