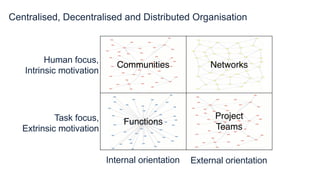
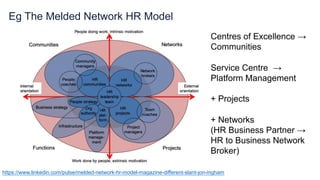
Jon Ingham is an expert in strategic human resources with over 20 years of experience, focusing on organizational effectiveness and the integration of remote work. He emphasizes the need for specialized, empowered teams that operate with trust and psychological safety, as well as the importance of communities and networks for collaboration and innovation. Ingham advocates for a strategic human capital management approach that reflects the complexities of modern work environments, especially in light of recent shifts towards decentralization in organizations.