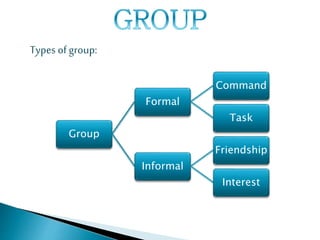
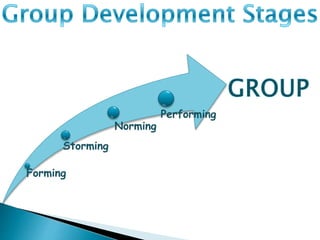
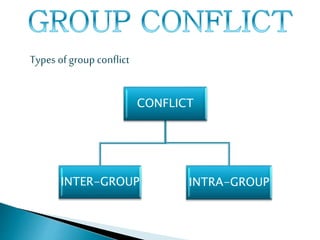
Groups form for reasons like security, recognition, power, and goal accomplishment. There are different types of groups like formal command groups and informal friendship groups. Groups typically go through stages of forming, storming, norming, and performing as members learn roles and develop cohesion. Leadership involves influencing groups toward goals, and groups use techniques like brainstorming, nominal groups, and Delphi to make decisions. Conflicts can be intra-group or inter-group regarding roles or norms, and strategies like compromising or withdrawing can help manage conflicts.