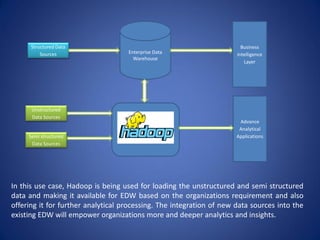
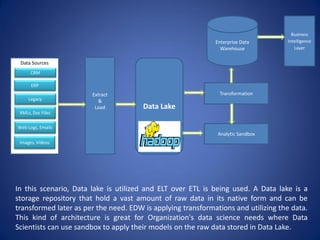
The document discusses the integration of Hadoop technologies into existing enterprise data warehouses (EDWs) to enhance performance rather than replace them. It outlines Hadoop's scalability, cost-effectiveness, and flexibility, as well as its limitations, including latency and security concerns. A thorough assessment of organizational needs is crucial for successful implementation, with several use cases demonstrating how Hadoop can improve data processing and analytics within an EDW framework.