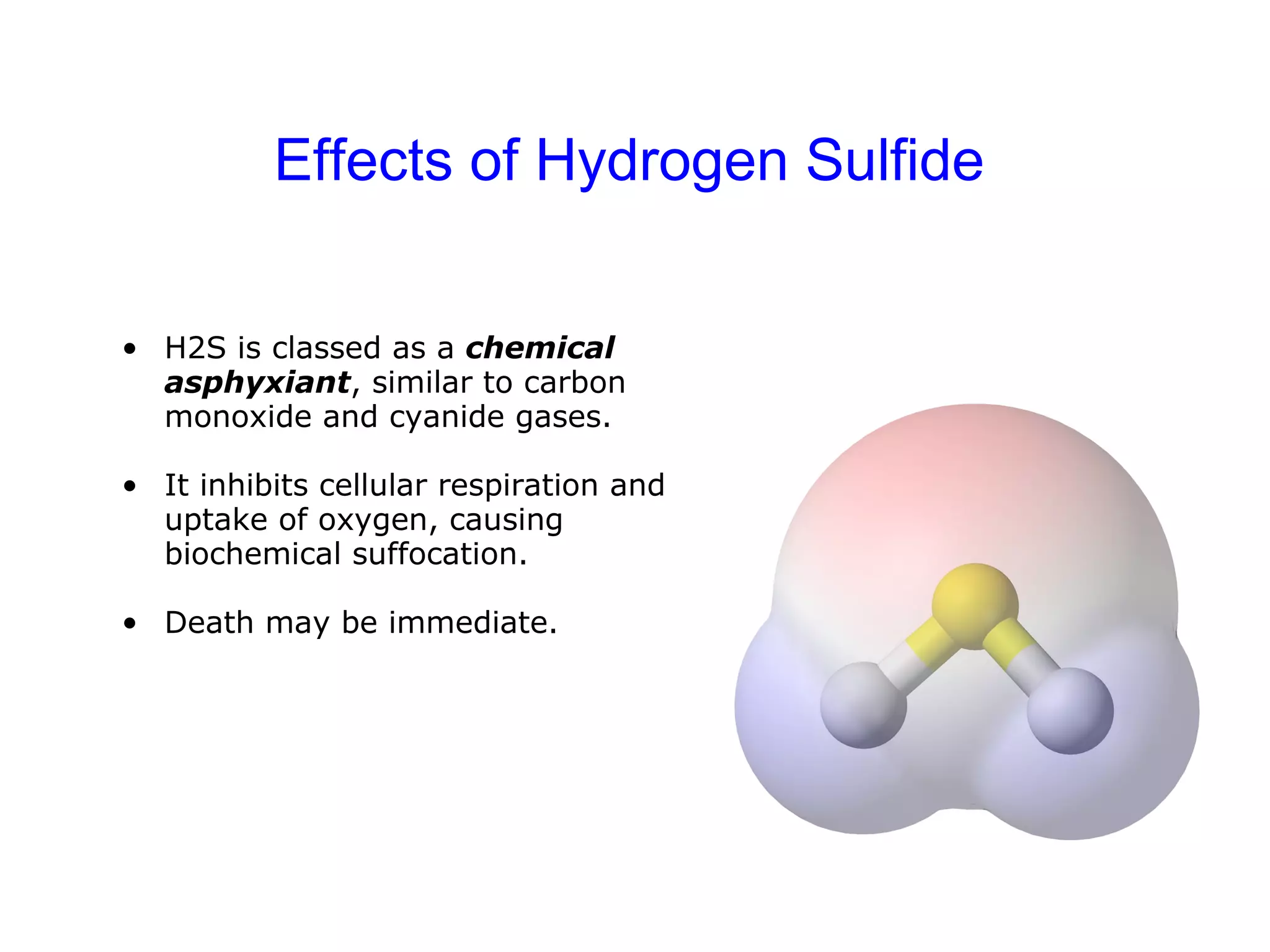
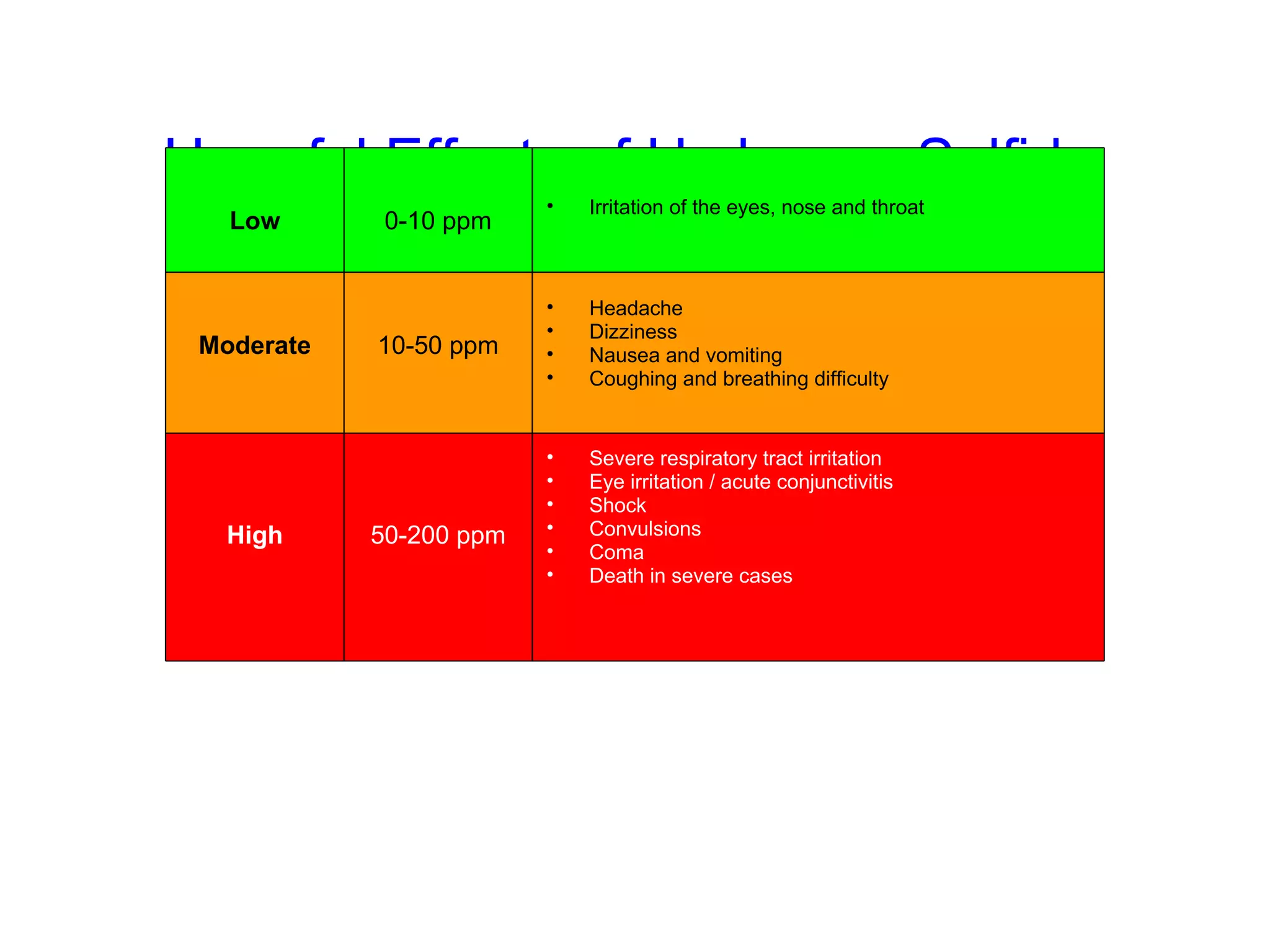
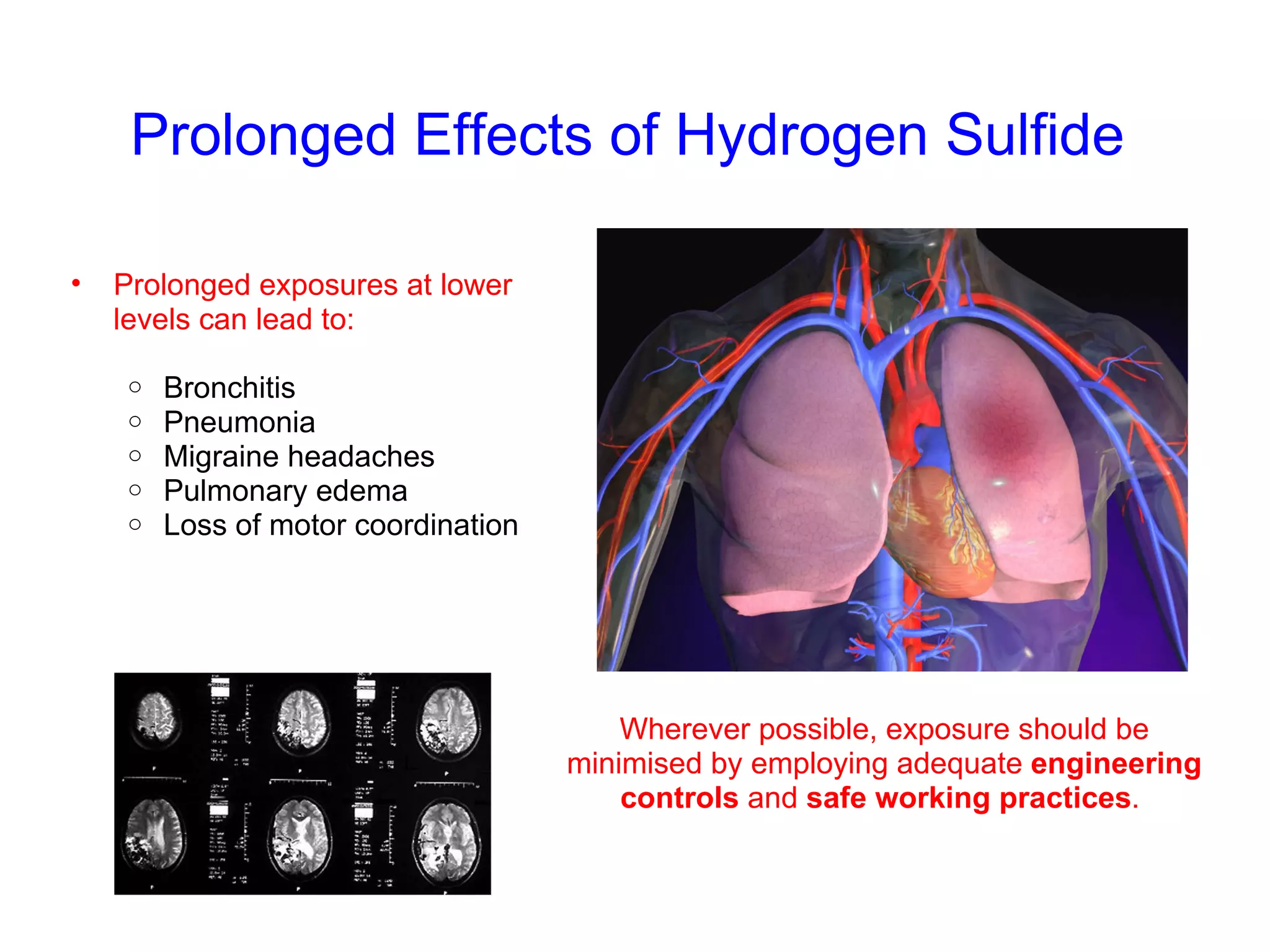
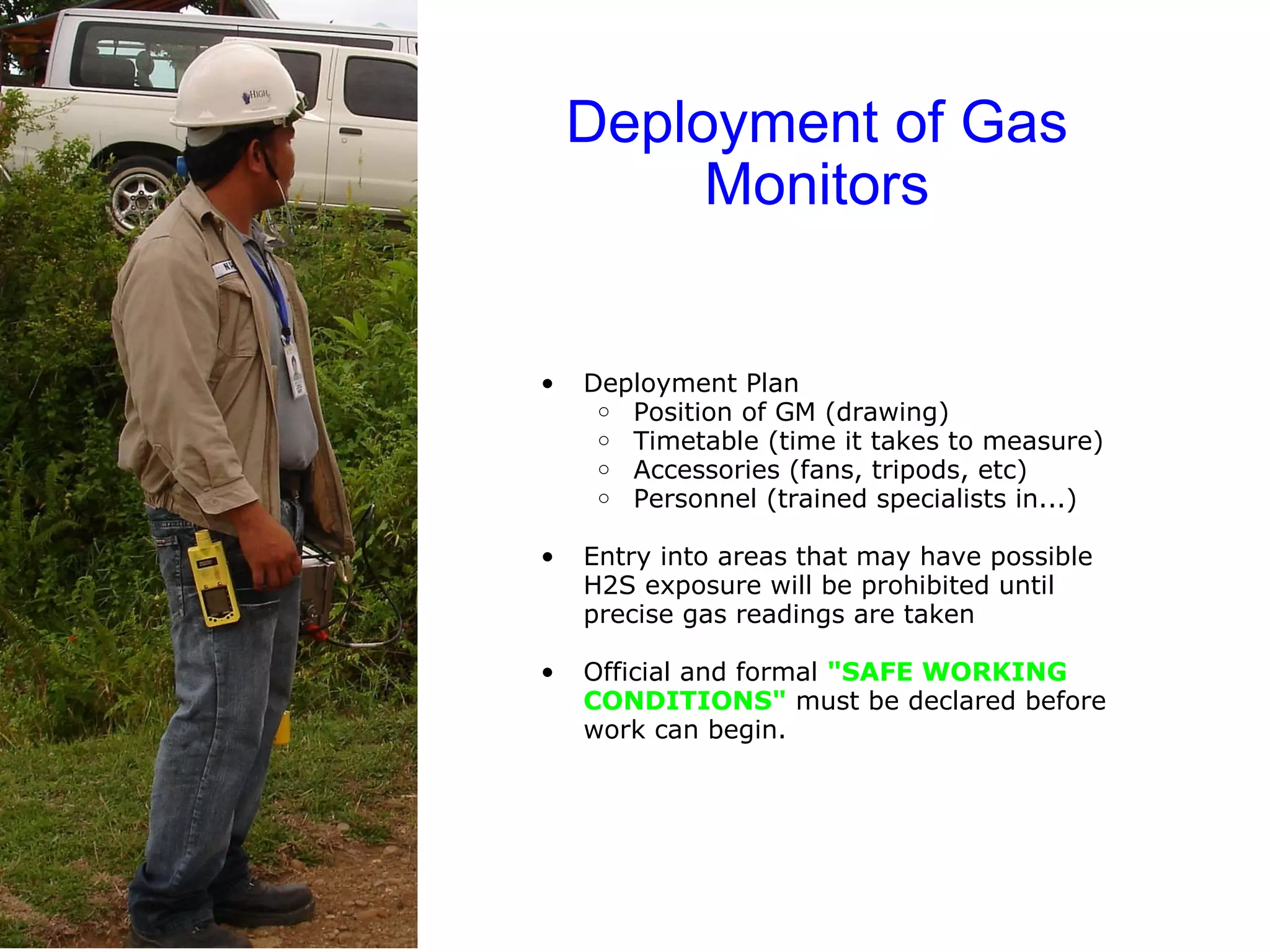
H2S is a chemical asphyxiant that inhibits cellular respiration, causing suffocation and death. Exposure can cause irritation, headaches, dizziness, vomiting, and respiratory issues. Prolonged low exposure may lead to bronchitis, pneumonia, and other health problems. When working in areas with potential H2S, gas monitors should be used to test air quality and ensure safe conditions before entry. Proper protective equipment like self-contained breathing apparatus is required for any rescue to avoid being overcome as well.