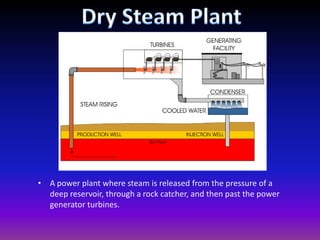
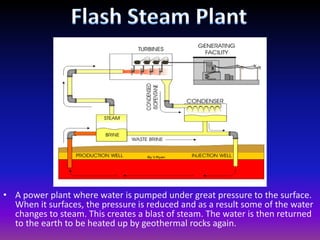
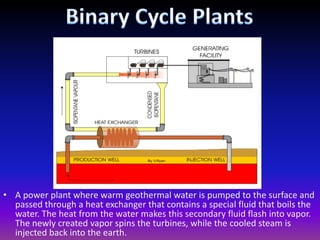
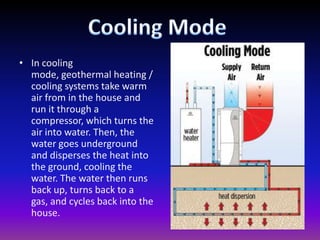
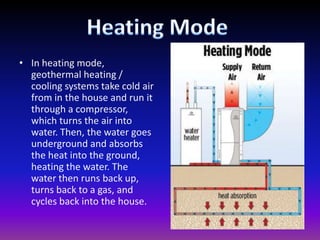
Geothermal energy harnesses heat from within the Earth and can be used for electricity generation and home heating/cooling. There are three main types of geothermal power plants - dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle - that generate electricity using steam or hot water from underground reservoirs. Geothermal energy has many benefits including being renewable, reliable, and having very low environmental impact and emissions. However, the high initial costs and limited geographic availability are challenges to wider adoption of geothermal power. Overall, geothermal is one of the most environmentally friendly and sustainable energy sources available.