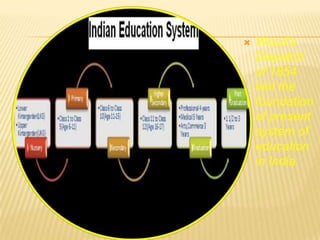
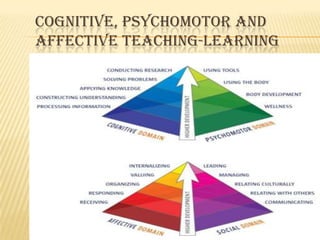
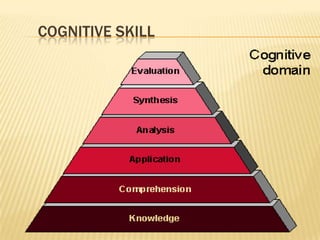
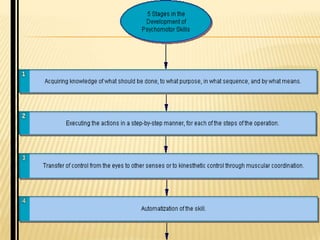
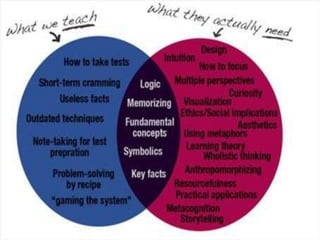
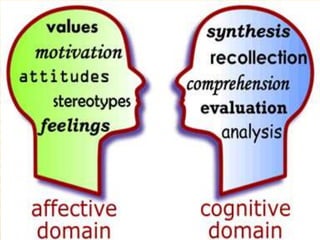
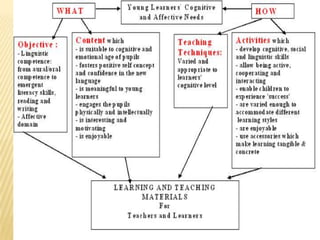
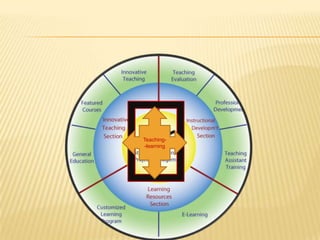
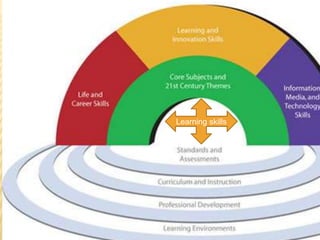
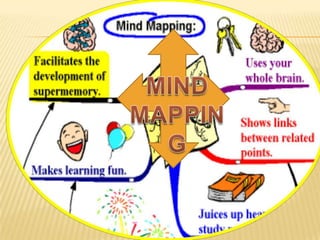
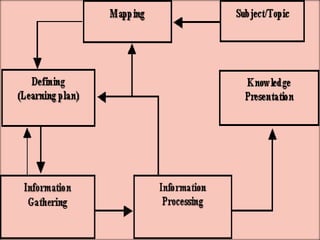
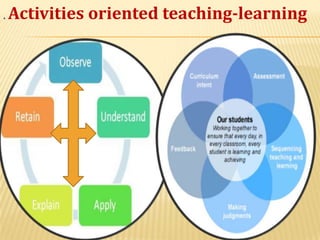
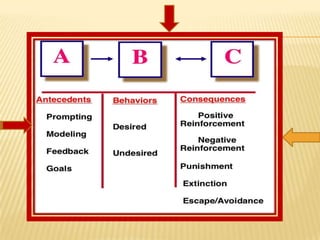
The document discusses traditional Indian education systems like the guru-shishya parampara and compares it to modern education systems. It covers topics like the teacher-student relationship, cognitive vs. psychomotor vs. affective learning, and innovative ways to enhance the learning process, such as using the KWL technique and analyzing photographs in small groups. The document provides examples of activities to develop cognitive skills like problem solving and ways to develop learning skills through activity-oriented teaching.