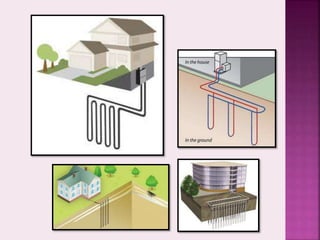
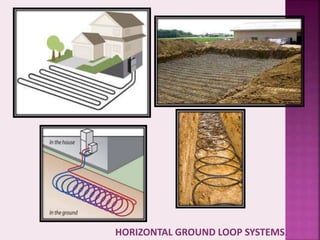
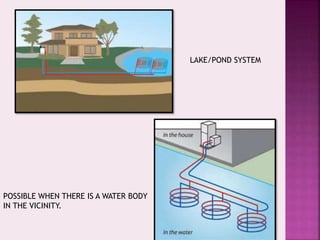
Passive cooling is a building design approach aimed at controlling heat gain and promoting natural cooling for improved indoor thermal comfort without significant energy use. Techniques like ground cooling utilize the earth as a heat sink, employing buried pipes to regulate air temperature through conductive heat transfer. Various systems, including vertical and horizontal ground loops and lake/pond loops, are used to harness the earth's stable temperatures, impacting energy efficiency in heating and cooling.