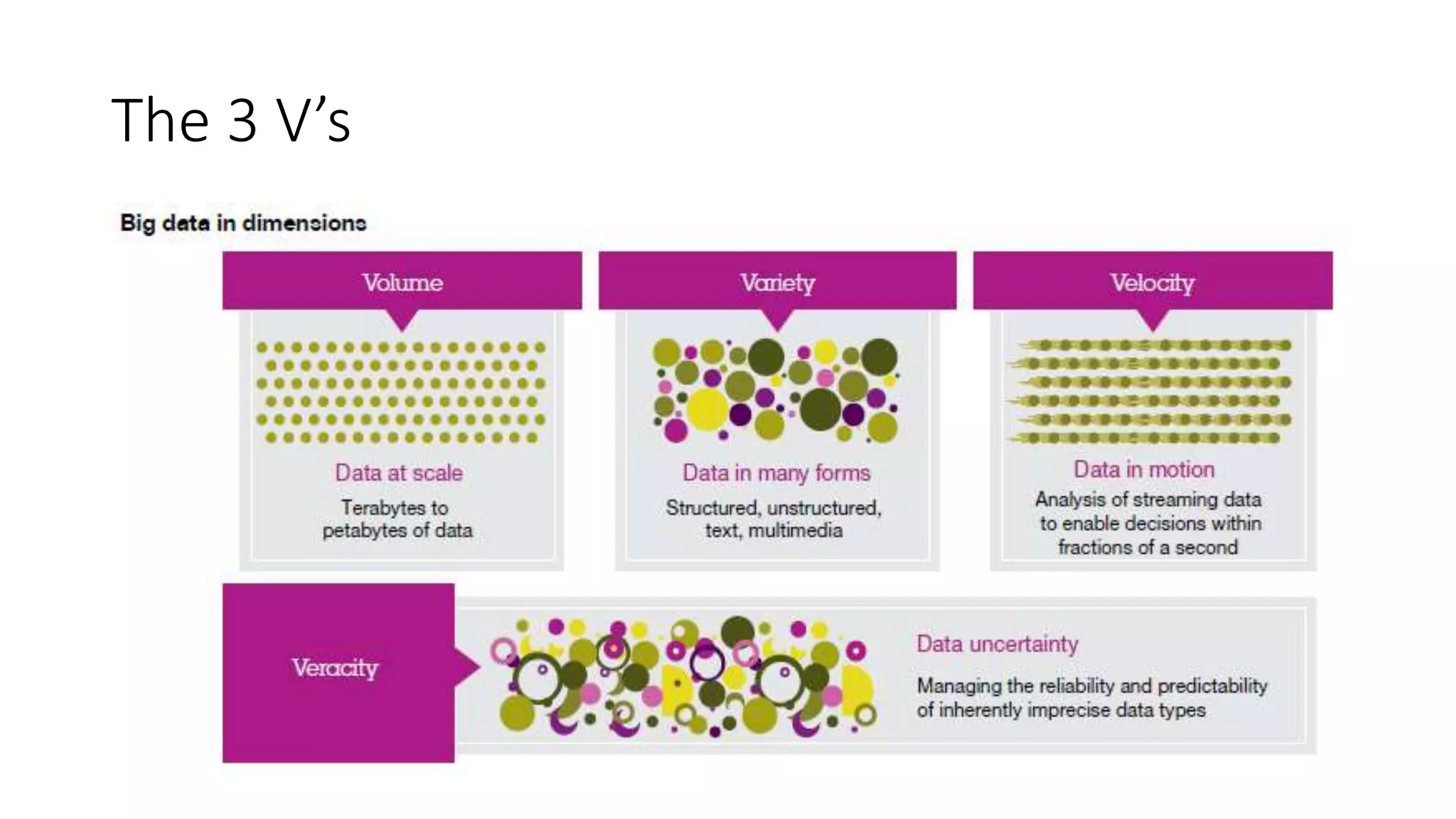
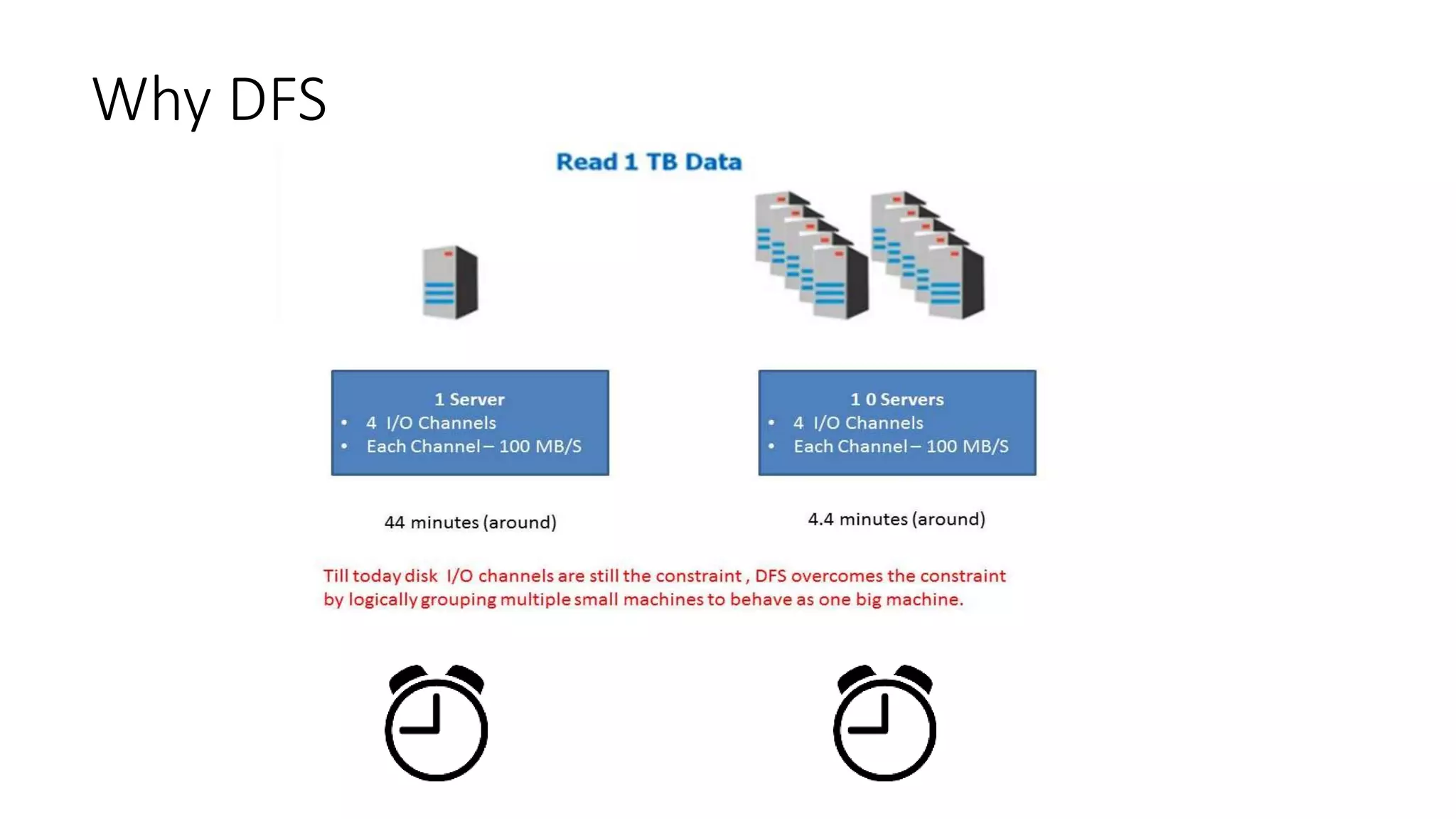
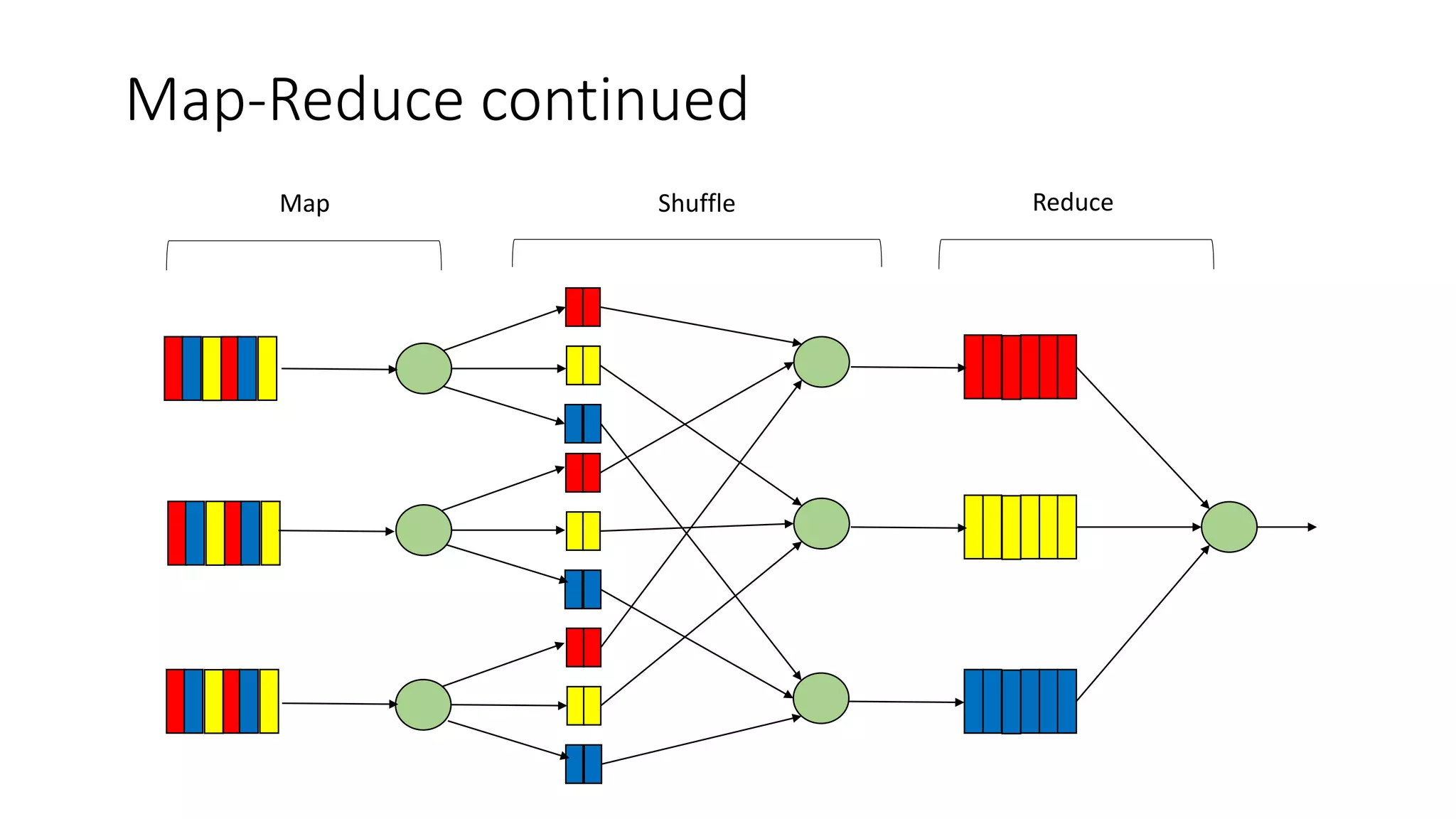
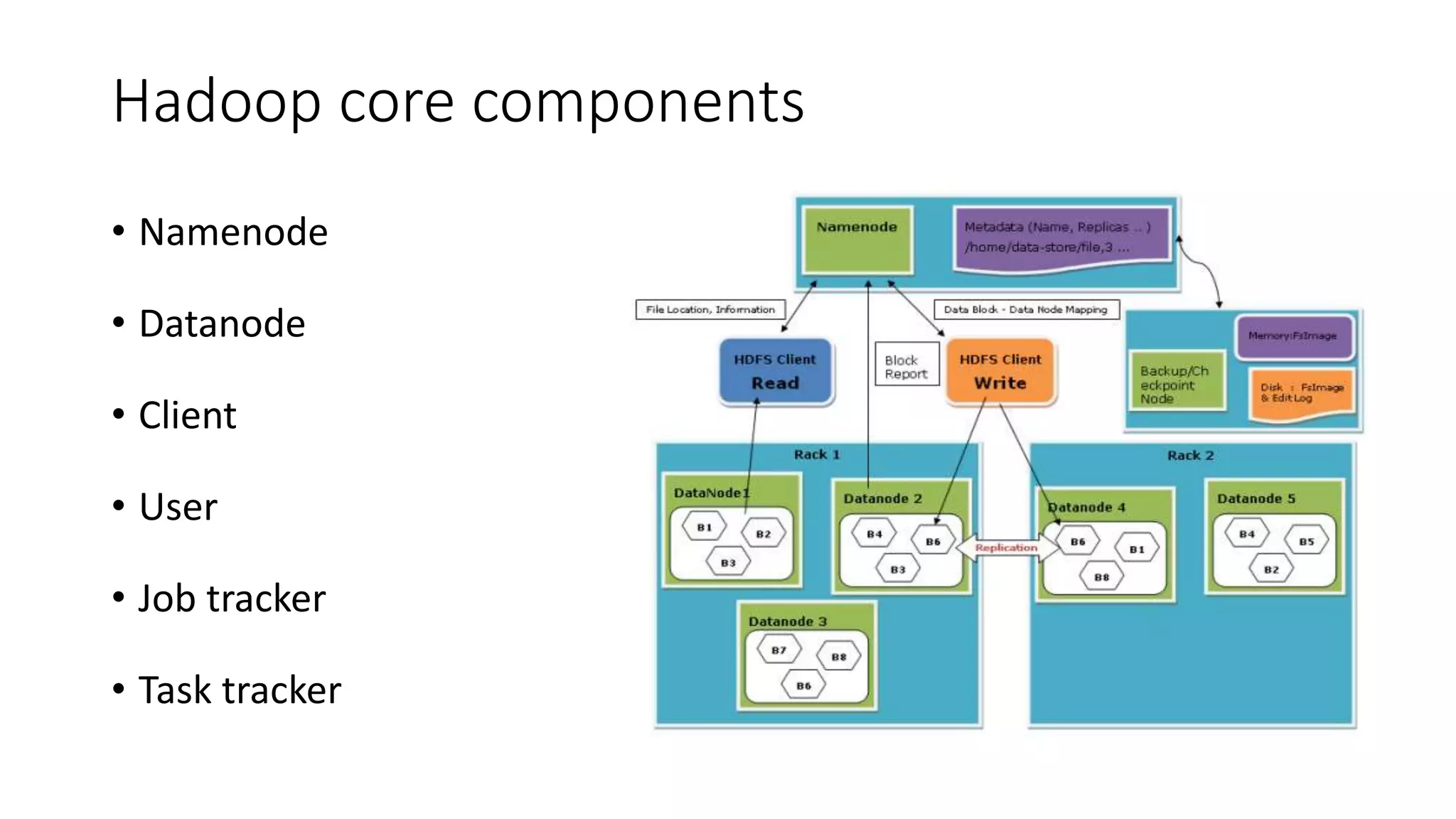
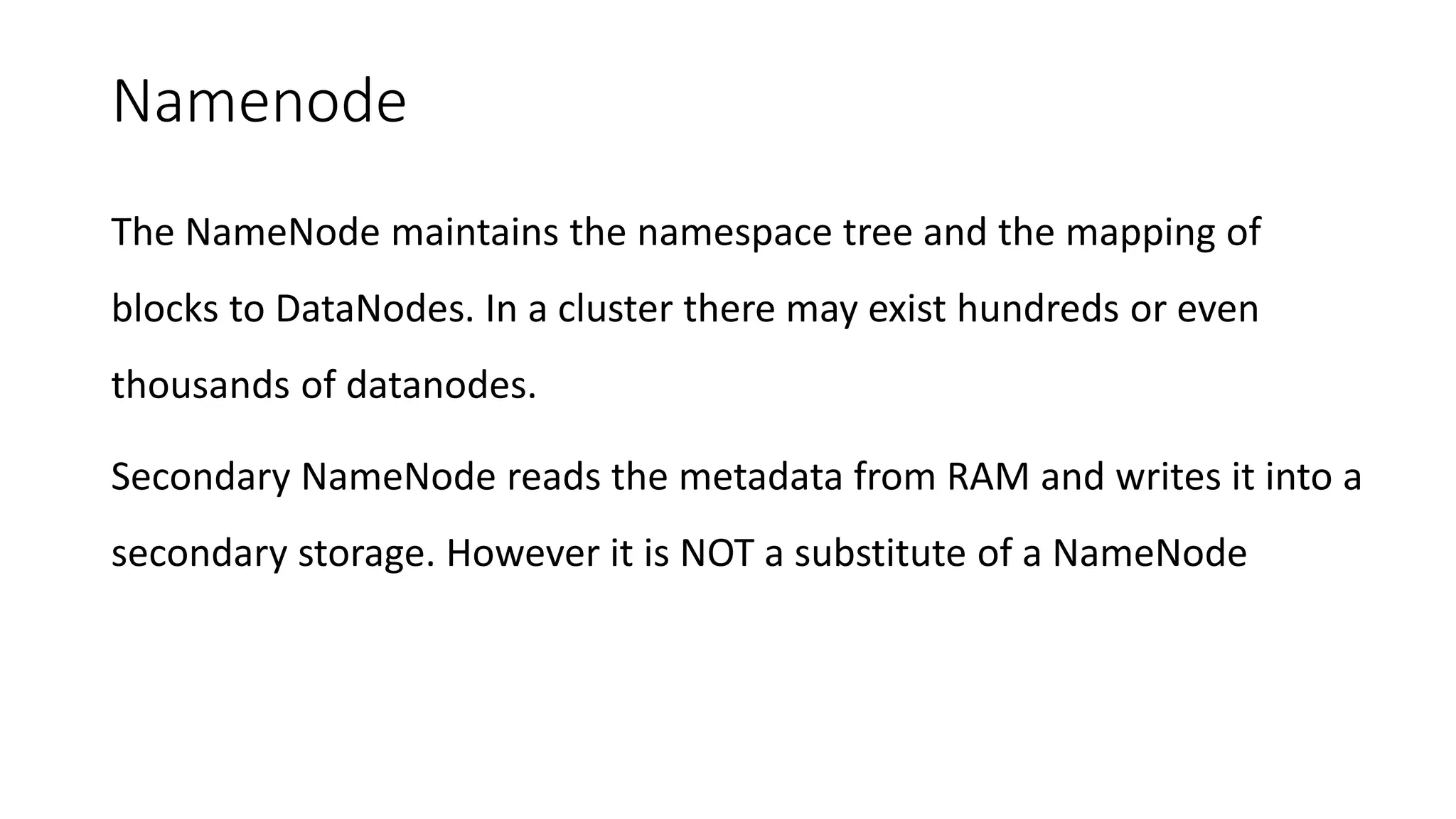
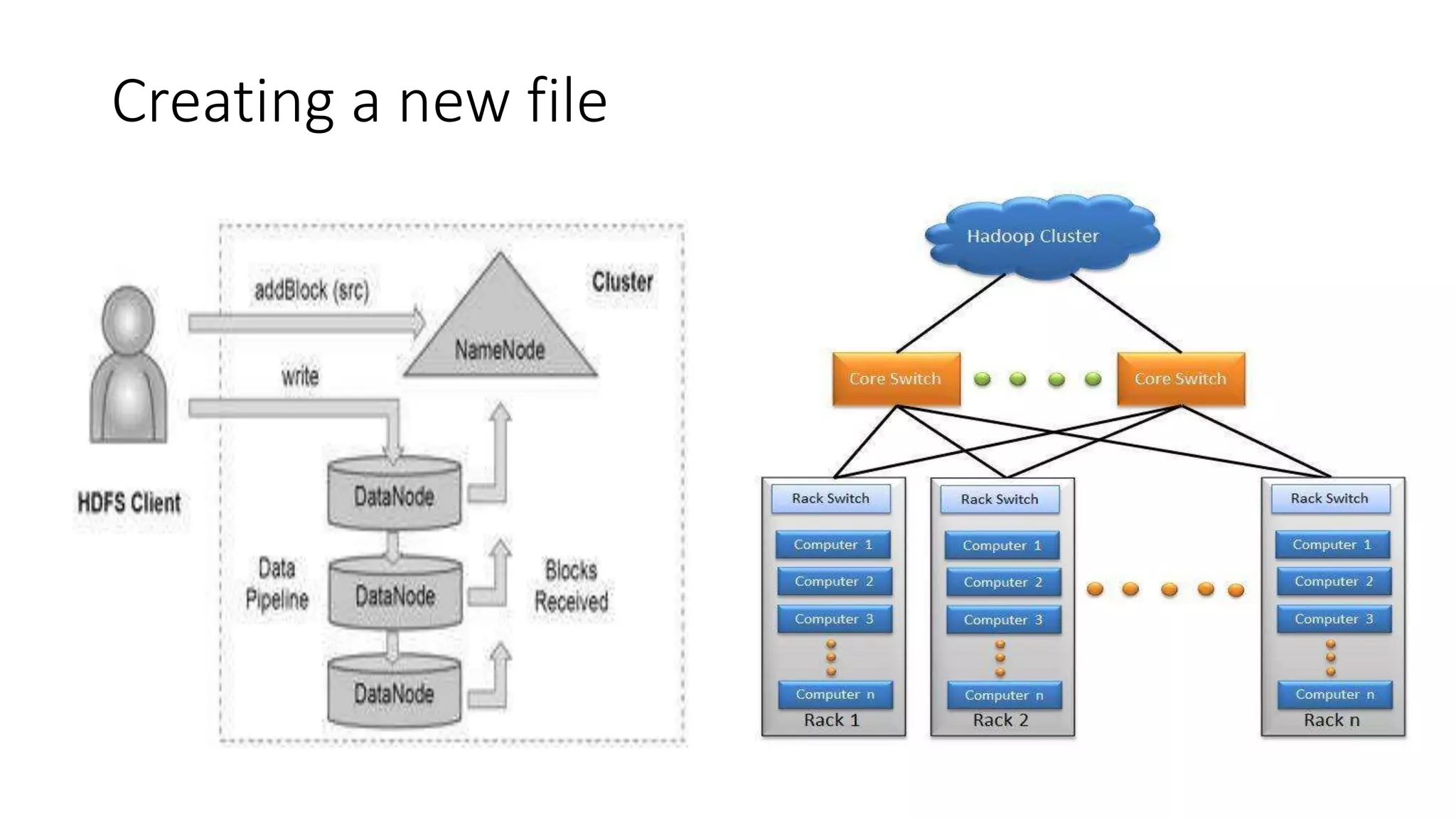
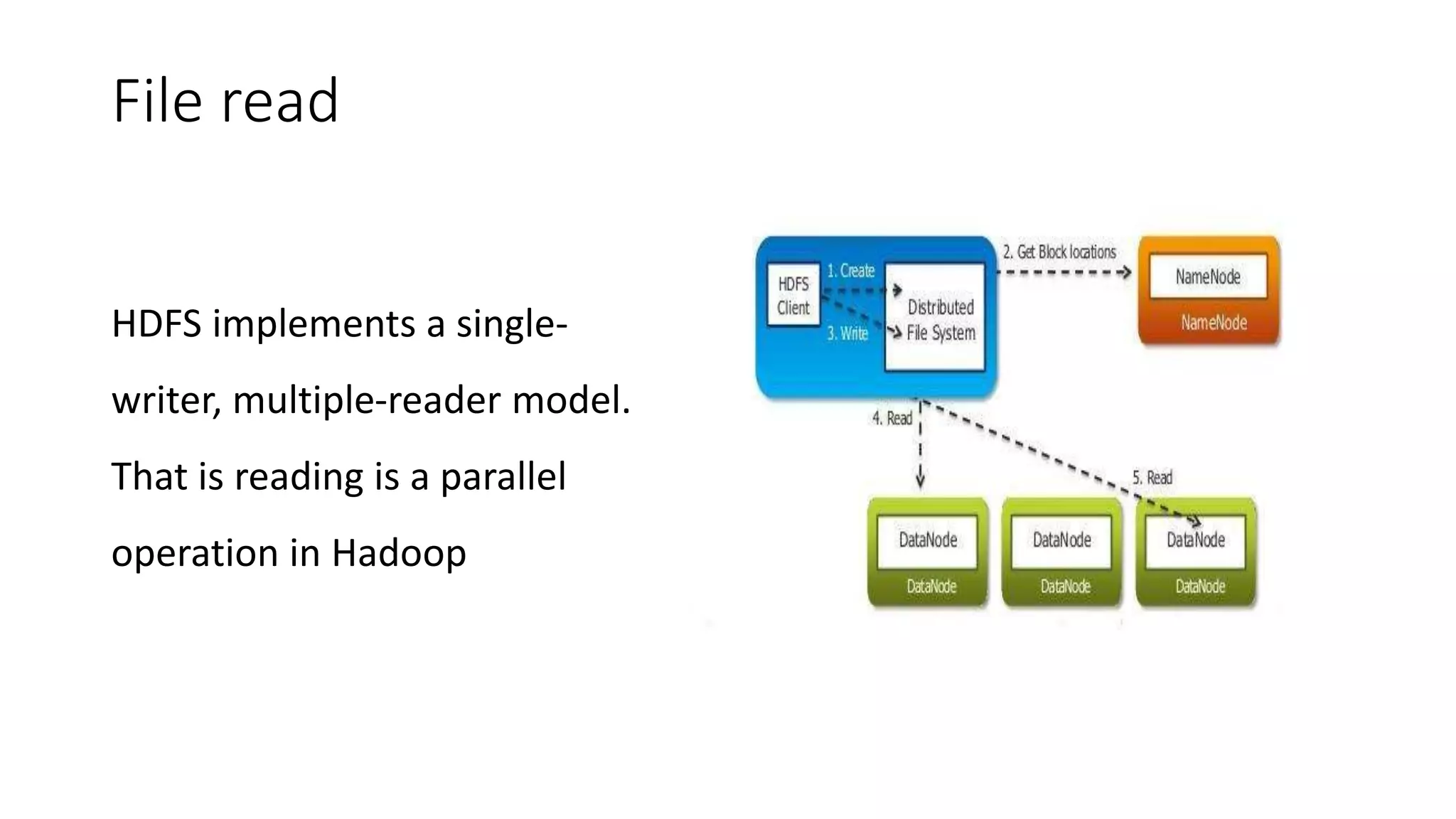
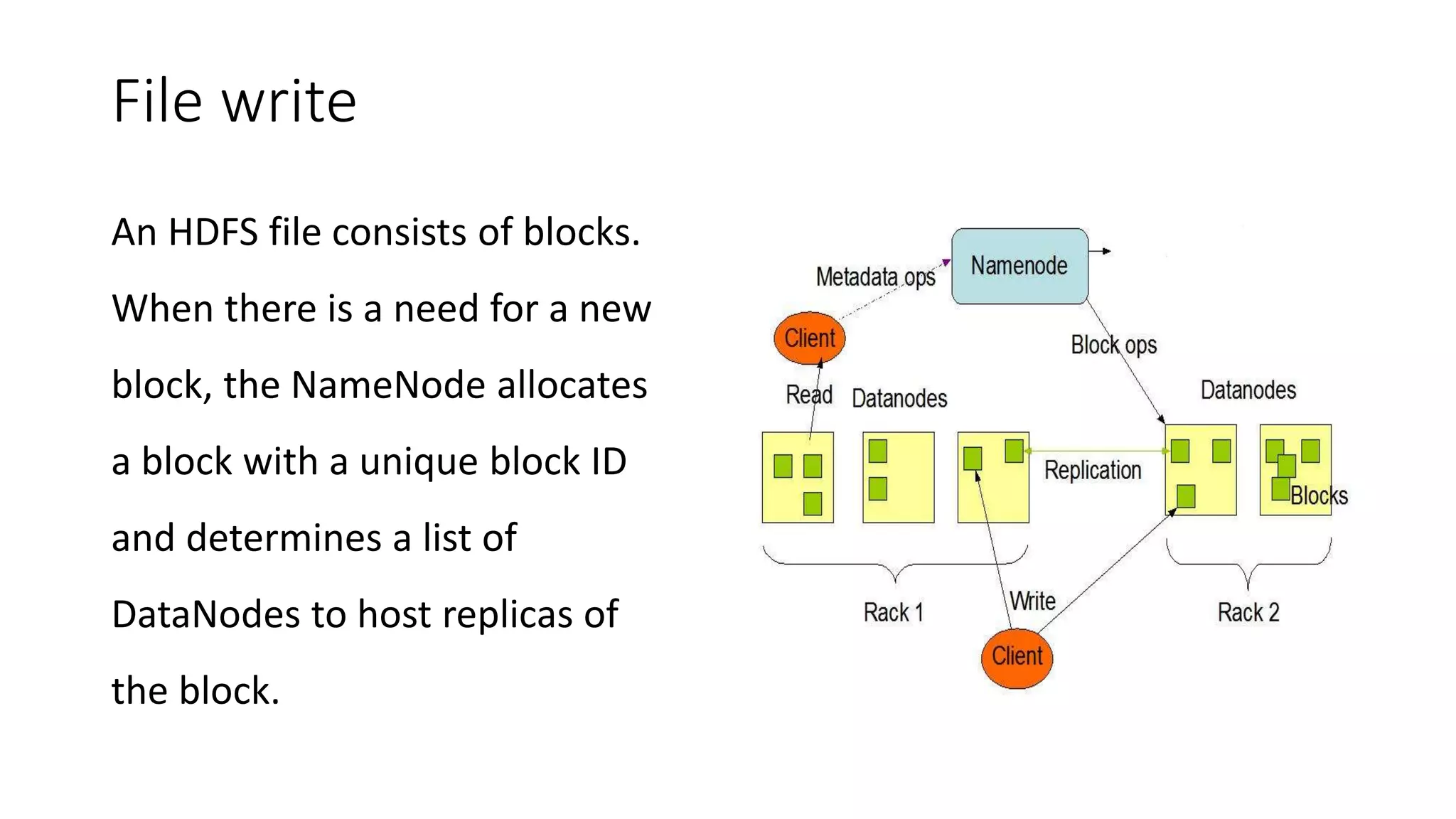
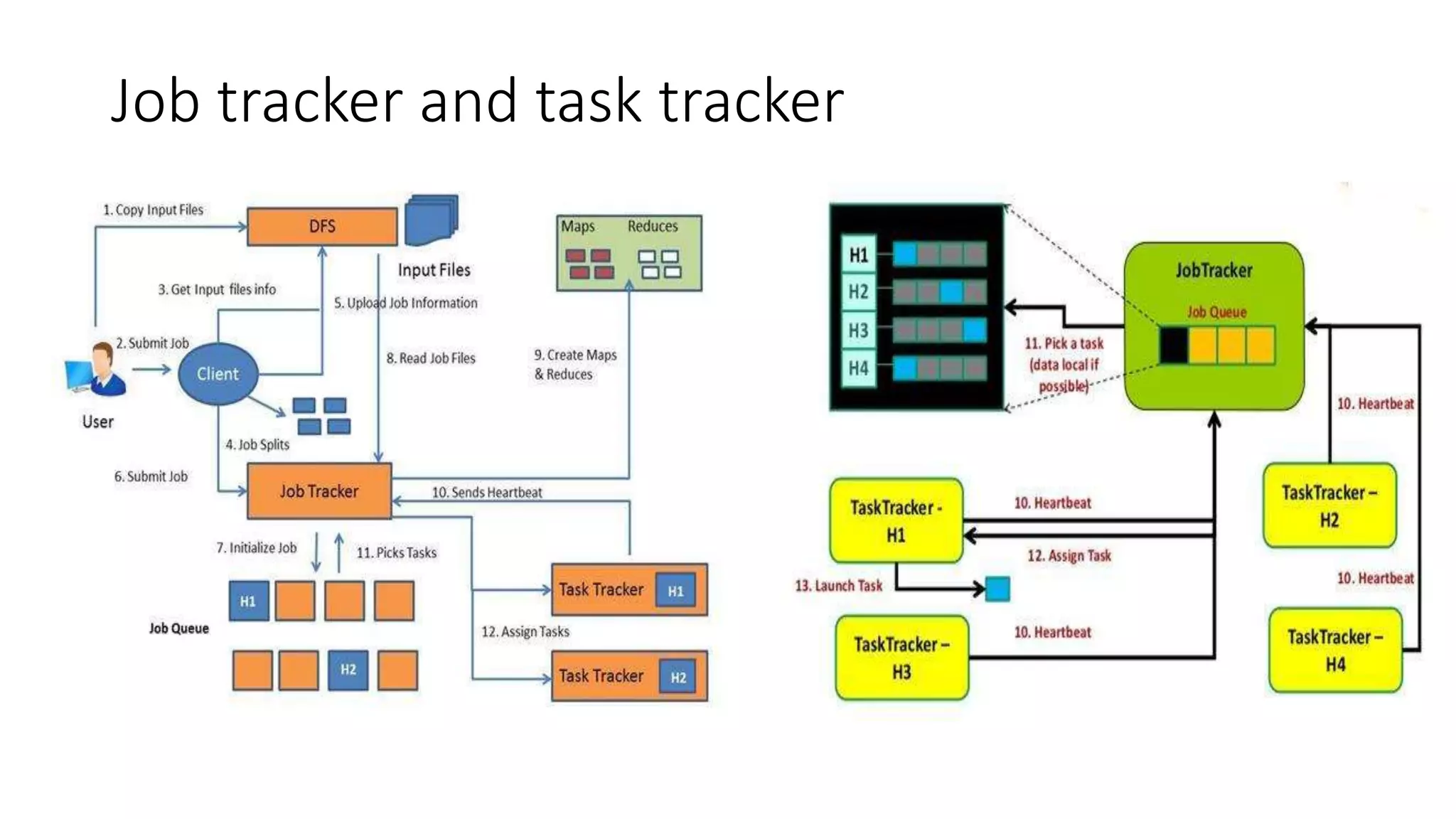
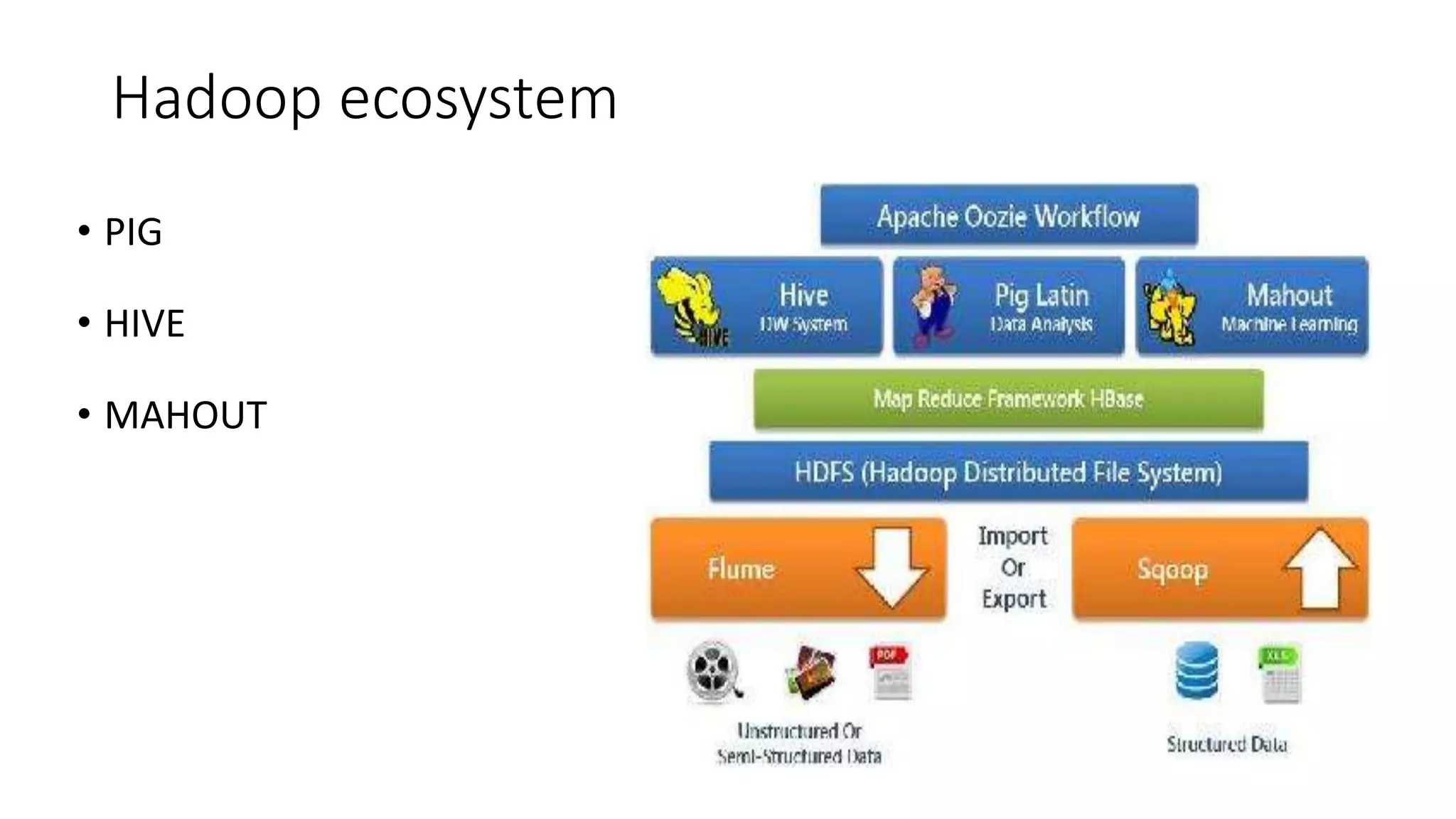
This document provides an overview of Hadoop and MapReduce. It discusses key concepts like big data, the three V's of big data, distributed file systems, and how MapReduce works. It also describes Hadoop components including the namenode, datanode, job tracker, and task tracker. Example MapReduce jobs and applications of Hadoop like Pig, Hive, and Mahout are mentioned.