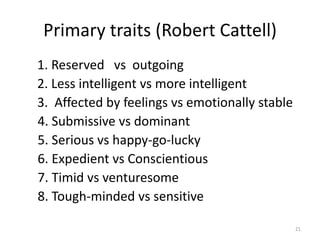
Personality is shaped by both heredity and environmental factors. Research shows genetics accounts for around 50% of personality differences. The document discusses several theories of personality including traits theory, psychodynamic theory, and the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator, which sorts people into 16 personality types based on preferences of extraversion/introversion, sensing/intuition, thinking/feeling, and judging/perceiving. The Big Five model identifies the main dimensions of personality as Extroversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Emotional Stability, and Openness to Experience.