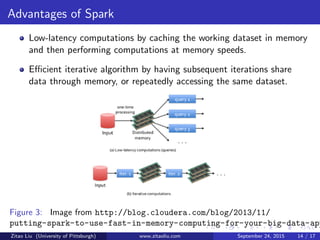
The document discusses Hadoop and Spark frameworks for big data analytics. It describes that Hadoop consists of HDFS for distributed storage and MapReduce for distributed processing. Spark is faster than MapReduce for iterative algorithms and interactive queries since it keeps data in-memory. While MapReduce is best for one-pass batch jobs, Spark performs better for iterative jobs that require multiple passes over datasets.