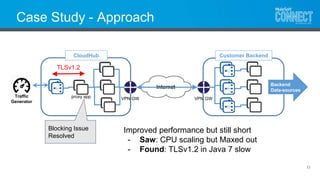
The document provides a comprehensive guide on application performance, emphasizing the importance of understanding the entire solution architecture and effectively tuning performance to enhance user experience. It includes a detailed case study of a global digital transformation initiative using Anypoint Platform, highlighting key takeaways on identifying bottlenecks and the significance of collaboration in troubleshooting. The conclusion stresses that effective performance engineering and attention to detail are critical for successful API-led connectivity.