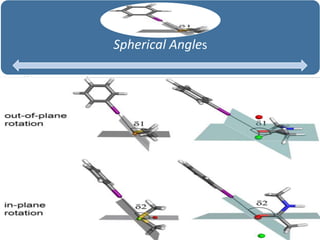
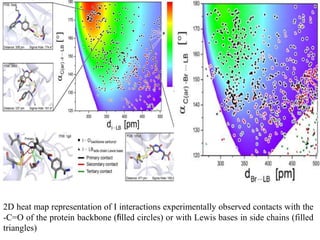
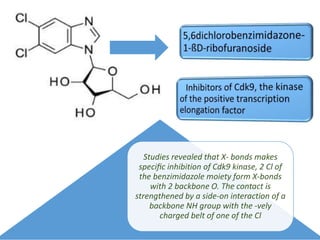
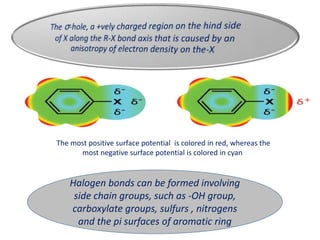
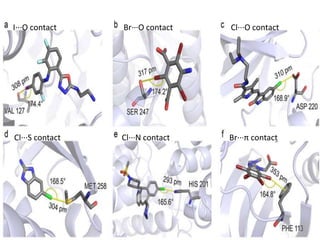
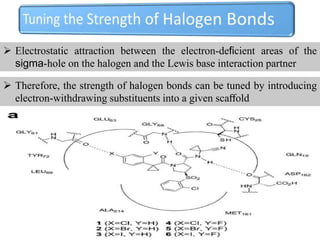
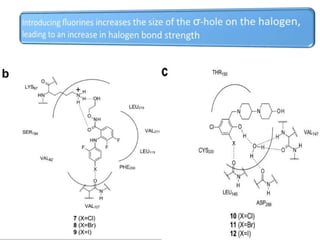
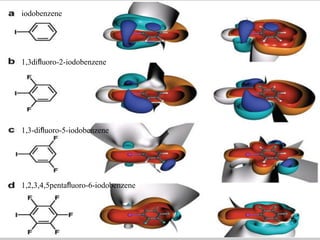
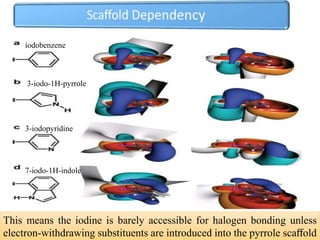
Halogen bonding occurs when a halogen acts as a Lewis acid to form close contacts with electron-rich species. It can range from weak to strong depending on factors like the halogen, substituents, and binding site environment. In drug design, halogen bonding has been successfully utilized to improve binding affinity and selectivity by targeting protein binding sites. Consideration of halogen bonding may prove beneficial in developing new drug molecules.



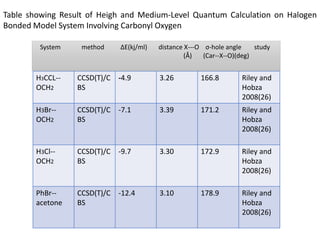
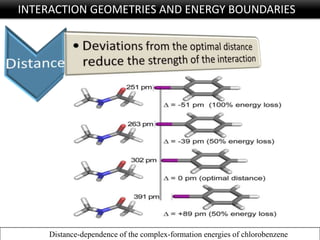
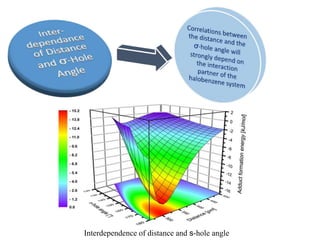
![σ-Hole angle dependence of the complex-formation energies[kJ/mol] of the backbone model
system N-methylacetamide & (C6H5 Cl, green curve),(C6H5 Br,brown curve), or (C6H5I, purple
curve)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/halogenbonding-151202051309-lva1-app6891/85/Halogen-bonding-13-320.jpg)