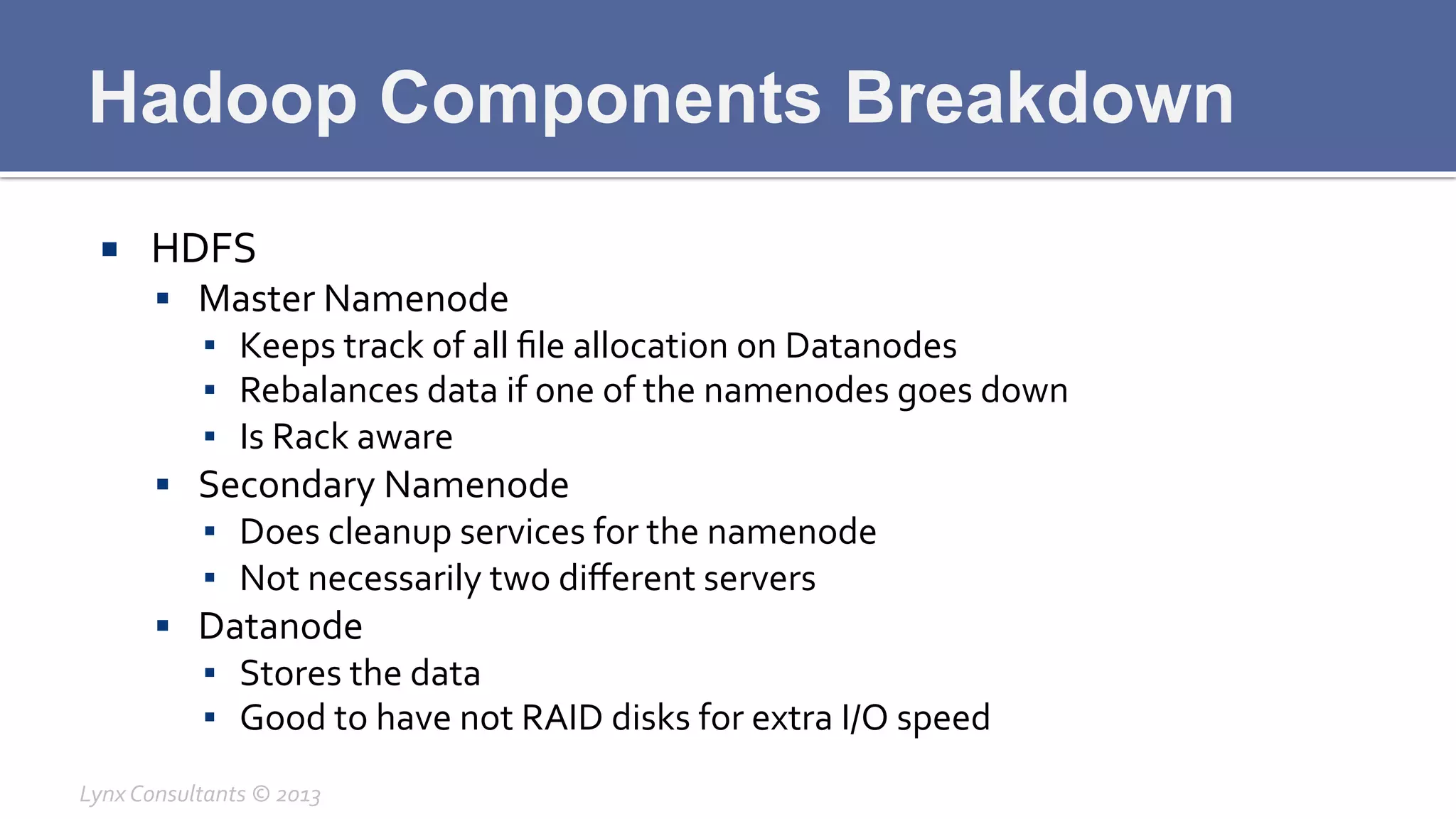
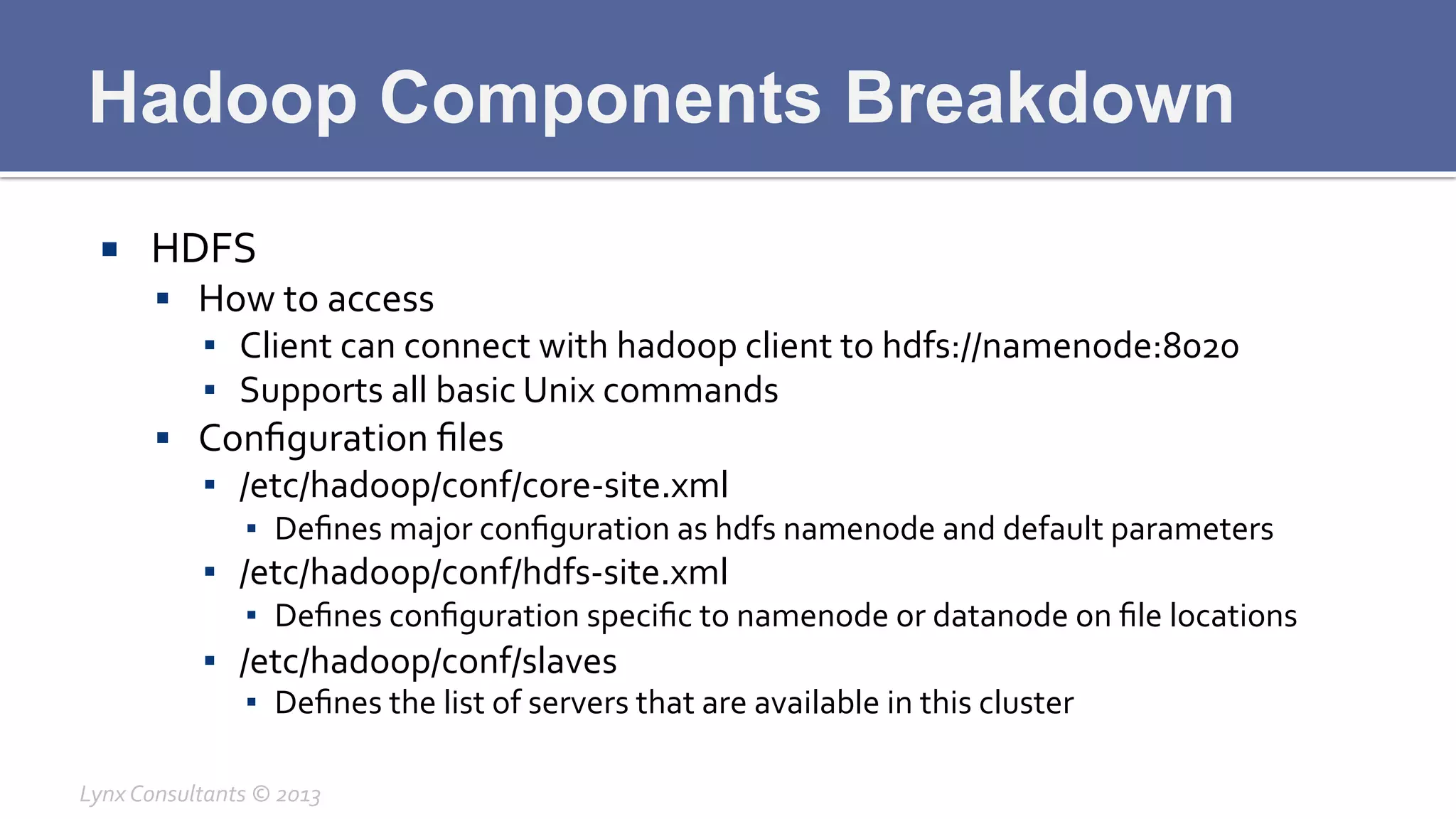
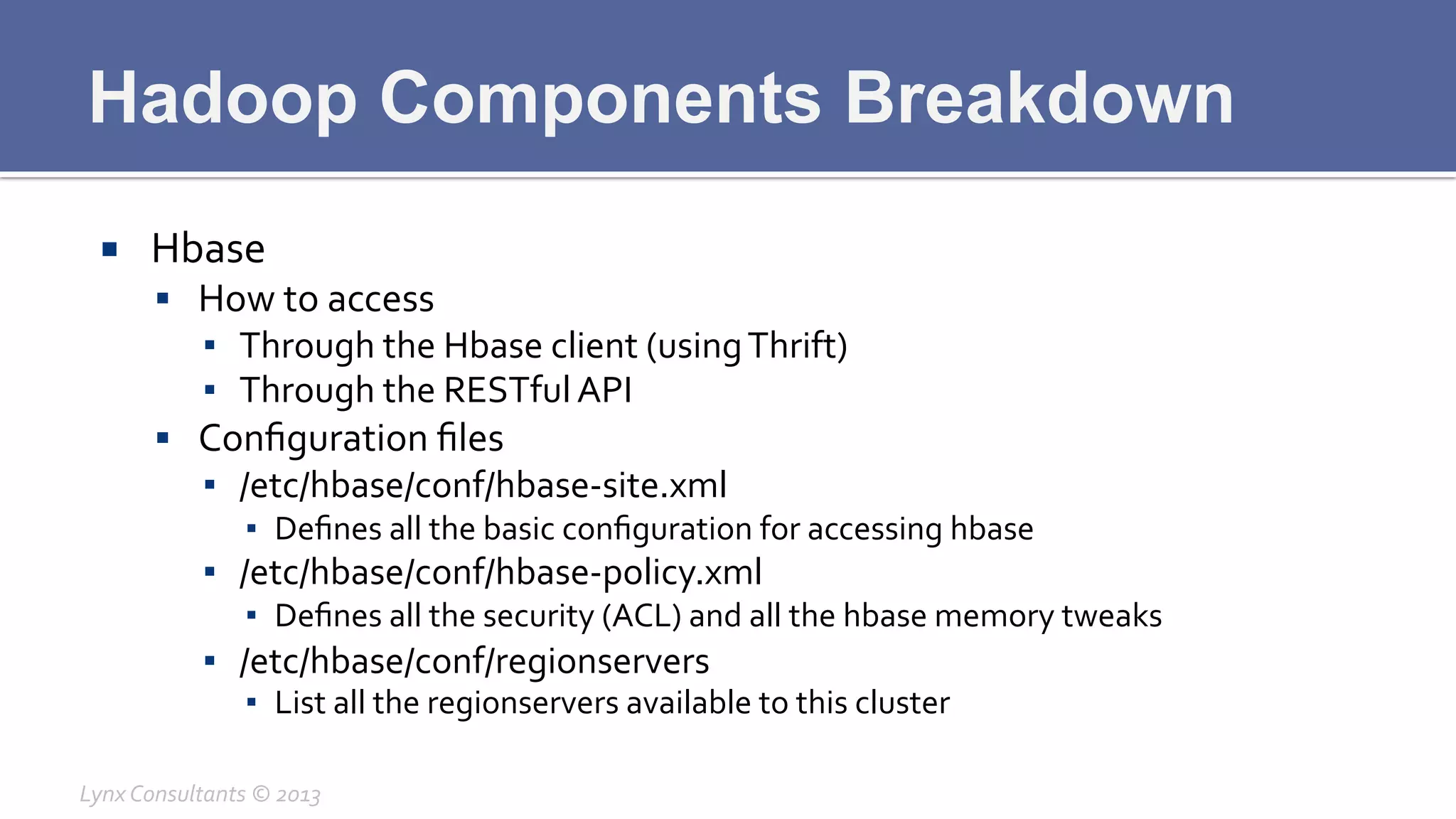
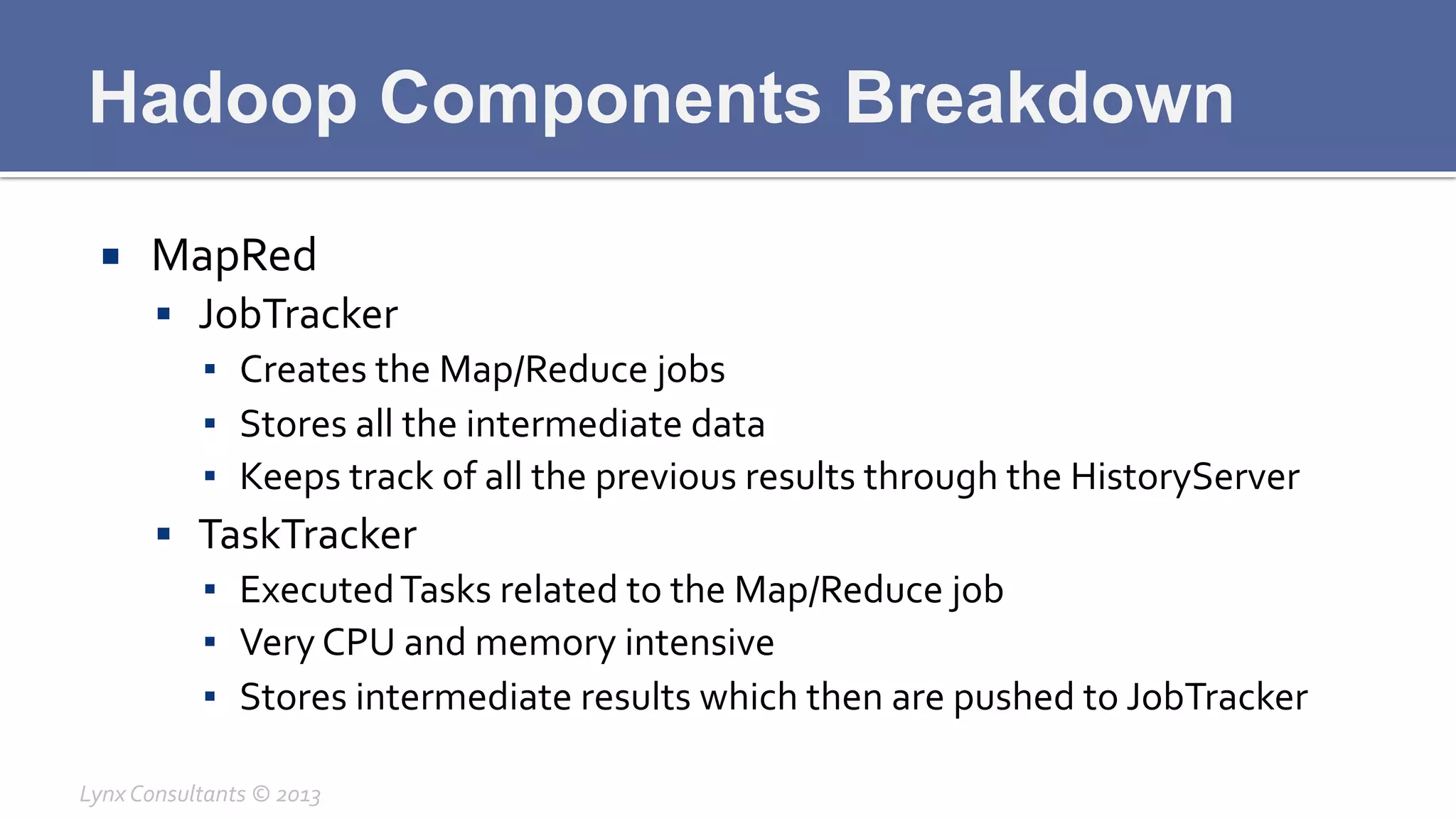
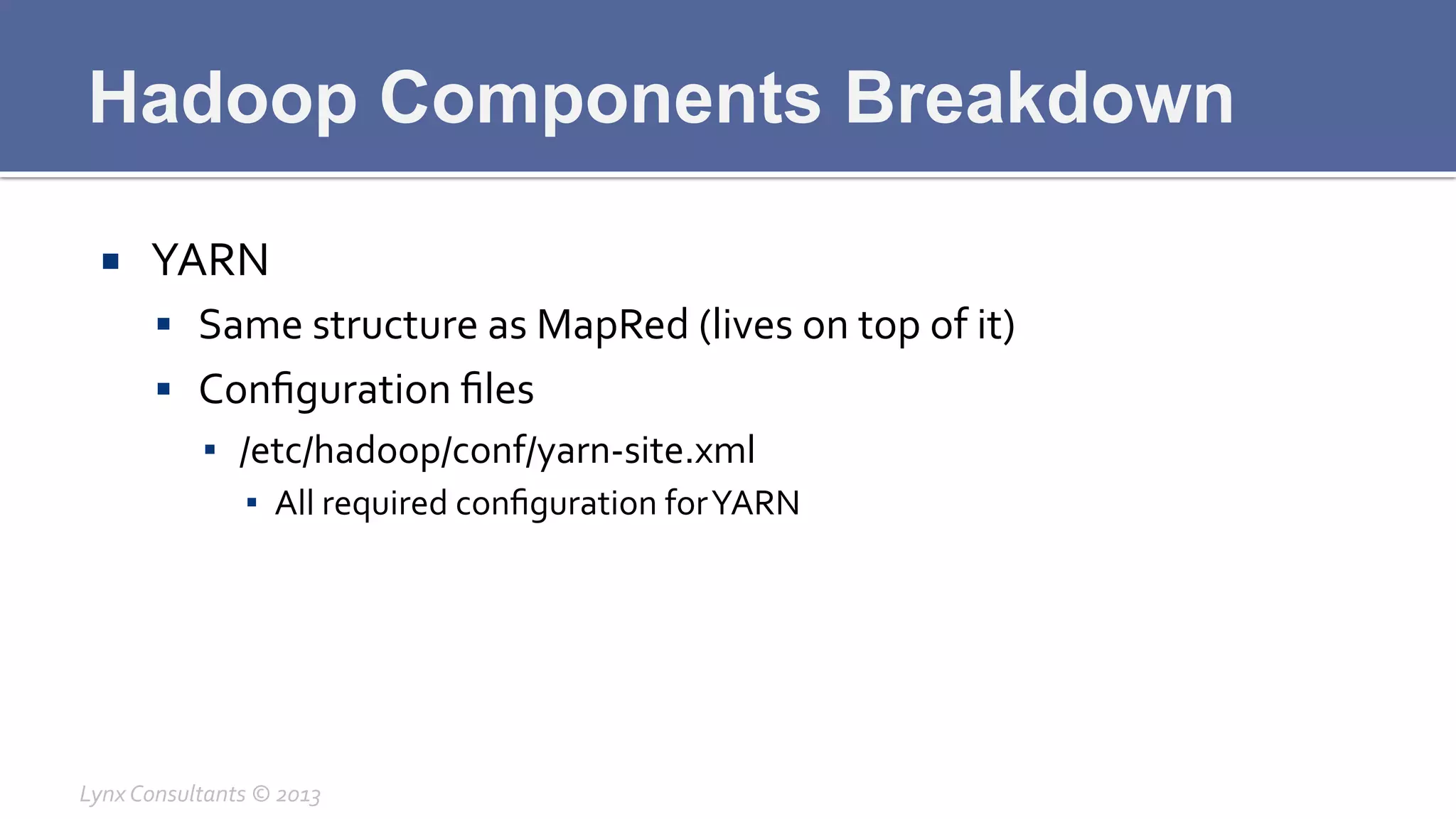
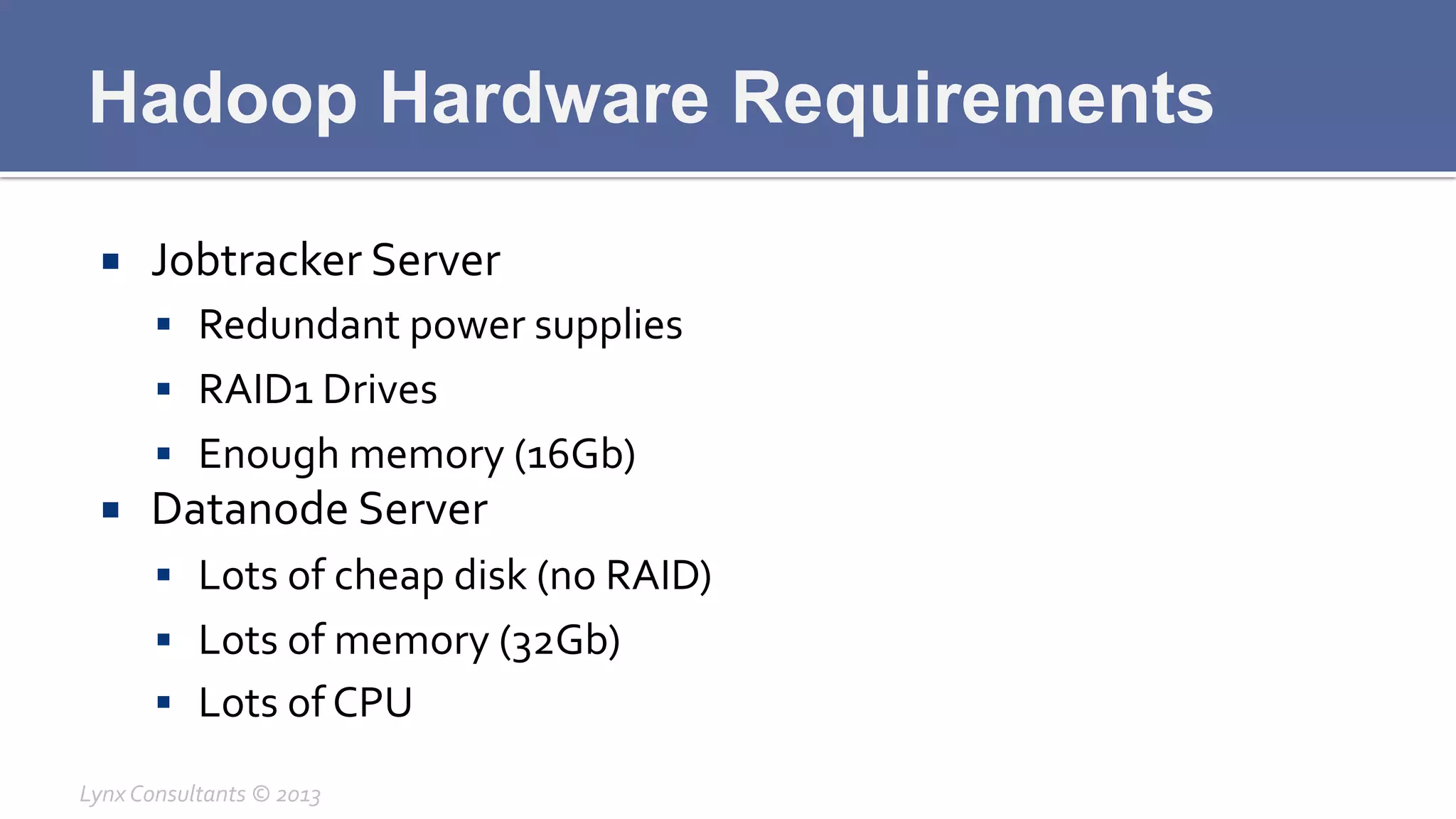
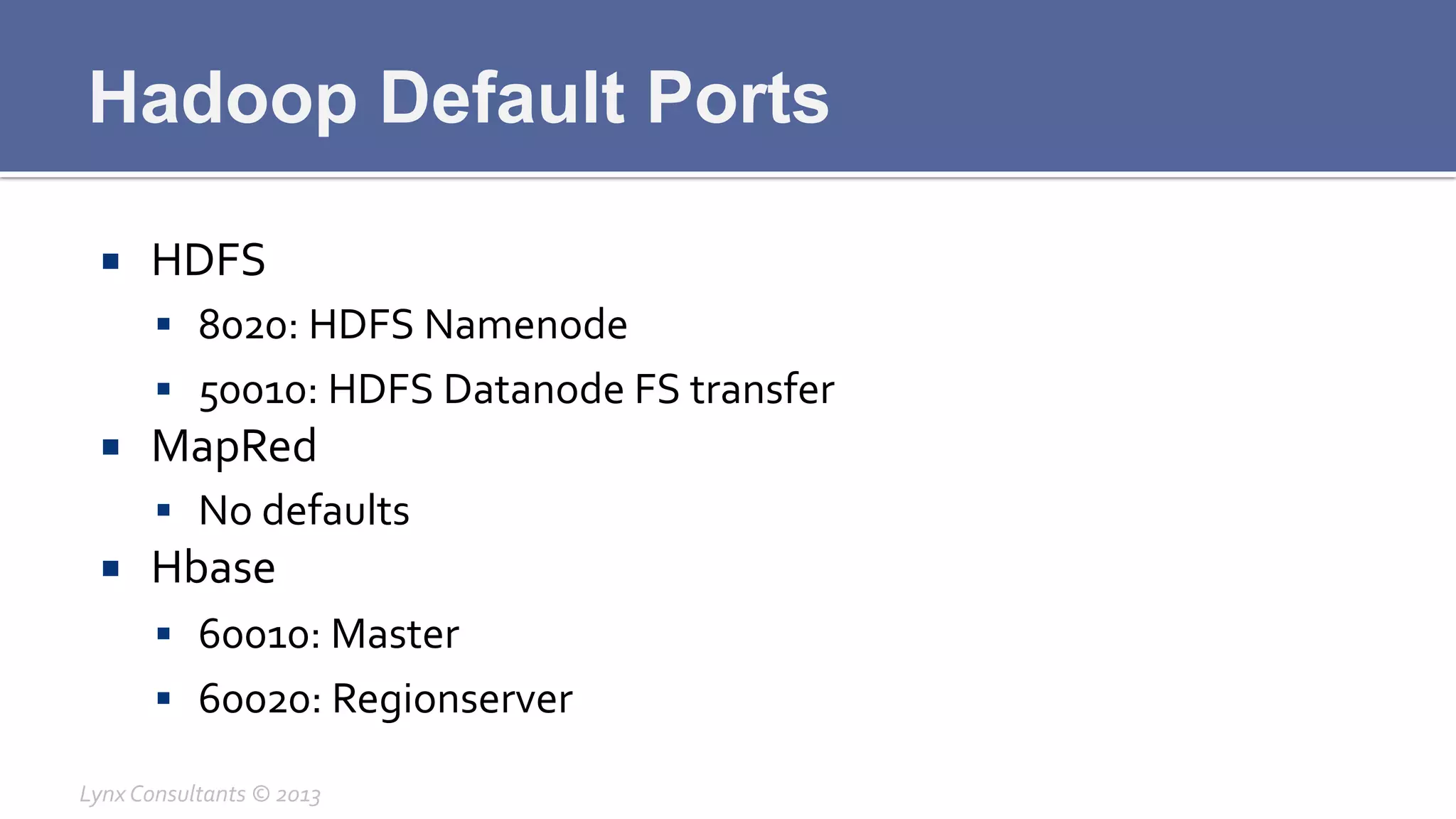
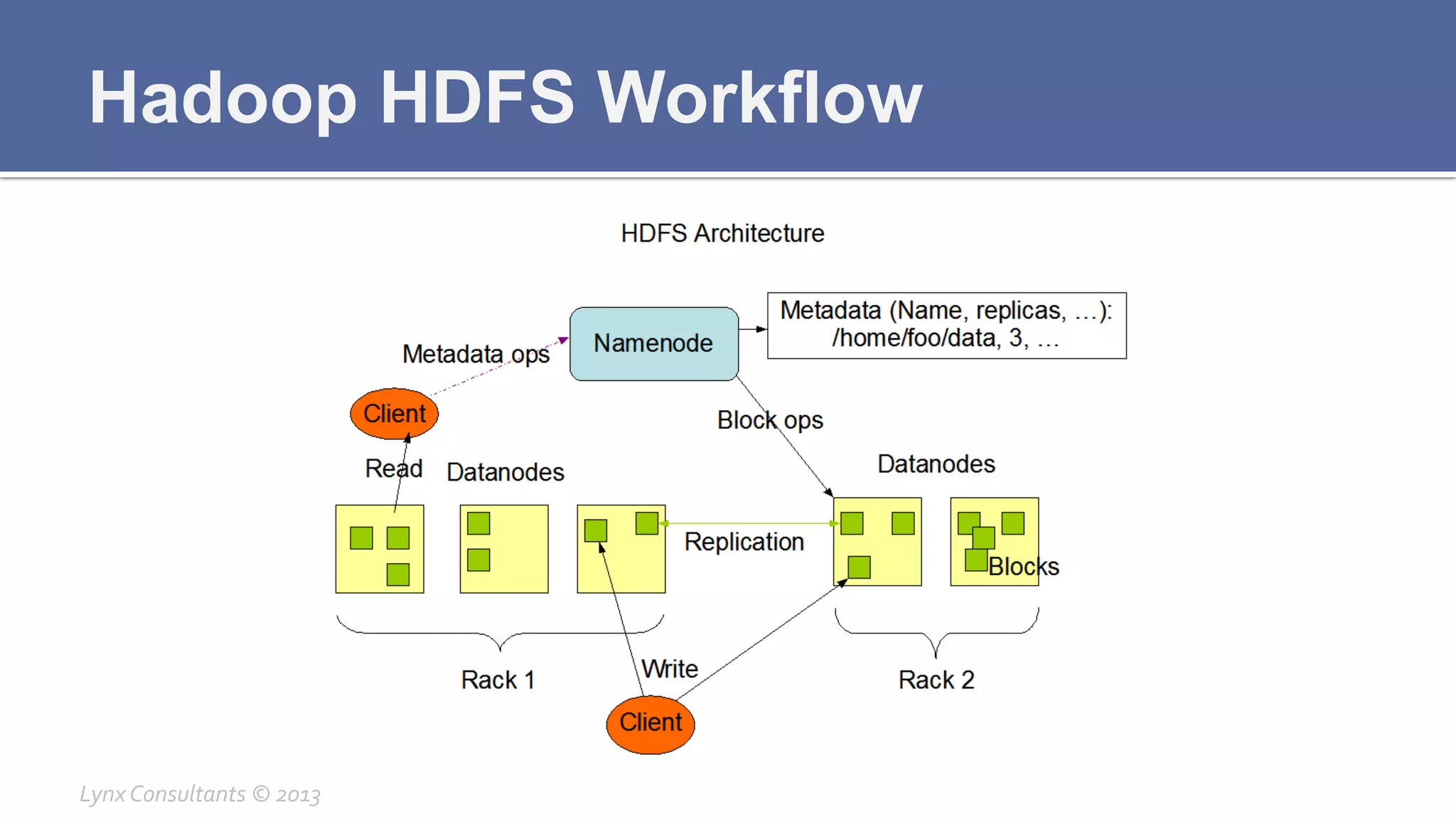
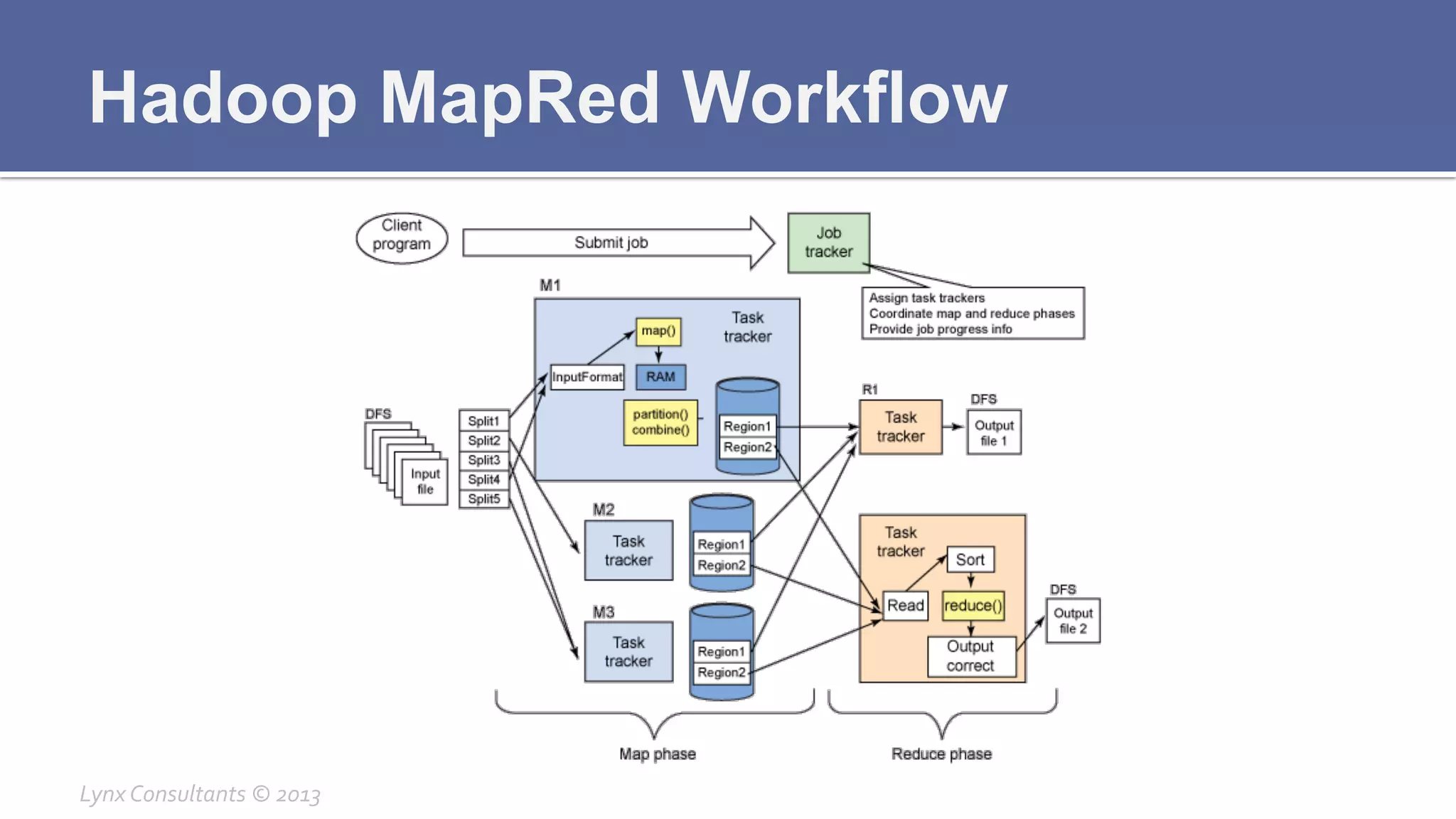
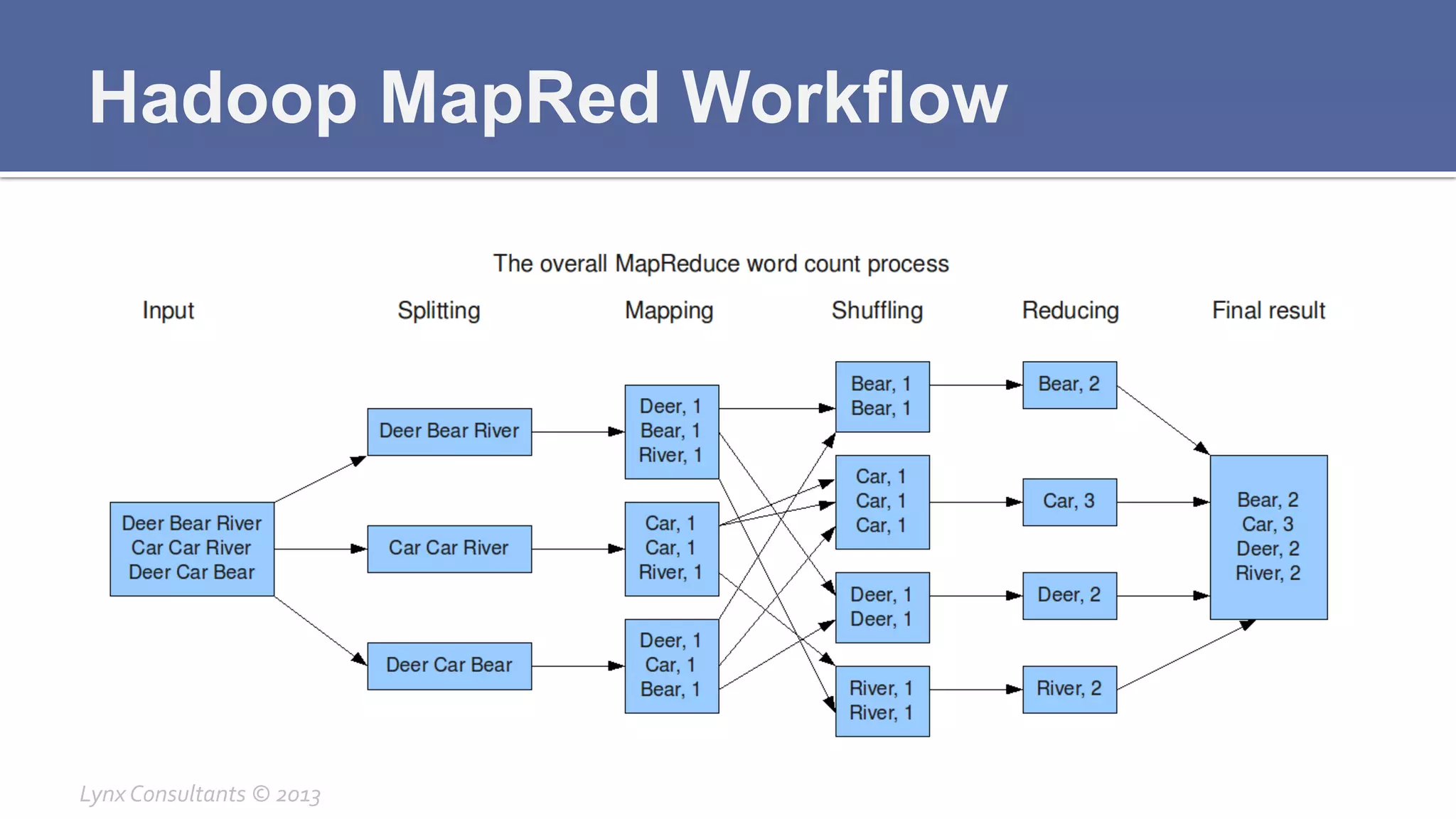
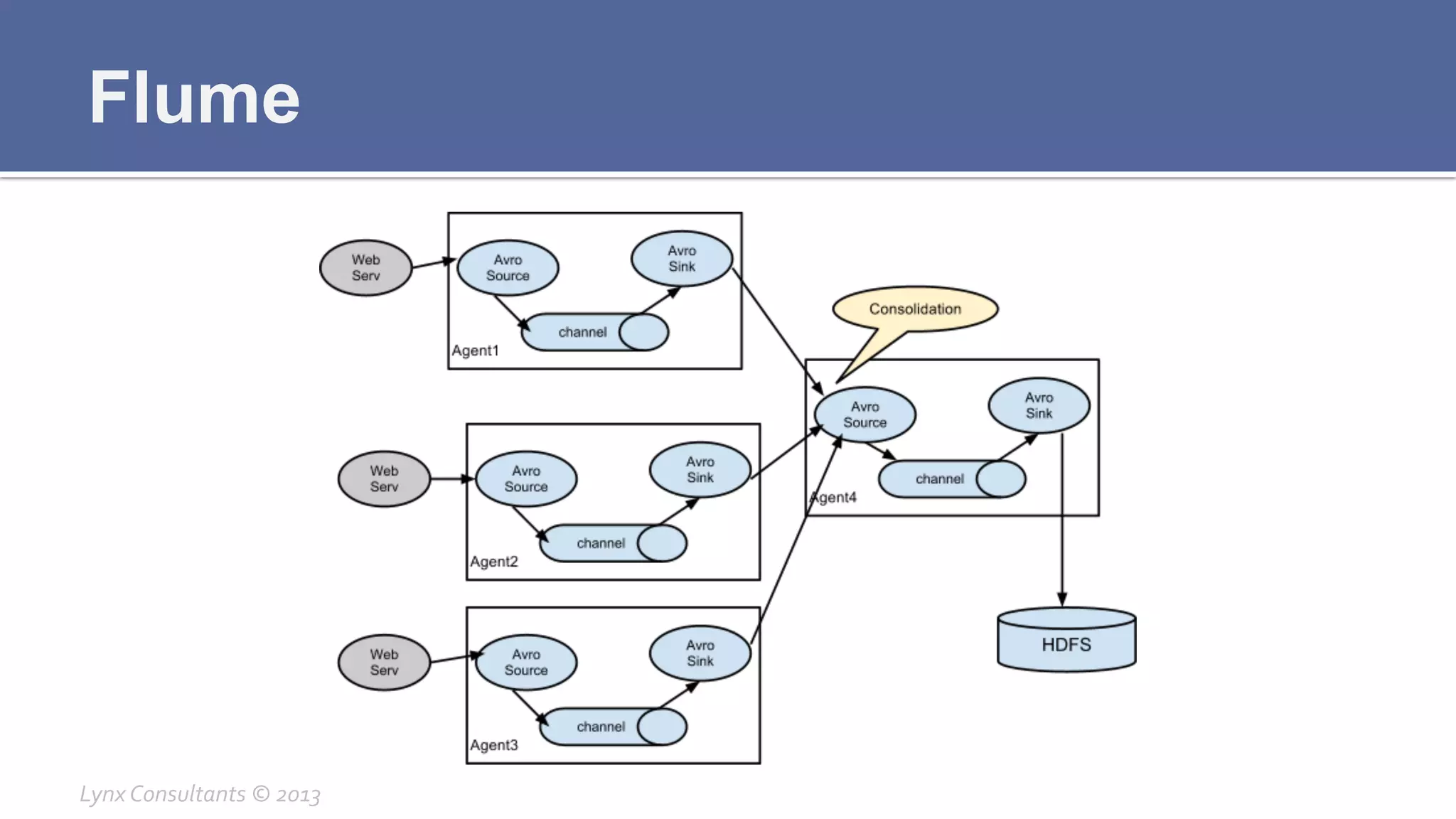
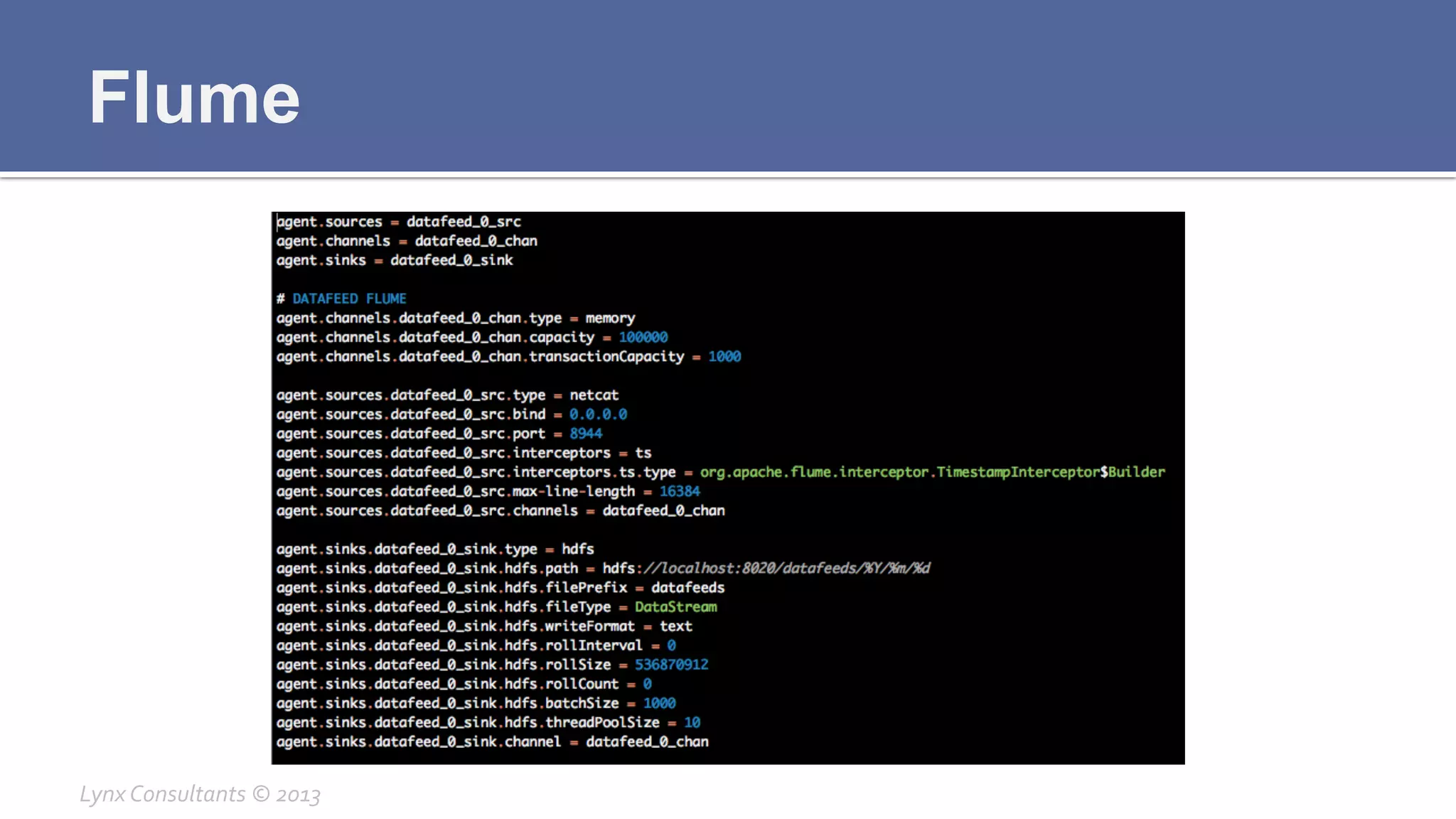
The document discusses the components of Hadoop, including HDFS, HBase, MapReduce, and YARN. It describes the roles of each component, such as the namenode tracking file locations in HDFS and regionservers storing data in HBase. It also provides breakdowns of the master/slave architecture of each component and the typical configuration files.