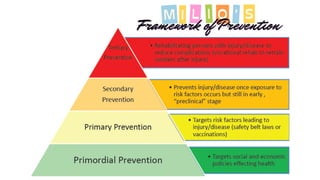
The document summarizes Nancy Milio's framework for prevention, which aims to explain the connection between individual and community health. It discusses the four levels of prevention - primordial, primary, secondary, and tertiary. The primordial level addresses systemic determinants of health before risk factors emerge. The primary level prevents disease before occurrence by addressing exposures. The secondary level uses early detection to prevent disease from occurring through screening programs. The tertiary level aims to soften the long-term impact of disease or injury through management programs.