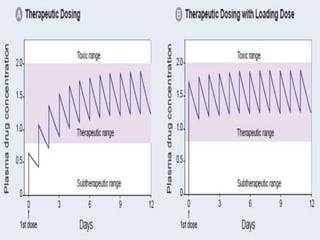
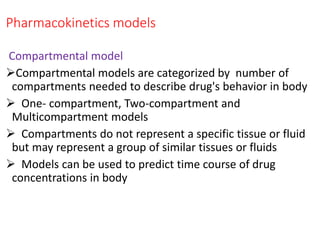
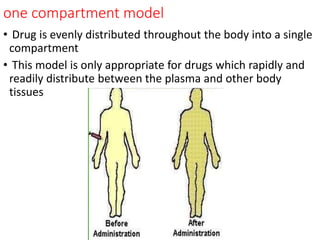
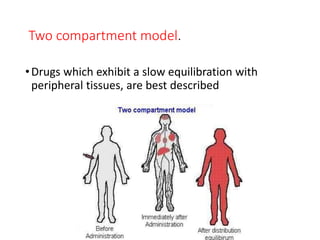
This document outlines the principles of pharmacokinetics, focusing on drug elimination, half-life, and steady-state concentration. Key concepts discussed include first-order and zero-order kinetics, compartmental models, the significance of half-life in drug dosing, and the importance of achieving steady-state for effective pharmacological management. It also highlights clinical applications, such as loading doses and fixed-dose drug combinations.













![Fixed-Dose Drug Combination
Rationale fixed-drug formulation of two drugs can be
advantageous drug should have equal t ½ Eg Cotrimoxazole
(Sulfamethoxazole [t ½ 11 hr]) & Trimethoprim [t ½ 10 hr]
Ratio of dose depends on aVd & plasma conc. Of individual
drug eg t ½ & Vd of Amoxycillin (1-2hr 0.21 L/kg) matches
with t ½ &Vd of Clavulanic acid (1-1.5hr 0.20 L/kg )
Advantage of Fixed-dose formulation
Convenient dose schedule
Better patient compliance
Enhanced effect
Minimal side effect](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/halflifeppt-200709095830/85/Half-life-ppt-26-320.jpg)