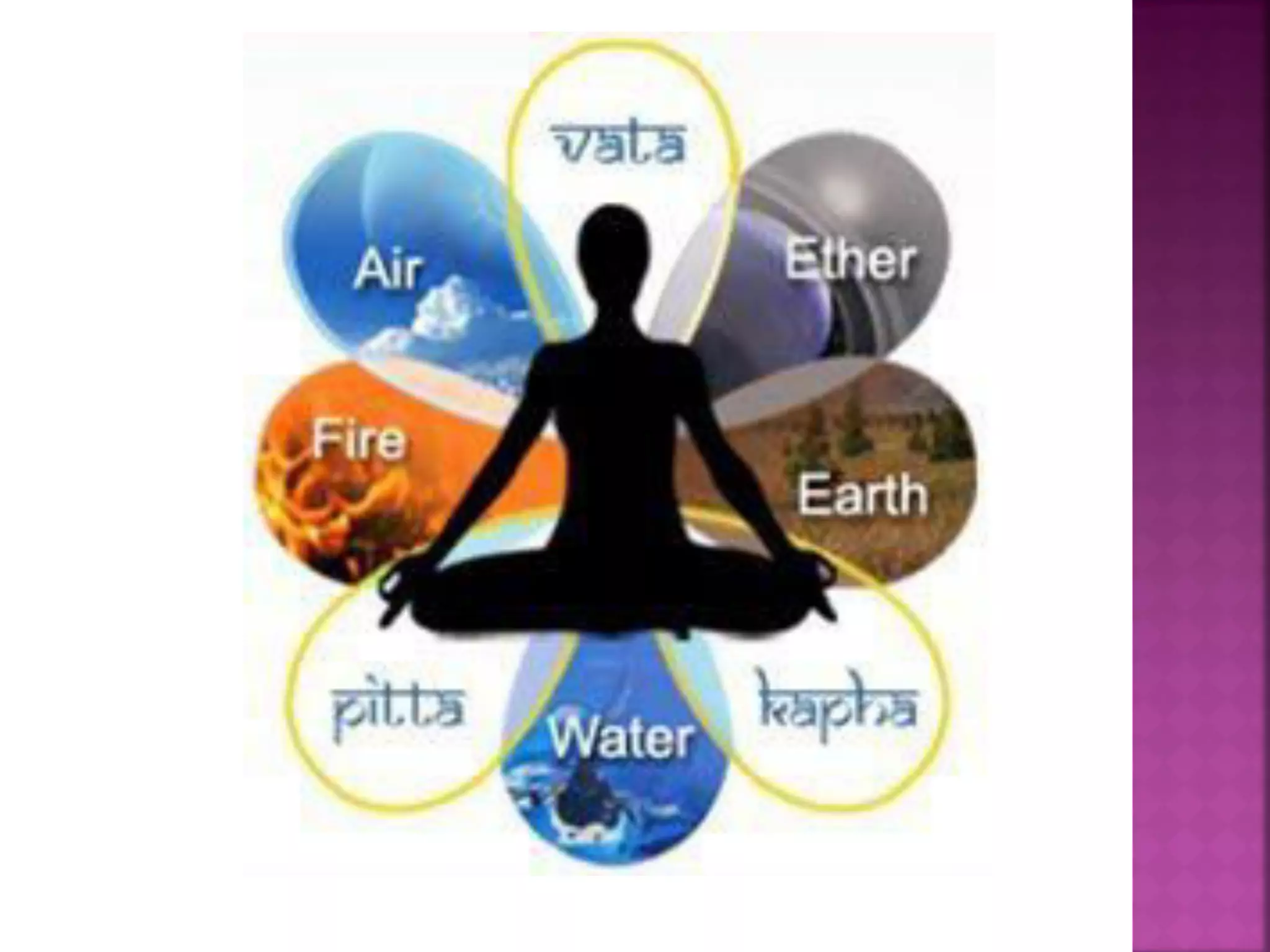
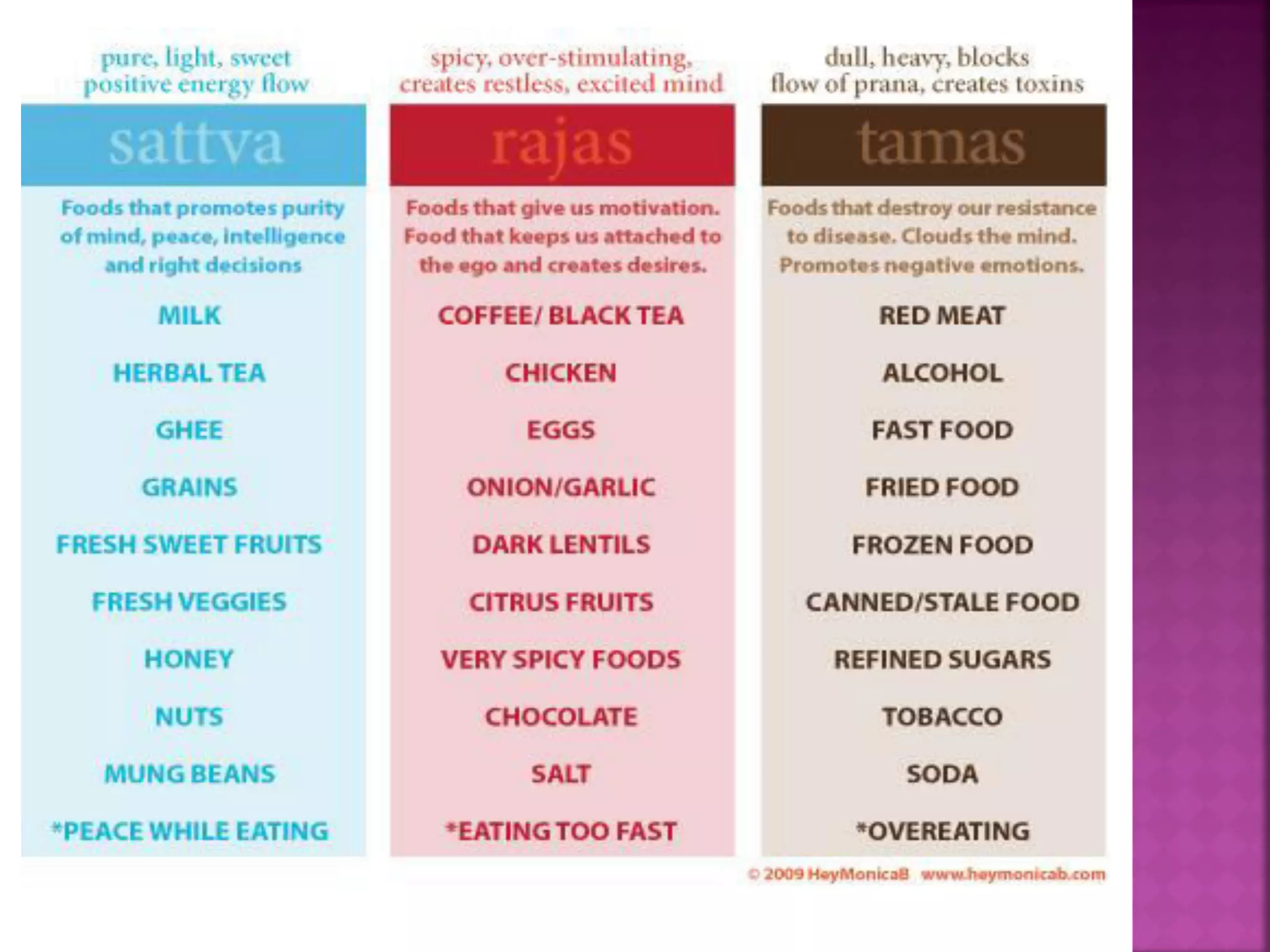
The document discusses the concepts of mind and mental constitution according to Ayurveda. It states that the mind and body are interconnected and influence each other. The mind is described as the faculty of thinking, judging, and perceiving. It also discusses the three gunas or mental qualities - sattva, rajas, and tamas - which govern one's mental state and disposition. A predominant balance of these gunas can influence one's behaviors and health. Ayurveda views the mind and mental health as integral to overall wellness.