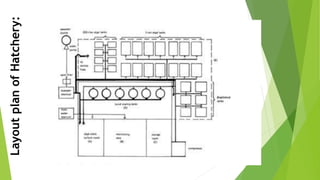
This document provides an overview of the design and construction of finfish hatcheries. It discusses the importance of hatcheries in aquaculture for producing fish seed out of season and improving genetics. Key factors to consider in hatchery design include the budget, production targets, site selection, and facilities like water supply and treatment systems. The document outlines various components of a hatchery such as brood fish ponds, hatchery tanks, nursery ponds, and rearing ponds. It provides details on selecting appropriate pond sizes and layout. Finally, the conclusion emphasizes that careful hatchery operation and management is needed due to the sensitivity of fry and fingerlings.