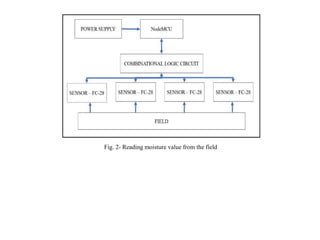
An automatic irrigation system is proposed that uses soil moisture sensors and a microcontroller to remotely control irrigation. Sensor nodes placed throughout the field measure soil moisture and send readings to a sink node. When a sensor detects moisture below a threshold, the sink node activates the water pump to irrigate only that area. The system aims to optimize water usage by irrigating only when needed and reducing labor. Components include a Node MCU microcontroller, soil moisture sensors, and relays to automate water flow. Benefits are timely irrigation, higher flow rates, reduced labor, and accurate water cutoff compared to manual systems.