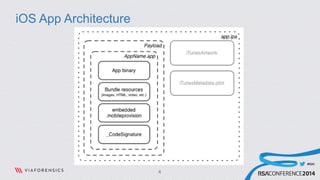
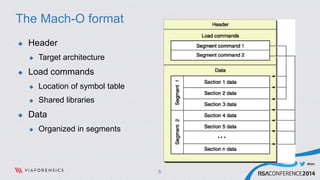
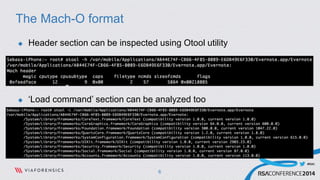
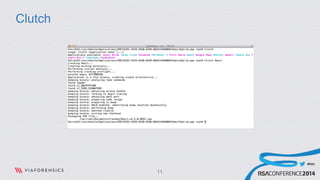
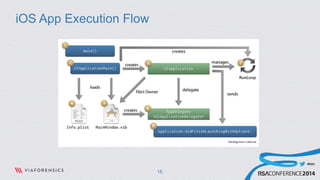
This document discusses analyzing and abusing iOS applications at runtime using Cycript. It begins with an overview of the Mach-O binary format and class-dump-z tool for analyzing iOS application binaries. It then covers decrypting encrypted App Store applications and using Cycript to modify runtime behavior by directly accessing classes, methods, and variables. Examples are given of bypassing locks and retrieving sensitive data from applications like Evernote. The document concludes with recommendations for securing applications by making the runtime more resistant to tampering.