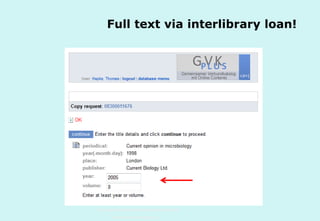
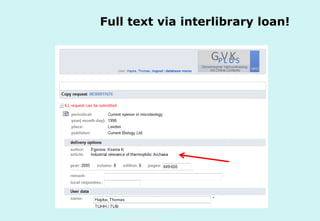
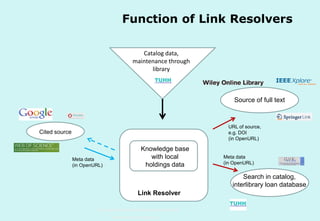
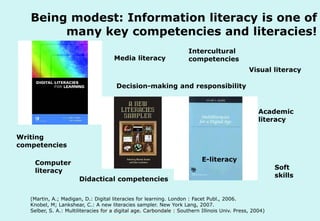
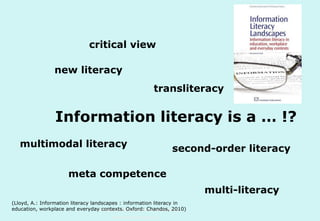
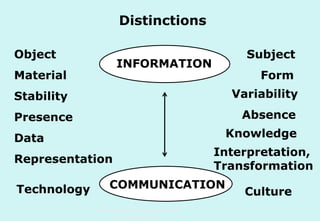
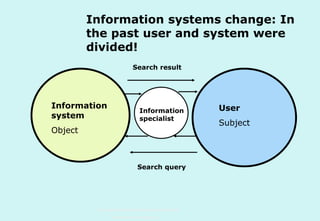
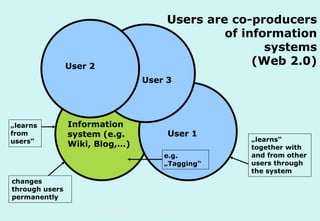
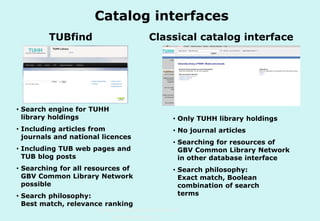
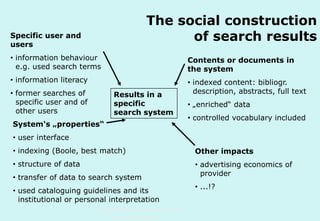
The document discusses the evolution and significance of information literacy in the context of modern information environments and discovery systems. It emphasizes the changing roles of users, information professionals, and libraries, advocating for a more experiential and collaborative approach to information access and usage. Key concepts include the critical assessment of information sources and the development of competencies required for navigating complex information landscapes.

















![A critical view on
discovery systems:
“Thinking the unthinkable: a library without a catalogue” Simone Kortekaas, Utrecht University Library,
Netherlands, 2012 [1]
„Giving up on discovery“ – Dale Askey, McMaster
University Library, Hamilton, Ontario, Canada, 2013 [2]
How to improve delivery of materials purchased
and licensed by the library?
[1] http://www.libereurope.eu/blog/thinking-the-unthinkable-a-library-without-acatalogue-reconsidering-the-future-of-discovery-to
[2] http://taiga-forum.org/giving-up-on-discovery/
Technische Universität Hamburg-Harburg
www.tub.tu-harburg.de](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hapke-haw2013-131121075416-phpapp01/85/Information-habits-in-continuously-changing-information-environments-digging-up-the-core-of-information-literacy-23-320.jpg)