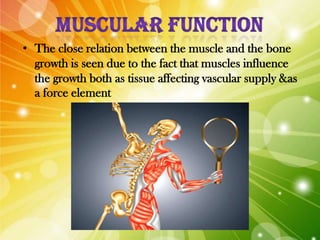
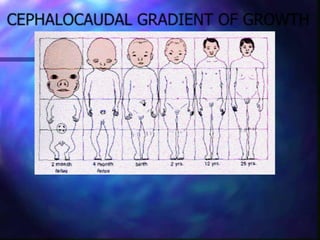
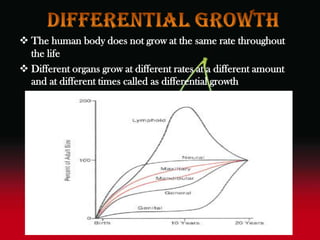
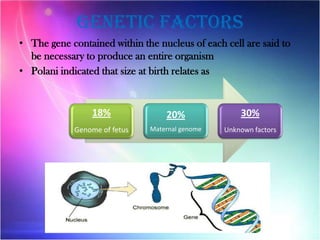
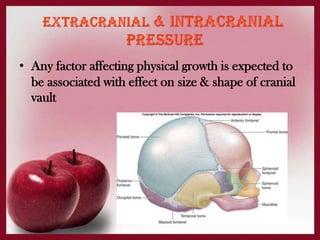
The document discusses the complex interplay of genetic and environmental factors affecting human growth and development, emphasizing aspects such as nutrition, socioeconomic status, and hormonal influences. It outlines how variations in growth patterns occur based on age, season, and climatic conditions, as well as highlighting the concept of catch-up growth in malnourished children. Additionally, it describes the differential growth of various body systems and the individual variations that exist within family members.







![•GROWTH HORMONE
•INSULIN
•THYROTROPIC HORMONE
Group I
[SKELETAL BONE GROWTH]
• PARATHORMONE
Group II
[OSSIFICATION OF BONE]
•ANDROGENS
•PROGESTRONE
•OESTROGEN
Group III
[PUBERTAL GROWTH SPURT]
• POLACTIN
Group IV
[MISCELLENOUS]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/growthassessment-131003074446-phpapp02/85/Growth-assessment-10-320.jpg)